正在加载图片...
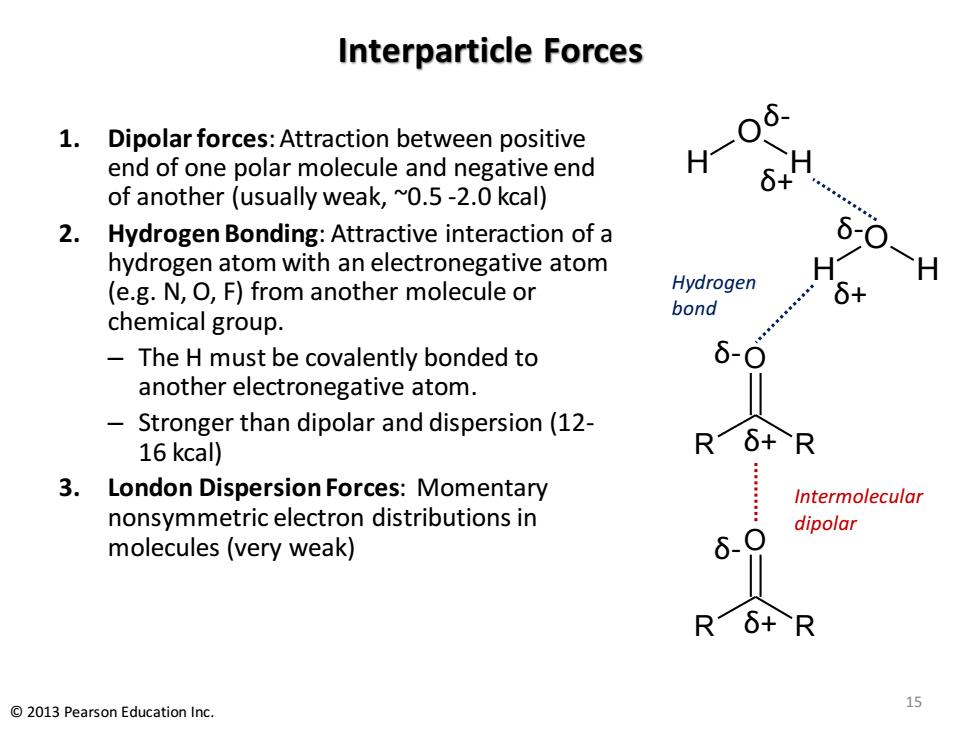
Interparticle Forces 6 1.Dipolar forces:Attraction between positive end of one polar molecule and negative end H- 6+ of another (usually weak,~0.5-2.0 kcal) 2. Hydrogen Bonding:Attractive interaction of a 6-0 hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom (e.g.N,O,F)from another molecule or Hydrogen 6+ bond chemical group. The H must be covalently bonded to 6-0 another electronegative atom. Stronger than dipolar and dispersion(12- 16 kcal) R6+R 3.London Dispersion Forces:Momentary Intermolecular nonsymmetric electron distributions in dipolar molecules (very weak) 6、O Rδ+R 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 15 Interparticle Forces 1. Dipolar forces: Attraction between positive end of one polar molecule and negative end of another (usually weak, ~0.5 -2.0 kcal) 2. Hydrogen Bonding: Attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom (e.g. N, O, F) from another molecule or chemical group. – The H must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom. – Stronger than dipolar and dispersion (12- 16 kcal) 3. London Dispersion Forces: Momentary nonsymmetric electron distributions in molecules (very weak) O R R O R R δ- δ- δ+ δ+ Intermolecular dipolar H H O Hydrogen bond δ+ δ- H H O δ+ δ- 15 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc