正在加载图片...
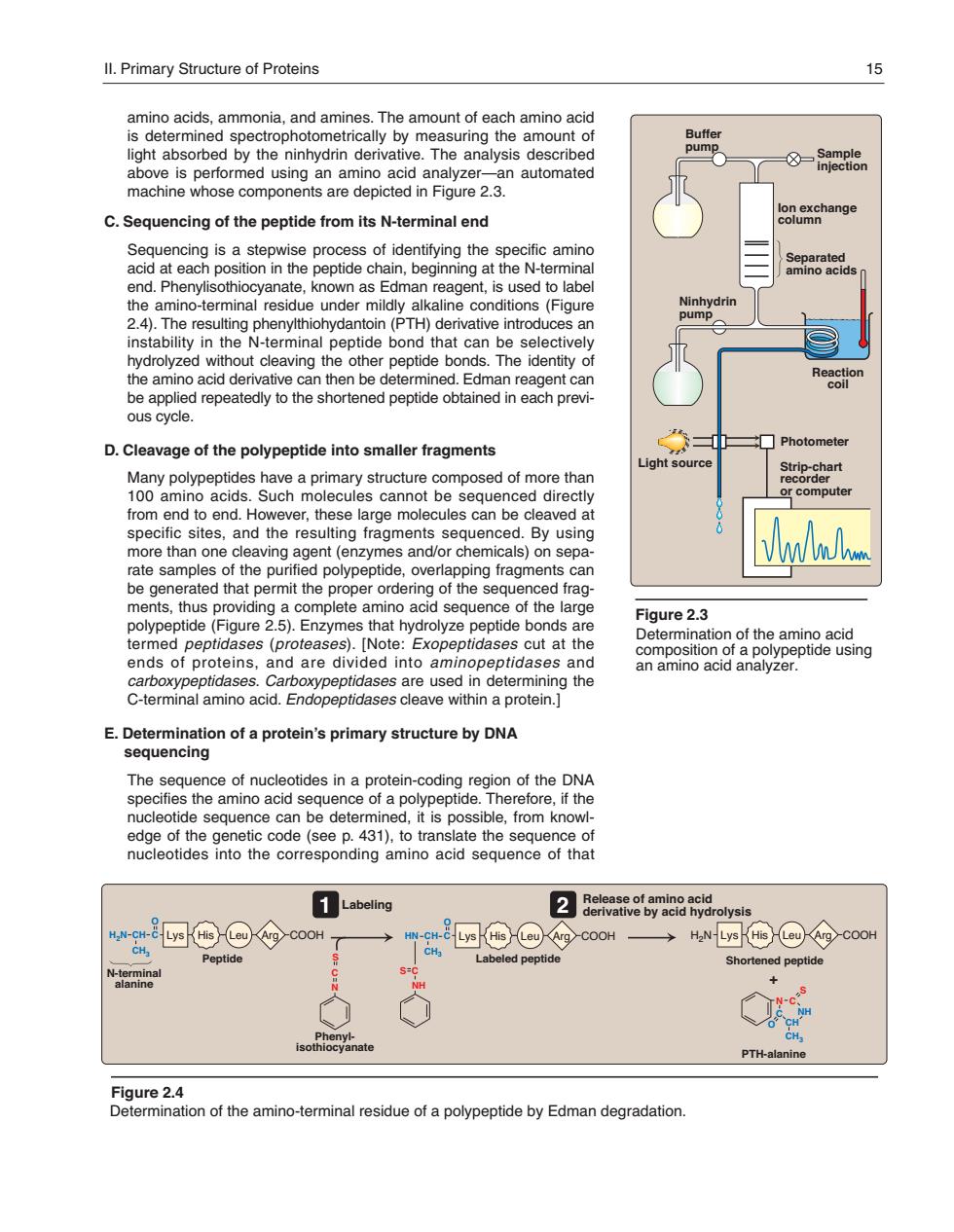
ll.Primary Structure of Proteins amino acids,ammonia,and amines.The amount of each amino acid is determined spectrophotometrically by measuring the amount of light absorbed by the ninhydrin derivative.The analysis described 8- ed using an amino n automated e componen C.Sequencing of the peptide from its N-terminal end Sequencing is a stepwise process of identifying the specific amino acid n position in t the peptide chain,beginning at the N-termina ions(Fig 2.4).The resulting phenylthiohydantoin(PTH)derivative introduces an instability in the N-terminal pep be applied repeatedly to the shortened peptide obtained ous cycle. D.Cleavage of the polypeptide into smaller fragments □ph omputer from end to end Ho these l es can be clea d a specific sites,and the resulting fragments sequenced.By using eaving agent (enzym es and/or chemicals)on sepa nit th of the ments.thus providing a complete amino acid sequence of the large polypeptide(Figure 2.5).Enzymes that hydrolyze peptide bonds are Figure2.3 terme ategongtiog fthaaepa8ciing ide ptidases.Carb used in determining the C-terminal amino acid.Endopeptidases cleave within a protein.] E.Determination of a protein's primary structure by DNA sequencing edge of the genetic code(see p.431).to translate the sequence of nucleotides into the corresponding amino acid sequence of that Labeling CH Peptid t'9 Shortened peptide PTH-alanine age2aontheanmot ninal residue of a polypeptide by Edman degradation.amino acids, ammonia, and amines. The amount of each amino acid is determined spectro photo metrically by measuring the amount of light absorbed by the ninhydrin derivative. The analysis described above is performed using an amino acid analyzer—an automated machine whose components are depicted in Figure 2.3. C. Sequencing of the peptide from its N-terminal end Sequencing is a stepwise process of identifying the specific amino acid at each position in the peptide chain, beginning at the N- terminal end. Phenylisothiocyanate, known as Edman reagent, is used to label the amino-terminal residue under mildly alkaline conditions (Figure 2.4). The resulting phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) derivative introduces an instability in the N-terminal peptide bond that can be selectively hydrolyzed without cleaving the other peptide bonds. The identity of the amino acid derivative can then be determined. Edman reagent can be applied repeatedly to the shortened peptide obtained in each previous cycle. D. Cleavage of the polypeptide into smaller fragments Many polypeptides have a primary structure composed of more than 100 amino acids. Such molecules cannot be sequenced directly from end to end. However, these large molecules can be cleaved at specific sites, and the resulting fragments sequenced. By using more than one cleaving agent (enzymes and/or chemicals) on separate samples of the purified polypeptide, overlapping fragments can be generated that permit the proper ordering of the sequenced fragments, thus providing a complete amino acid sequence of the large polypeptide (Figure 2.5). Enzymes that hydrolyze peptide bonds are termed peptidases (proteases). [Note: Exopeptidases cut at the ends of proteins, and are divided into aminopeptidases and carboxy peptidases. Carboxypeptidases are used in determining the C-terminal amino acid. Endopeptidases cleave within a protein.] E. Determination of a protein’s primary structure by DNA sequencing The sequence of nucleotides in a protein-coding region of the DNA specifies the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. Therefore, if the nucleotide sequence can be determined, it is possible, from knowledge of the genetic code (see p. 431), to translate the sequence of nucleotides into the corresponding amino acid sequence of that Figure 2.4 Determination of the amino-terminal residue of a polypeptide by Edman degradation. PTH-alanine N C S NH CH C O CH3 + Shortened peptide H2N Peptide Labeled peptide His Leu Arg COOH C N S H2N C NH S HN CH C CH3 O Phenylisothiocyanate N-terminal alanine CH C CH3 O His Leu Arg COOH His Leu Arg COOH Release of amino acid derivative by acid hydrolysis Labeling Lys Lys Lys 1 2 II. Primary Structure of Proteins 15 Figure 2.3 Determination of the amino acid composition of a polypeptide using an amino acid analyzer. Photometer Light source Separated amino acids Reaction coil Ninhydrin pump Buffer pump Ion exchange column Sample injection Strip-chart recorder or computer 168397_P013-024.qxd7.0:02 Protein structure 5-20-04 2010.4.4 11:31 AM Page 15