正在加载图片...
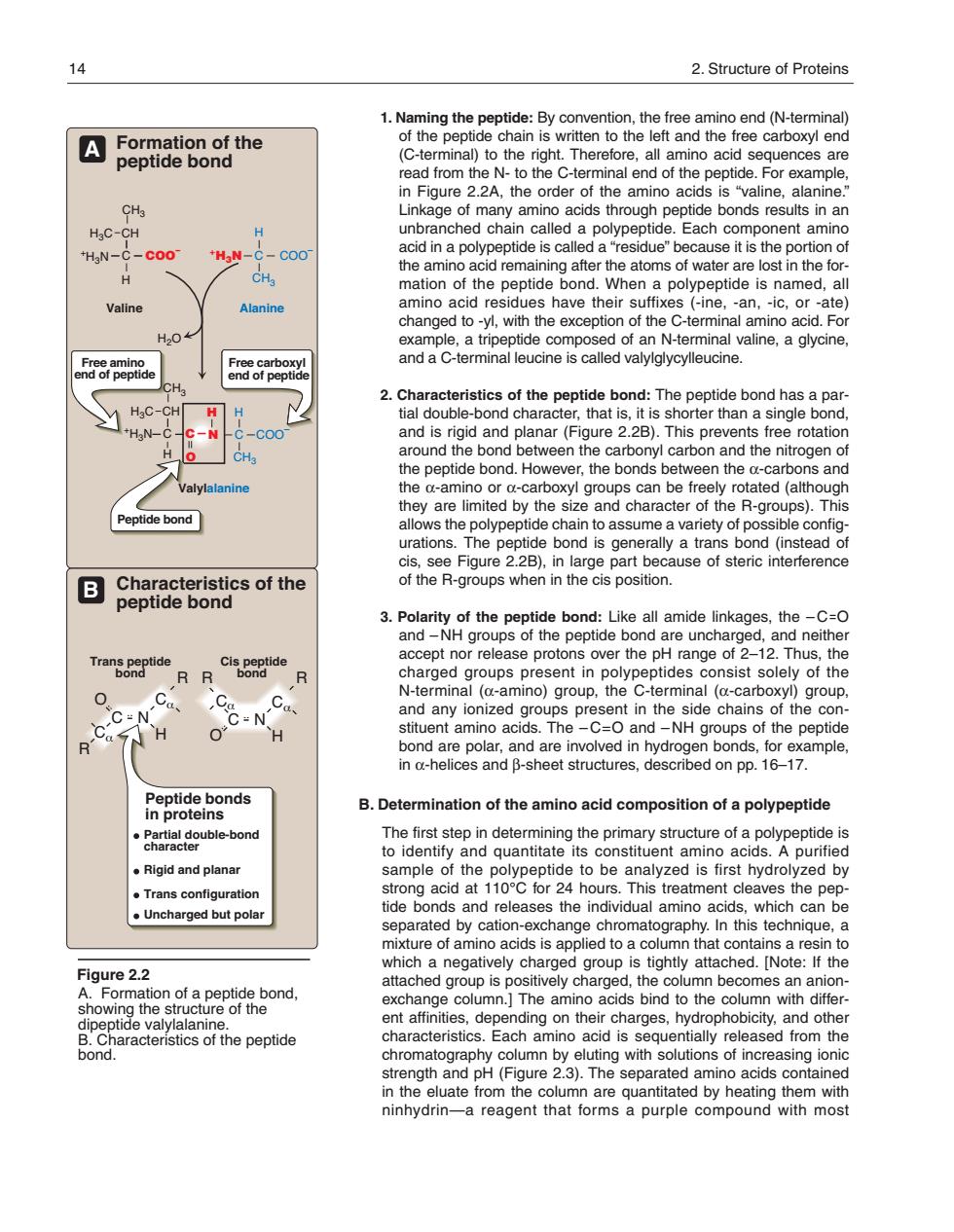
14 2.Structure of Proteins 1.Naming the peptide:By convention,the free amino end(N-terminal) A tion of the of the peptide chain is written to the left and the free carboxyl end (C-te Theretore. no aci uences ar in Figure 2.2A.the order of the amino acids is"valine. CHa Linkage of many amino acids through peptide bonds results in an HaC-CH H nbrancned cnal called a polypeptide. HgN-C-coo- C-coc atoms of water are lost in the for H CH mation of the peptide bond.When a polypeptide is named,all Valine amino acid ues have their suffixe (-in e.an.-ic.or ate H04 a tr d of ar ninal valine and a C-terminal leucine is called valvlalycvlleucine. cfge8rpopae 2.c HaC-Ch H bond has a par 'HgN- and is rigid and planar(Figure 2.2B).This prevents free rotation around the bond between the e carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen o the peptide bond.However,the bonds b een th s an by the sized character of the R-groups).This Peptide bond allows the polypeptide chain to assume a variety of possible config urations.The peptide bond is gene ally a trans bond d(instead o B Cha 3.Polarity of the peptide bond:Like all amide linkages,the -C=0 roups o h haf9ei2ananeith9 charged groups present in poly ptides consist solely of the 0 C-N-C C N-terminal (-amino)group.the C-terminal (a-carboxyl)group. C:N group in the the H 0 bond are polar.and are involved in hydrogen bonds.for example. in a-helices and B-sheet structures,described on pp.16-17. Peptide bonds in proteins B.Determination of the amino acid composition of a polypeptide double-bon .Rigid and planar sample of the polypeptide to be analyzed is first hydrolyzed by 。Trans config for 4 hours. his treatment .Uncharged but ato mixture of amino acids is applied to a column that contains a resin to Figure 2.2 which a negatively charged group is tightly atta hed.[Note:If the group is vely cna sho ogaeaiaPePebond ide ent affinities,de nding on their charo es,hydrophobicity,and other of the peptide characteristics.Each amino acid is sequentially released from the chromatography eluting with solutions of inc easing ninhydrin-a reagent that forms a purple compound with most 1. Naming the peptide: By convention, the free amino end (N-terminal) of the peptide chain is written to the left and the free carboxyl end (C-terminal) to the right. Therefore, all amino acid sequences are read from the N- to the C-terminal end of the peptide. For example, in Figure 2.2A, the order of the amino acids is “valine, alanine.” Linkage of many amino acids through peptide bonds results in an unbranched chain called a polypeptide. Each component amino acid in a polypeptide is called a “residue” because it is the portion of the amino acid remaining after the atoms of water are lost in the formation of the peptide bond. When a polypeptide is named, all amino acid residues have their suffixes (-ine, -an, -ic, or -ate) changed to -yl, with the exception of the C-terminal amino acid. For example, a tripeptide composed of an N-terminal valine, a glycine, and a C-terminal leucine is called valyl glycyl leucine. 2. Characteristics of the peptide bond: The peptide bond has a partial double-bond character, that is, it is shorter than a single bond, and is rigid and planar (Figure 2.2B). This prevents free rotation around the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen of the peptide bond. However, the bonds between the α-carbons and the α-amino or α-carboxyl groups can be freely rotated (although they are limited by the size and character of the R-groups). This allows the polypeptide chain to assume a variety of possible configurations. The peptide bond is generally a trans bond (instead of cis, see Figure 2.2B), in large part because of steric interference of the R-groups when in the cis position. 3. Polarity of the peptide bond: Like all amide linkages, the – C=O and – NH groups of the peptide bond are uncharged, and neither accept nor release protons over the pH range of 2–12. Thus, the charged groups present in polypeptides consist solely of the N-terminal (α-amino) group, the C-terminal (α-carboxyl) group, and any ionized groups present in the side chains of the constituent amino acids. The – C=O and – NH groups of the peptide bond are polar, and are involved in hydrogen bonds, for example, in α-helices and β-sheet structures, described on pp. 16–17. B. Determination of the amino acid composition of a polypeptide The first step in determining the primary structure of a polypeptide is to identify and quantitate its constituent amino acids. A purified sample of the polypeptide to be analyzed is first hydrolyzed by strong acid at 110°C for 24 hours. This treatment cleaves the peptide bonds and releases the individual amino acids, which can be separated by cation-exchange chromatography. In this technique, a mixture of amino acids is applied to a column that contains a resin to which a negatively charged group is tightly attached. [Note: If the attached group is positively charged, the column becomes an anionexchange column.] The amino acids bind to the column with different affinities, depending on their charges, hydrophobicity, and other characteristics. Each amino acid is sequentially released from the chromatography column by eluting with sol utions of increasing ionic strength and pH (Figure 2.3). The separated amino acids contained in the eluate from the column are quantitated by heating them with ninhydrin—a reagent that forms a purple compound with most Figure 2.2 A. Formation of a peptide bond, showing the structure of the dipeptide valylalanine. B. Characteristics of the peptide bond. C COO– H Valine Valylalanine C +H3N COO– H CH3 Alanine C C H N C COO– H O CH3 H Free carboxyl end of peptide H3C CH CH3 H2O Free amino end of peptide Peptide bond +H3N H3C CH CH3 +H3N A B Trans peptide bond C N H O Cα Cα C N O H Cα Cα Peptide bonds in proteins Partial double-bond character Rigid and planar Trans configuration Uncharged but polar Cis peptide bond R R R R Characteristics of the peptide bond Formation of the peptide bond 14 2. Structure of Proteins 168397_P013-024.qxd7.0:02 Protein structure 5-20-04 2010.4.4 11:31 AM Page 14