正在加载图片...
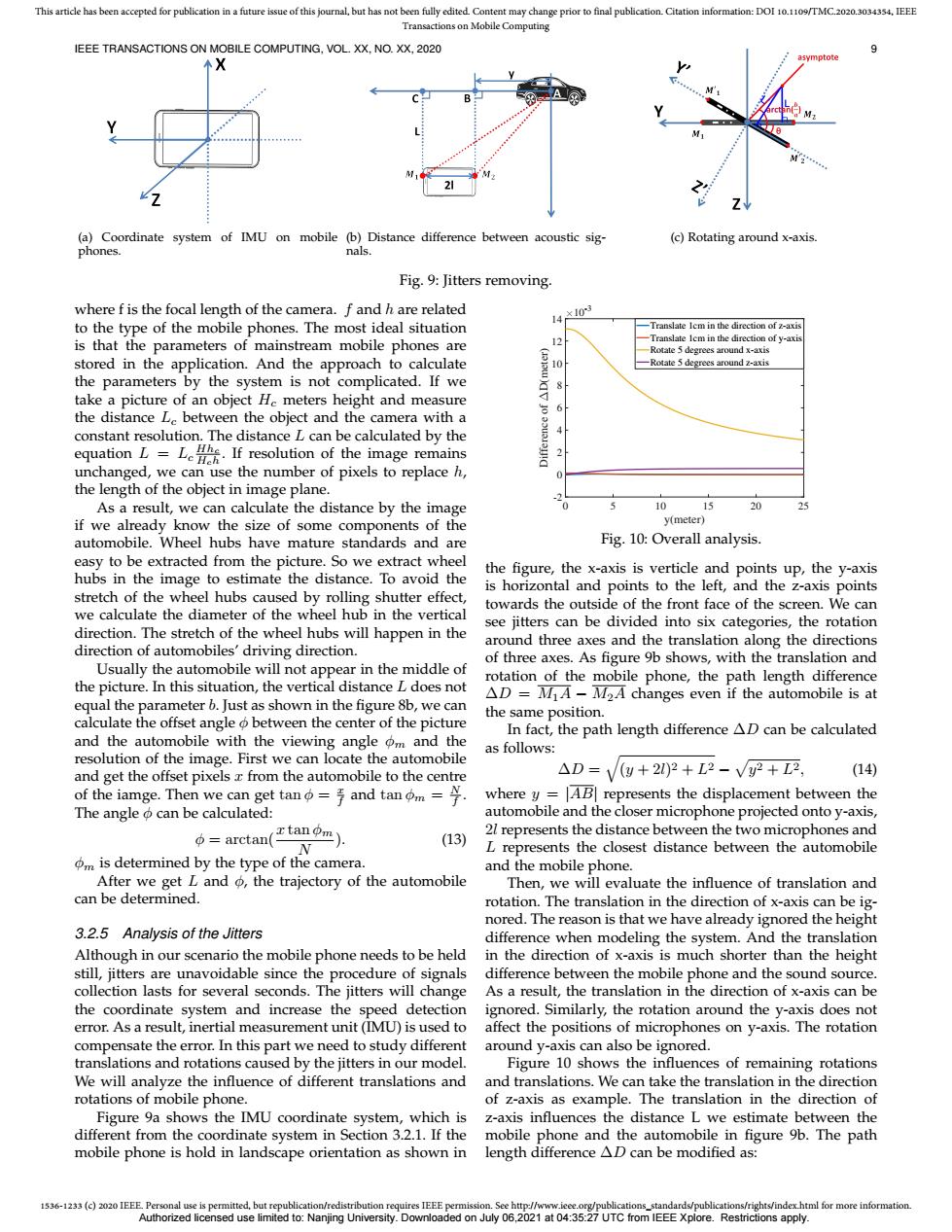
This article has been accepted for publication in a future issue of this journal,but has not been fully edited.Content may change prior to final publication.Citation information:DOI 10.1109/TMC.2020.3034354.IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTING,VOL.XX,NO.XX,2020 (a)Coordinate system of IMU on mobile (b)Distance difference between acoustic sig- (c)Rotating around x-axis. phones. nals. Fig.9:Jitters removing. where f is the focal length of the camera.f and h are related 14 10 to the type of the mobile phones.The most ideal situation Translate lem in the direction of z-axis is that the parameters of mainstream mobile phones are 12 Translate Iem in the direction of y-axt Rotate 5 degrees around x-axis stored in the application.And the approach to calculate -Rotate 5 degrees around z-axis the parameters by the system is not complicated.If we 8 take a picture of an object He meters height and measure the distance L.between the object and the camera with a constant resolution.The distance L can be calculated by the equationL If resolution of the image remains unchanged,we can use the number of pixels to replace h, the length of the object in image plane. As a result,we can calculate the distance by the image 10 15 20 if we already know the size of some components of the y(meter) automobile.Wheel hubs have mature standards and are Fig.10:Overall analysis. easy to be extracted from the picture.So we extract wheel hubs in the image to estimate the distance.To avoid the the figure,the x-axis is verticle and points up,the y-axis is horizontal and points to the left,and the z-axis points stretch of the wheel hubs caused by rolling shutter effect, towards the outside of the front face of the screen.We can we calculate the diameter of the wheel hub in the vertical see jitters can be divided into six categories,the rotation direction.The stretch of the wheel hubs will happen in the direction of automobiles'driving direction. around three axes and the translation along the directions of three axes.As figure 9b shows,with the translation and Usually the automobile will not appear in the middle of the picture.In this situation,the vertical distance L does not rotation of the mobile phone,the path length difference AD MIA-M2A changes even if the automobile is at equal the parameter b.Just as shown in the figure 8b,we can the same position. calculate the offset angle o between the center of the picture In fact,the path length difference AD can be calculated and the automobile with the viewing angle om and the as follows: resolution of the image.First we can locate the automobile and get the offset pixels x from the automobile to the centre △D=V(g+22+L2-V2+亚, (14) of the iamge.Then we can get tan=and tanom= where y=AB represents the displacement between the The angle can be calculated: automobile and the closer microphone projected onto y-axis, b=arctan(tanom)】 (13) 2l represents the distance between the two microphones and L represents the closest distance between the automobile m is determined by the type of the camera. and the mobile phone. After we get L and o,the trajectory of the automobile Then,we will evaluate the influence of translation and can be determined. rotation.The translation in the direction of x-axis can be ig- nored.The reason is that we have already ignored the height 3.2.5 Analysis of the Jitters difference when modeling the system.And the translation Although in our scenario the mobile phone needs to be held in the direction of x-axis is much shorter than the height still,jitters are unavoidable since the procedure of signals difference between the mobile phone and the sound source. collection lasts for several seconds.The jitters will change As a result,the translation in the direction of x-axis can be the coordinate system and increase the speed detection ignored.Similarly,the rotation around the y-axis does not error.As a result,inertial measurement unit(IMU)is used to affect the positions of microphones on y-axis.The rotation compensate the error.In this part we need to study different around y-axis can also be ignored. translations and rotations caused by the jitters in our model. Figure 10 shows the influences of remaining rotations We will analyze the influence of different translations and and translations.We can take the translation in the direction rotations of mobile phone. of z-axis as example.The translation in the direction of Figure 9a shows the IMU coordinate system,which is z-axis influences the distance L we estimate between the different from the coordinate system in Section 3.2.1.If the mobile phone and the automobile in figure 9b.The path mobile phone is hold in landscape orientation as shown in length difference AD can be modified as: 1536-1233(c)2020 IEEE Personal use is permitted,but republication/redistribution requires IEEE permission.See http://www.ieee.org/publications_standards/publications/rights/index.html for more information. Authorized licensed use limited to:Nanjing University.Downloaded on July 06,2021 at 04:35:27 UTC from IEEE Xplore.Restrictions apply.1536-1233 (c) 2020 IEEE. Personal use is permitted, but republication/redistribution requires IEEE permission. See http://www.ieee.org/publications_standards/publications/rights/index.html for more information. This article has been accepted for publication in a future issue of this journal, but has not been fully edited. Content may change prior to final publication. Citation information: DOI 10.1109/TMC.2020.3034354, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTING, VOL. XX, NO. XX, 2020 9 (a) Coordinate system of IMU on mobile phones. (b) Distance difference between acoustic signals. (c) Rotating around x-axis. Fig. 9: Jitters removing. where f is the focal length of the camera. f and h are related to the type of the mobile phones. The most ideal situation is that the parameters of mainstream mobile phones are stored in the application. And the approach to calculate the parameters by the system is not complicated. If we take a picture of an object Hc meters height and measure the distance Lc between the object and the camera with a constant resolution. The distance L can be calculated by the equation L = Lc Hhc Hch . If resolution of the image remains unchanged, we can use the number of pixels to replace h, the length of the object in image plane. As a result, we can calculate the distance by the image if we already know the size of some components of the automobile. Wheel hubs have mature standards and are easy to be extracted from the picture. So we extract wheel hubs in the image to estimate the distance. To avoid the stretch of the wheel hubs caused by rolling shutter effect, we calculate the diameter of the wheel hub in the vertical direction. The stretch of the wheel hubs will happen in the direction of automobiles’ driving direction. Usually the automobile will not appear in the middle of the picture. In this situation, the vertical distance L does not equal the parameter b. Just as shown in the figure 8b, we can calculate the offset angle φ between the center of the picture and the automobile with the viewing angle φm and the resolution of the image. First we can locate the automobile and get the offset pixels x from the automobile to the centre of the iamge. Then we can get tan φ = x f and tan φm = N f . The angle φ can be calculated: φ = arctan(x tan φm N ). (13) φm is determined by the type of the camera. After we get L and φ, the trajectory of the automobile can be determined. 3.2.5 Analysis of the Jitters Although in our scenario the mobile phone needs to be held still, jitters are unavoidable since the procedure of signals collection lasts for several seconds. The jitters will change the coordinate system and increase the speed detection error. As a result, inertial measurement unit (IMU) is used to compensate the error. In this part we need to study different translations and rotations caused by the jitters in our model. We will analyze the influence of different translations and rotations of mobile phone. Figure 9a shows the IMU coordinate system, which is different from the coordinate system in Section 3.2.1. If the mobile phone is hold in landscape orientation as shown in 0 5 10 15 20 25 y(meter) -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Difference of D(meter) 10-3 Translate 1cm in the direction of z-axis Translate 1cm in the direction of y-axis Rotate 5 degrees around x-axis Rotate 5 degrees around z-axis Fig. 10: Overall analysis. the figure, the x-axis is verticle and points up, the y-axis is horizontal and points to the left, and the z-axis points towards the outside of the front face of the screen. We can see jitters can be divided into six categories, the rotation around three axes and the translation along the directions of three axes. As figure 9b shows, with the translation and rotation of the mobile phone, the path length difference ∆D = M1A − M2A changes even if the automobile is at the same position. In fact, the path length difference ∆D can be calculated as follows: ∆D = q (y + 2l) 2 + L2 − p y 2 + L2, (14) where y = |AB| represents the displacement between the automobile and the closer microphone projected onto y-axis, 2l represents the distance between the two microphones and L represents the closest distance between the automobile and the mobile phone. Then, we will evaluate the influence of translation and rotation. The translation in the direction of x-axis can be ignored. The reason is that we have already ignored the height difference when modeling the system. And the translation in the direction of x-axis is much shorter than the height difference between the mobile phone and the sound source. As a result, the translation in the direction of x-axis can be ignored. Similarly, the rotation around the y-axis does not affect the positions of microphones on y-axis. The rotation around y-axis can also be ignored. Figure 10 shows the influences of remaining rotations and translations. We can take the translation in the direction of z-axis as example. The translation in the direction of z-axis influences the distance L we estimate between the mobile phone and the automobile in figure 9b. The path length difference ∆D can be modified as: Authorized licensed use limited to: Nanjing University. Downloaded on July 06,2021 at 04:35:27 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply