正在加载图片...
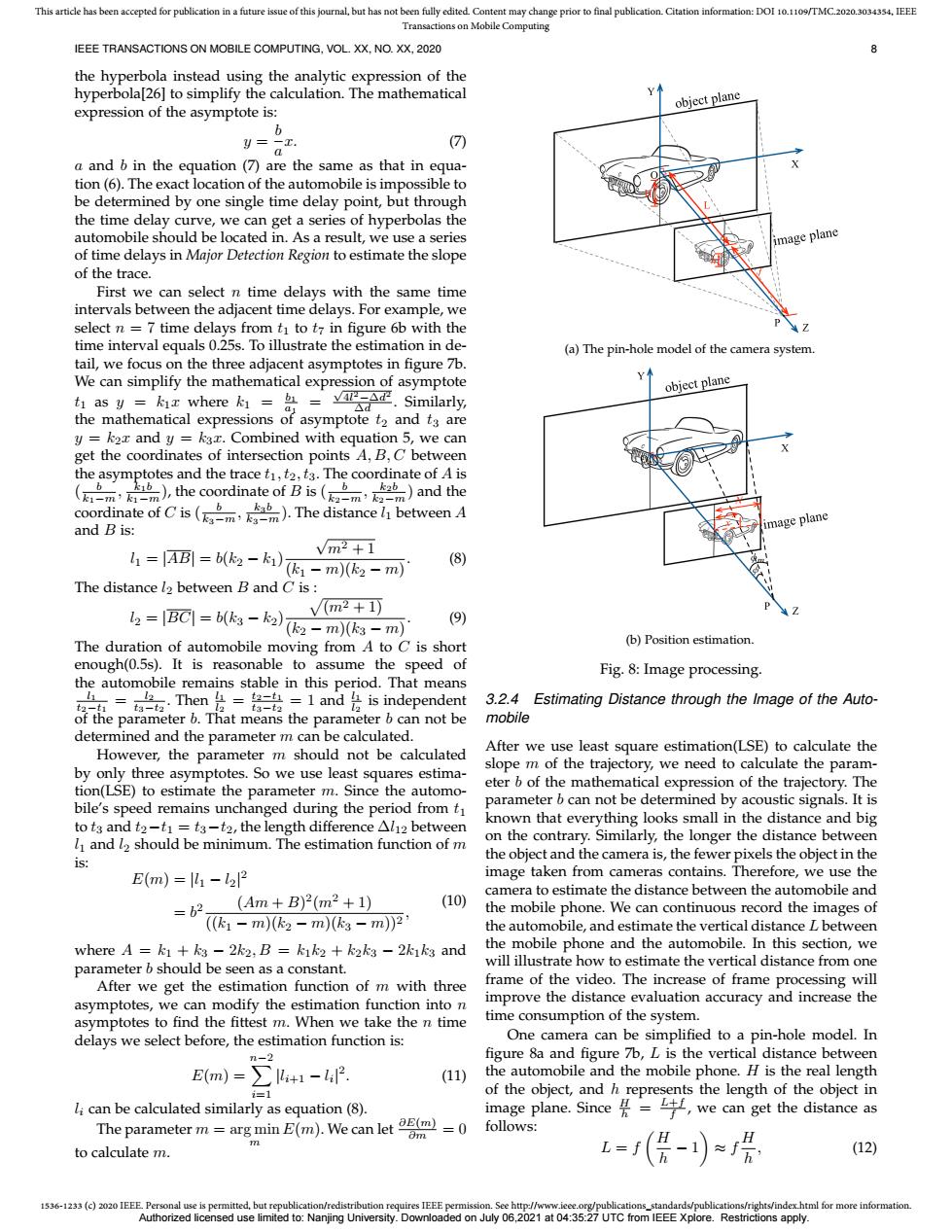
This article has been accepted for publication in a future issue of this journal,but has not been fully edited.Content may change prior to final publication.Citation information:DOI 10.1109/TMC.2020.3034354.IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTING,VOL.XX,NO.XX,2020 the hyperbola instead using the analytic expression of the hyperbola[26]to simplify the calculation.The mathematical object plane expression of the asymptote is: y= (7 a and b in the equation (7)are the same as that in equa- tion(6).The exact location of the automobile is impossible to be determined by one single time delay point,but through the time delay curve,we can get a series of hyperbolas the automobile should be located in.As a result,we use a series image plane of time delays in Major Detection Region to estimate the slope of the trace. First we can select n time delays with the same time intervals between the adjacent time delays.For example,we select n =7 time delays from ti to t7 in figure 6b with the time interval equals 0.25s.To illustrate the estimation in de- (a)The pin-hole model of the camera system. tail,we focus on the three adjacent asymptotes in figure 7b. We can simplify the mathematical expression of asymptote Y object plane t1 as y kix where k =bL= vPAd.Similarly, △d the mathematical expressions of asymptote t2 and t3 are y k2x and y kax.Combined with equation 5,we can get the coordinates of intersection points A,B,C between the asymptotes and the trace t,t2,t3.The coordinate of A is ()the coordinate of B is (and the coordinate of Cis(The distance between A and B is: image plane vm2+1 =[ABl=b(k2-k1)(-m)(k2 -m) (8) The distance l2 between B and C is: vm2+1 12 BCl=b(ks-ka)(ka m)(k3 -m) (9) The duration of automobile moving from A to C is short (b)Position estimation. enough(0.5s).It is reasonable to assume the speed of Fig.8:Image processing. the automobile remains stable in this period.That means gk-aia:Then是=名-t=land&is independent 1 3.2.4 Estimating Distance through the Image of the Auto- of the parameter b.That means the parameter b can not be mobile determined and the parameter m can be calculated. However,the parameter m should not be calculated After we use least square estimation(LSE)to calculate the slope m of the trajectory,we need to calculate the param- by only three asymptotes.So we use least squares estima- tion(LSE)to estimate the parameter m.Since the automo- eter b of the mathematical expression of the trajectory.The bile's speed remains unchanged during the period from t1 parameter b can not be determined by acoustic signals.It is to t3 and t2-t1=t3-t2,the length difference Al12 between known that everything looks small in the distance and big l and l2 should be minimum.The estimation function of m on the contrary.Similarly,the longer the distance between s the object and the camera is,the fewer pixels the object in the E(m)=l-122 image taken from cameras contains.Therefore,we use the =b2(4m+B)2(m2+1) camera to estimate the distance between the automobile and (10) the mobile phone.We can continuous record the images of (61-m)(2-m)(-m)2 the automobile,and estimate the vertical distance L between where A k1+k3 -2k2,B k1k2 k2k3 -2k1k3 and the mobile phone and the automobile.In this section,we parameter b should be seen as a constant. will illustrate how to estimate the vertical distance from one After we get the estimation function of m with three frame of the video.The increase of frame processing will asymptotes,we can modify the estimation function into n improve the distance evaluation accuracy and increase the asymptotes to find the fittest m.When we take the n time time consumption of the system. delays we select before,the estimation function is: One camera can be simplified to a pin-hole model.In n-2 figure 8a and figure 7b,L is the vertical distance between E(m)=∑l+1-42. (11) the automobile and the mobile phone.H is the real length i=1 of the object,and h represents the length of the object in li can be calculated similarly as equation(8). image plane.Since,we can get the distance as The parameter m=arg min E(m).We can let(m)=0 follows: to calculate m. =(层-≈层 (12) 1536-1233(c)2020 IEEE Personal use is permitted,but republication/redistribution requires IEEE permission.See http://www.ieee.org/publications_standards/publications/rights/index.html for more information. Authorized licensed use limited to:Nanjing University.Downloaded on July 06,2021 at 04:35:27 UTC from IEEE Xplore.Restrictions apply.1536-1233 (c) 2020 IEEE. Personal use is permitted, but republication/redistribution requires IEEE permission. See http://www.ieee.org/publications_standards/publications/rights/index.html for more information. This article has been accepted for publication in a future issue of this journal, but has not been fully edited. Content may change prior to final publication. Citation information: DOI 10.1109/TMC.2020.3034354, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MOBILE COMPUTING, VOL. XX, NO. XX, 2020 8 the hyperbola instead using the analytic expression of the hyperbola[26] to simplify the calculation. The mathematical expression of the asymptote is: y = b a x. (7) a and b in the equation (7) are the same as that in equation (6). The exact location of the automobile is impossible to be determined by one single time delay point, but through the time delay curve, we can get a series of hyperbolas the automobile should be located in. As a result, we use a series of time delays in Major Detection Region to estimate the slope of the trace. First we can select n time delays with the same time intervals between the adjacent time delays. For example, we select n = 7 time delays from t1 to t7 in figure 6b with the time interval equals 0.25s. To illustrate the estimation in detail, we focus on the three adjacent asymptotes in figure 7b. We can simplify the mathematical expression of asymptote t1 as y = k1x where k1 = b1 a1 = √ 4l 2−∆d2 ∆d . Similarly, the mathematical expressions of asymptote t2 and t3 are y = k2x and y = k3x. Combined with equation 5, we can get the coordinates of intersection points A, B, C between the asymptotes and the trace t1, t2, t3. The coordinate of A is ( b k1−m , k1b k1−m ), the coordinate of B is ( b k2−m , k2b k2−m ) and the coordinate of C is ( b k3−m , k3b k3−m ). The distance l1 between A and B is: l1 = |AB| = b(k2 − k1) √ m2 + 1 (k1 − m)(k2 − m) . (8) The distance l2 between B and C is : l2 = |BC| = b(k3 − k2) p (m2 + 1) (k2 − m)(k3 − m) . (9) The duration of automobile moving from A to C is short enough(0.5s). It is reasonable to assume the speed of the automobile remains stable in this period. That means l1 t2−t1 = l2 t3−t2 . Then l1 l2 = t2−t1 t3−t2 = 1 and l1 l2 is independent of the parameter b. That means the parameter b can not be determined and the parameter m can be calculated. However, the parameter m should not be calculated by only three asymptotes. So we use least squares estimation(LSE) to estimate the parameter m. Since the automobile’s speed remains unchanged during the period from t1 to t3 and t2−t1 = t3−t2, the length difference ∆l12 between l1 and l2 should be minimum. The estimation function of m is: E(m) = |l1 − l2| 2 = b 2 (Am + B) 2 (m2 + 1) ((k1 − m)(k2 − m)(k3 − m))2 , (10) where A = k1 + k3 − 2k2, B = k1k2 + k2k3 − 2k1k3 and parameter b should be seen as a constant. After we get the estimation function of m with three asymptotes, we can modify the estimation function into n asymptotes to find the fittest m. When we take the n time delays we select before, the estimation function is: E(m) = nX−2 i=1 |li+1 − li | 2 . (11) li can be calculated similarly as equation (8). The parameter m = arg min m E(m). We can let ∂E(m) ∂m = 0 to calculate m. (a) The pin-hole model of the camera system. (b) Position estimation. Fig. 8: Image processing. 3.2.4 Estimating Distance through the Image of the Automobile After we use least square estimation(LSE) to calculate the slope m of the trajectory, we need to calculate the parameter b of the mathematical expression of the trajectory. The parameter b can not be determined by acoustic signals. It is known that everything looks small in the distance and big on the contrary. Similarly, the longer the distance between the object and the camera is, the fewer pixels the object in the image taken from cameras contains. Therefore, we use the camera to estimate the distance between the automobile and the mobile phone. We can continuous record the images of the automobile, and estimate the vertical distance L between the mobile phone and the automobile. In this section, we will illustrate how to estimate the vertical distance from one frame of the video. The increase of frame processing will improve the distance evaluation accuracy and increase the time consumption of the system. One camera can be simplified to a pin-hole model. In figure 8a and figure 7b, L is the vertical distance between the automobile and the mobile phone. H is the real length of the object, and h represents the length of the object in image plane. Since H h = L+f f , we can get the distance as follows: L = f H h − 1 ≈ f H h , (12) Authorized licensed use limited to: Nanjing University. Downloaded on July 06,2021 at 04:35:27 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply