
Pesticide Toxicology and Risk Assessment Jeffrey J Jenkins Department of Environmental Molecular Toxicology Dose http://emt.orst.edu OSU Oregon State UNIVERSITY
Pesticide Toxicology and Risk Assessment Jeffrey J Jenkins Department of Environmental & Molecular Toxicology http://emt.orst.edu

2 29 Toxicology 22 9 The science of poisons The study of adverse effects of chemicals on living systems 08 (nim) OSU 0regomstate
Toxicology • The science of poisons • The study of adverse effects of chemicals on living systems
92 Bag of chemicals (You) 080 OSU regon
(You) Bag of chemicals
(ag) Toxicology studies how external chemicals interact with your body's chemicals to cause damage or illness OSU 0regonstae
Toxicology studies how external chemicals interact with your body’s chemicals to cause damage or illness

Science Breakthrough of the Year: Human Genetic Variation Science 2001:Human genome project-DNA sequence (~3 billion bases;~30,000 genes)for a few individuals 2007:faster,cheaper technologies for sequencing DNA and assessing variation in genomes; BREAKTHROUGH OF THE YEAR Human Genetic Variation much more is known about how different we are from one another. 23andMe.com-understand your DNA for ~$1000 OSU 0re9onsa邮
Science Breakthrough of the Year: Human Genetic Variation 2001: Human genome project – DNA sequence (~3 billion bases; ~30,000 genes) for a few individuals 2007: faster, cheaper technologies for sequencing DNA and assessing variation in genomes; much more is known about how different we are from one another. 23andMe.com – understand your DNA for ~$1000
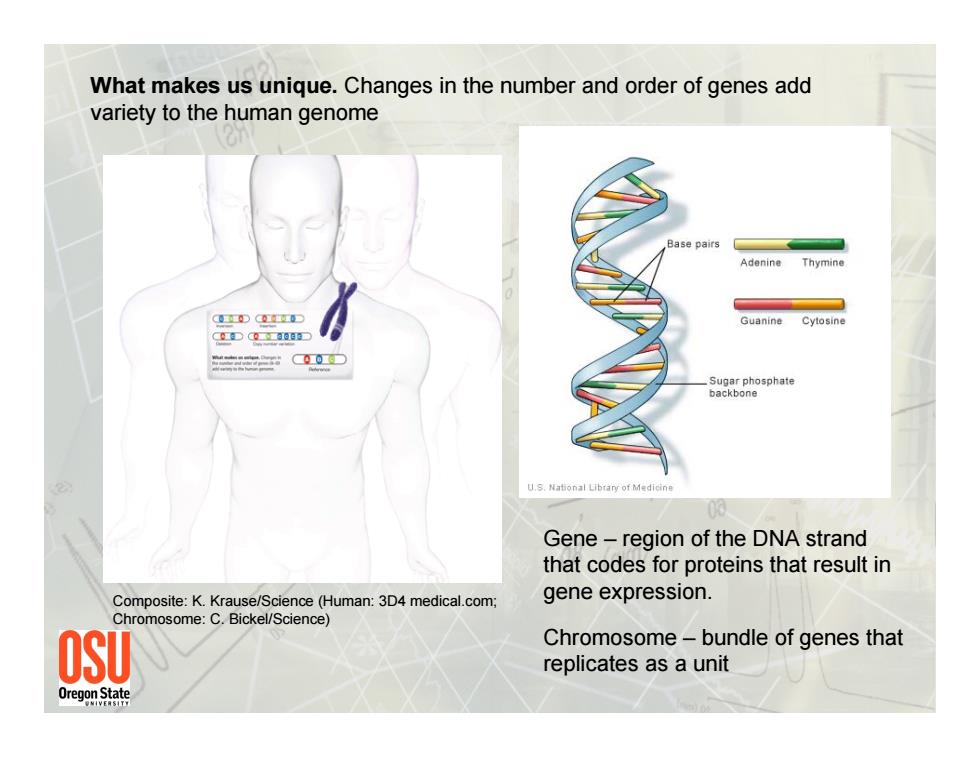
What makes us unique.Changes in the number and order of genes add variety to the human genome ase pairs Adenine Thymine CID Guanine 9DC098 0 Sugar phosphate backbone U.S.National Library of Medicine Gene-region of the DNA strand that codes for proteins that result in Composite:K.Krause/Science(Human:3D4 medical.com; gene expression. Chromosome:C.Bickel/Science) OS Chromosome-bundle of genes that replicates as a unit 0regonstate
Composite: K. Krause/Science (Human: 3D4 medical.com; Chromosome: C. Bickel/Science) What makes us unique. Changes in the number and order of genes add variety to the human genome Gene – region of the DNA strand that codes for proteins that result in gene expression. Chromosome – bundle of genes that replicates as a unit

In humans two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)occur in about 2,200 nucleotides (~15 million differences between individuals,~3 million charted). Nucleotide (base pair) differences SNPs-single letter(base pair)differences www.hapmap.org Does not account for missing,deleted,repetitive DNA sequences Used to determine common genetic variants that occur in humans Link genetic variants to risk(disease,chemical exposure) OSU rgo
In humans two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur in about 2,200 nucleotides (~15 million differences between individuals, ~3 million charted). SNPs – single letter (base pair) differences Does not account for missing, deleted, repetitive DNA sequences Used to determine common genetic variants that occur in humans Link genetic variants to risk (disease, chemical exposure) www.hapmap.org Nucleotide (base pair) differences
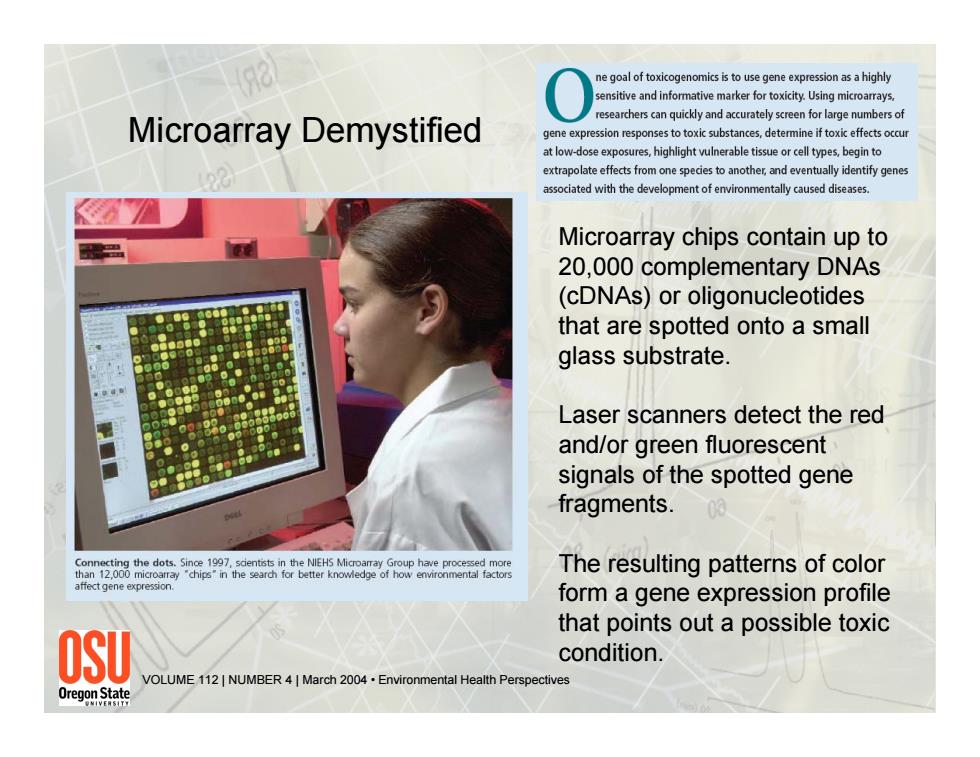
ne goal of toxicogenomics is to use gene expression as a highly sensitive and informative marker for toxicity.Using microarrays esearchers can quickly and accurately screen for large numbers of Microarray Demystified gene expression responses to toxic substances,determine if toxic effects occu at low-dose exposures,highlight vulnerable tissue or cell types,begin to extrapolate effects from one species to another,and eventually identify genes associated with the development of environmentally caused diseases. Microarray chips contain up to 20,000 complementary DNAs (cDNAs)or oligonucleotides that are spotted onto a small glass substrate. Laser scanners detect the red and/or green fluorescent signals of the spotted gene fragments. 00 The resulting patterns of color affect gene expression. form a gene expression profile that points out a possible toxic OSU condition. VOLUME 112 NUMBER 4 March 2004.Environmental Health Perspectives 0regomstate
Microarray chips contain up to 20,000 complementary DNAs (cDNAs) or oligonucleotides that are spotted onto a small glass substrate. Laser scanners detect the red and/or green fluorescent signals of the spotted gene fragments. The resulting patterns of color form a gene expression profile that points out a possible toxic condition. Microarray Demystified VOLUME 112 | NUMBER 4 | March 2004 • Environmental Health Perspectives
会m HOME Soore View Chromorome View Pathway View Advanced Search BLAST Download Publications Quick Search By Entrez Gene ID (examuple:9252): Ouick Search! KARG>>Addiction Related Genes And Sensitive Points On Chromosome (Homo Sapiens) e over or click'+. OSU Center for Bioinformatics(CBD),Peking Univ Any Comments and suggestions to KARG GROUP reo

Understanding you as a bag of chemicals Systems Biology and the“omics” Genomics Epigenomics Transcriptomics Proteomics Metabolomics Metabonomics Pharmacogenomics Toxicogenomics 08 (nim) Bioinformatics
Understanding you as a bag of chemicals Systems Biology and the “omics” Genomics Epigenomics Transcriptomics Proteomics Metabolomics Metabonomics Pharmacogenomics Toxicogenomics Bioinformatics