正在加载图片...
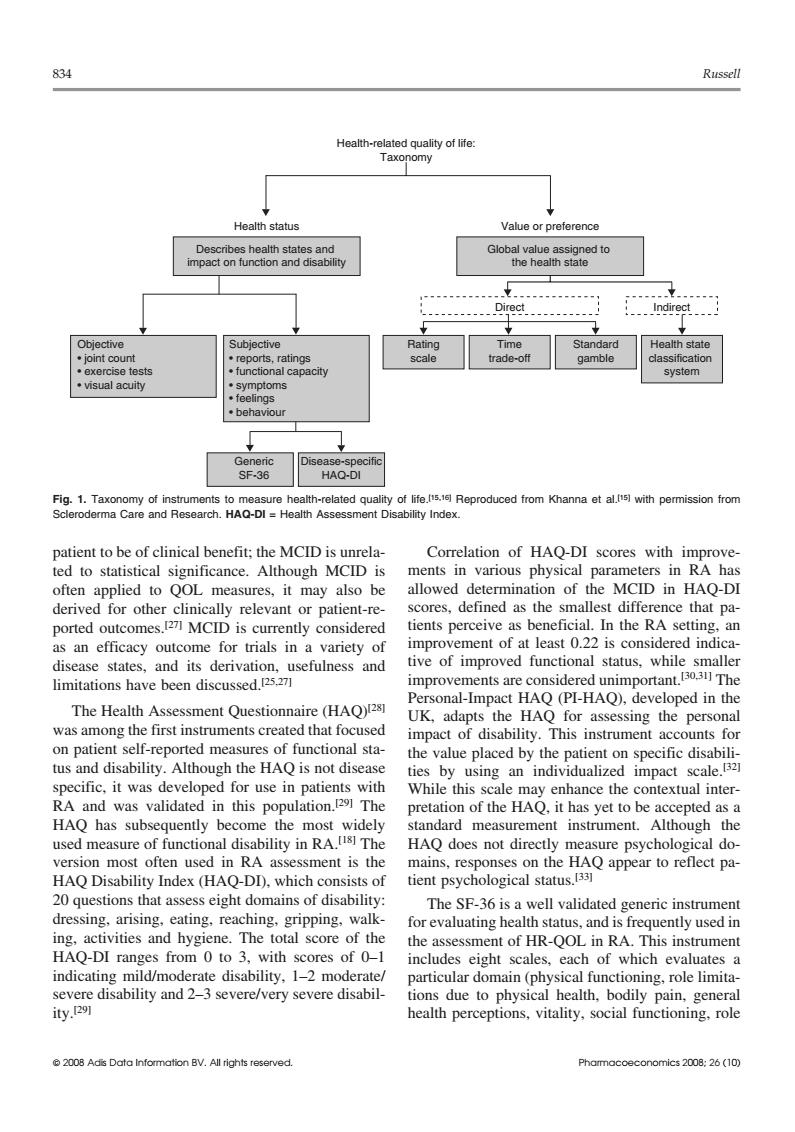
834 Russell Health-related quality of life Taxonomy Health status Value or preference Global value assigned to the health state dHealth state system sF-36 HAG-DI nts to measure health-related quality of life Reproduced from Khanna et a)with pemmission from earch.HAQ-DI Health Asses patient to be of clinical benefit:th MCID is s unrela- Correlation of HAQ-DI scores with improve ted to statis I significance. Although MCID is ments physic 0Q0 measures,It may also be of HAQ-D r oth rele vant or paned t-re eive as he neficial.In the RA setti improvement of at least 0.22 is considered indica s an efficacy ou s in a tive of improved functional status,while smaller improvements are considered unimportant30 The Personal-Impact HAQ(PI-HAQ).developed in the The Health Assessment Ouestionnaire (HAO) the HAQ was among the first instruments created that focused instrument on patient self-reported measures of functional sta- tus and disability although the hao is not disease by the Lomspecifcd specific.it was developed for use in patients with enhance the xtual inter RA and was validated in this population.The retation of the Had it has vet to be accer nted as a thd mee ou e standard measurement instrument.Although the HAQ does not directly measure psychological do version most often used in RA assessment is the mains,responses on the HAQ appear to reflect pa- HAQ Disability Index(HAQ-DD).which consists of tient psychological status. 20 questions that assess eight domains of disability. The SF-36 is a well validated s eric instrumen dressing,arising,eating,reaching,gripping,walk for evaluating health status.and is frequently used in the assessment of HR-QOL in RA.This instrument includes eight scales,each of which evaluates a particular domain (physical functioning.role limita severe/very severe due to phys oning,role834 Russell Indirect Health-related quality of life: Taxonomy Health status Value or preference Describes health states and impact on function and disability Global value assigned to the health state Health state classification system Direct Rating scale Time trade-off Standard gamble Objective • joint count • exercise tests • visual acuity Subjective • reports, ratings • functional capacity • symptoms • feelings • behaviour Generic SF-36 Disease-specific HAQ-DI Fig. 1. Taxonomy of instruments to measure health-related quality of life.[15,16] Reproduced from Khanna et al.[15] with permission from Scleroderma Care and Research. HAQ-DI = Health Assessment Disability Index. patient to be of clinical benefit; the MCID is unrela- Correlation of HAQ-DI scores with improveted to statistical significance. Although MCID is ments in various physical parameters in RA has often applied to QOL measures, it may also be allowed determination of the MCID in HAQ-DI derived for other clinically relevant or patient-re- scores, defined as the smallest difference that paported outcomes.[27] MCID is currently considered tients perceive as beneficial. In the RA setting, an improvement of at least 0.22 is considered indica- as an efficacy outcome for trials in a variety of tive of improved functional status, while smaller disease states, and its derivation, usefulness and improvements are considered unimportant.[30,31] The limitations have been discussed.[25,27] Personal-Impact HAQ (PI-HAQ), developed in the The Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)[28] UK, adapts the HAQ for assessing the personal was among the first instruments created that focused impact of disability. This instrument accounts for on patient self-reported measures of functional sta- the value placed by the patient on specific disabilitus and disability. Although the HAQ is not disease ties by using an individualized impact scale.[32] specific, it was developed for use in patients with While this scale may enhance the contextual interRA and was validated in this population.[29] The pretation of the HAQ, it has yet to be accepted as a HAQ has subsequently become the most widely standard measurement instrument. Although the used measure of functional disability in RA.[18] The HAQ does not directly measure psychological doversion most often used in RA assessment is the mains, responses on the HAQ appear to reflect patient psychological status.[33] HAQ Disability Index (HAQ-DI), which consists of 20 questions that assess eight domains of disability: The SF-36 is a well validated generic instrument dressing, arising, eating, reaching, gripping, walk- for evaluating health status, and is frequently used in ing, activities and hygiene. The total score of the the assessment of HR-QOL in RA. This instrument HAQ-DI ranges from 0 to 3, with scores of 0–1 includes eight scales, each of which evaluates a indicating mild/moderate disability, 1–2 moderate/ particular domain (physical functioning, role limitasevere disability and 2–3 severe/very severe disabil- tions due to physical health, bodily pain, general ity.[29] health perceptions, vitality, social functioning, role © 2008 Adis Data Information BV. All rights reserved. Pharmacoeconomics 2008; 26 (10)