正在加载图片...
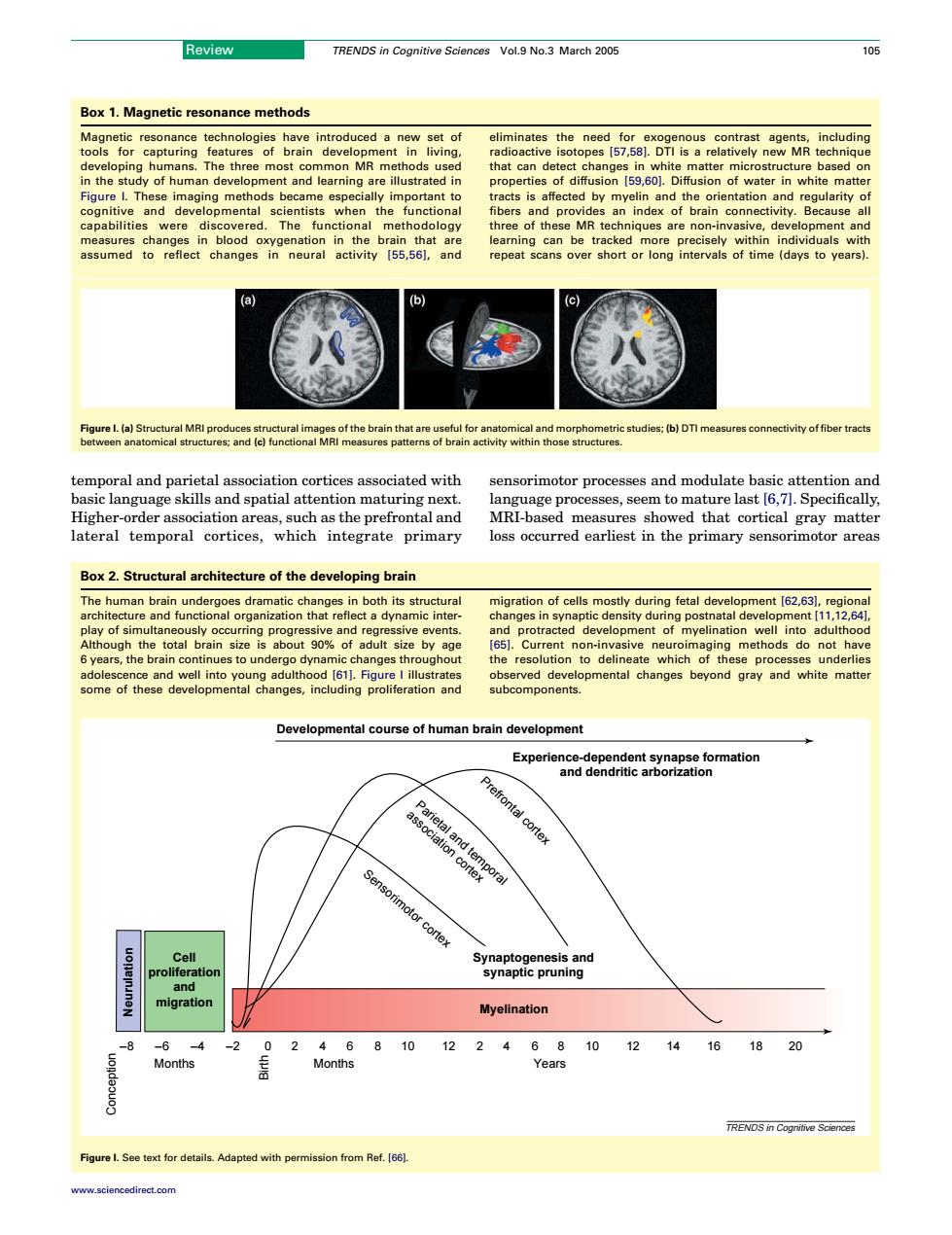
Review TRENDS in Cognitive Sciences Vol.9 No.3 March 2005 105 Box 1.Magnetic resonance methods have introduced nw set of including is for st c that can d ct cha ed by ind non-invasive assumed to reflect”ch (c) mporncriceswth sensorimotor processes and modulate basic attention and and spatia Ru3earoeseeentoathe1ast6n1.specic lateral temporal cortices.which integrate primary loss occurred earliest in the primary sensorimotor areas Box 2.Structural architecture of the developing brain The human brain ami changes in both migration of cem ing pro well into 90%ot It size by and white anges,in subcomponents. Developmental course of human brain development Experie Myelination 8 0246810122468101214161820temporal and parietal association cortices associated with basic language skills and spatial attention maturing next. Higher-order association areas, such as the prefrontal and lateral temporal cortices, which integrate primary sensorimotor processes and modulate basic attention and language processes, seem to mature last [6,7]. Specifically, MRI-based measures showed that cortical gray matter loss occurred earliest in the primary sensorimotor areas Box 1. Magnetic resonance methods Magnetic resonance technologies have introduced a new set of tools for capturing features of brain development in living, developing humans. The three most common MR methods used in the study of human development and learning are illustrated in Figure I. These imaging methods became especially important to cognitive and developmental scientists when the functional capabilities were discovered. The functional methodology measures changes in blood oxygenation in the brain that are assumed to reflect changes in neural activity [55,56], and eliminates the need for exogenous contrast agents, including radioactive isotopes [57,58]. DTI is a relatively new MR technique that can detect changes in white matter microstructure based on properties of diffusion [59,60]. Diffusion of water in white matter tracts is affected by myelin and the orientation and regularity of fibers and provides an index of brain connectivity. Because all three of these MR techniques are non-invasive, development and learning can be tracked more precisely within individuals with repeat scans over short or long intervals of time (days to years). Figure I. (a) Structural MRI produces structural images of the brain that are useful for anatomical and morphometric studies; (b) DTI measures connectivity of fiber tracts between anatomical structures; and (c) functional MRI measures patterns of brain activity within those structures. Box 2. Structural architecture of the developing brain The human brain undergoes dramatic changes in both its structural architecture and functional organization that reflect a dynamic interplay of simultaneously occurring progressive and regressive events. Although the total brain size is about 90% of adult size by age 6 years, the brain continues to undergo dynamic changes throughout adolescence and well into young adulthood [61]. Figure I illustrates some of these developmental changes, including proliferation and migration of cells mostly during fetal development [62,63], regional changes in synaptic density during postnatal development [11,12,64], and protracted development of myelination well into adulthood [65]. Current non-invasive neuroimaging methods do not have the resolution to delineate which of these processes underlies observed developmental changes beyond gray and white matter subcomponents. TRENDS in Cognitive Sciences –8 –6 –4 –2 0 6 10 12 14 4 8 Developmental course of human brain development Experience-dependent synapse formation and dendritic arborization Synaptogenesis and synaptic pruning Sensorimotor cortex Parietal and temporal association cortex Prefrontal cortex Myelination Conception Birth Months Months Years 2 2 6 10 12 16 18 20 4 8 Neurulation Cell proliferation and migration Figure I. See text for details. Adapted with permission from Ref. [66]. Review TRENDS in Cognitive Sciences Vol.9 No.3 March 2005 105 www.sciencedirect.com