正在加载图片...
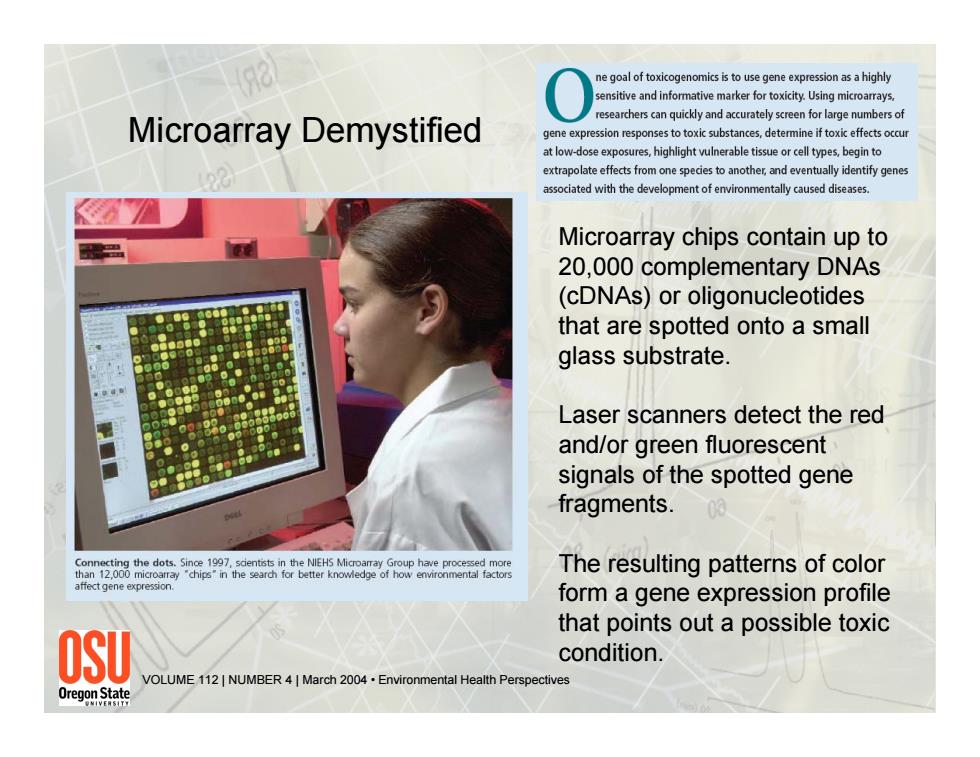
ne goal of toxicogenomics is to use gene expression as a highly sensitive and informative marker for toxicity.Using microarrays esearchers can quickly and accurately screen for large numbers of Microarray Demystified gene expression responses to toxic substances,determine if toxic effects occu at low-dose exposures,highlight vulnerable tissue or cell types,begin to extrapolate effects from one species to another,and eventually identify genes associated with the development of environmentally caused diseases. Microarray chips contain up to 20,000 complementary DNAs (cDNAs)or oligonucleotides that are spotted onto a small glass substrate. Laser scanners detect the red and/or green fluorescent signals of the spotted gene fragments. 00 The resulting patterns of color affect gene expression. form a gene expression profile that points out a possible toxic OSU condition. VOLUME 112 NUMBER 4 March 2004.Environmental Health Perspectives 0regomstate Microarray chips contain up to 20,000 complementary DNAs (cDNAs) or oligonucleotides that are spotted onto a small glass substrate. Laser scanners detect the red and/or green fluorescent signals of the spotted gene fragments. The resulting patterns of color form a gene expression profile that points out a possible toxic condition. Microarray Demystified VOLUME 112 | NUMBER 4 | March 2004 • Environmental Health Perspectives