
Organic Chemistry, ORGANIC 8th Edition CHEMISTRY L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 6 Lecture Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination G.WADE,J R Rizalia Klausmeyer Baylor University Waco,TX 2013 Pearson Education,Inc ALWAYS LEARNING PEARSON
Chapter 6 Lecture Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Rizalia Klausmeyer Baylor University Waco, TX
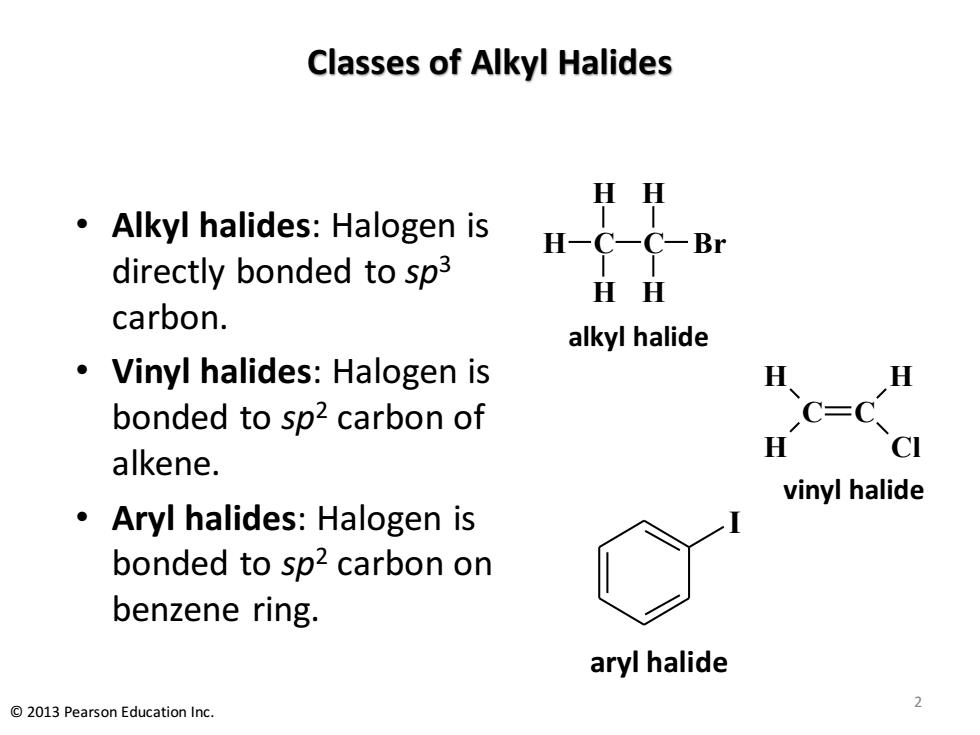
Classes of Alkyl Halides HH Alkyl halides:Halogen is H-C-C-Br directly bonded to sp3 HH carbon. alkyl halide Vinyl halides:Halogen is 及、 H bonded to sp2 carbon of C=C H CI alkene. vinyl halide Aryl halides:Halogen is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. aryl halide 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Classes of Alkyl Halides • Alkyl halides: Halogen is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. • Vinyl halides: Halogen is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene. • Aryl halides: Halogen is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring. C C H H H Cl vinyl halide C H H H C H H Br alkyl halide I aryl halide 2 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
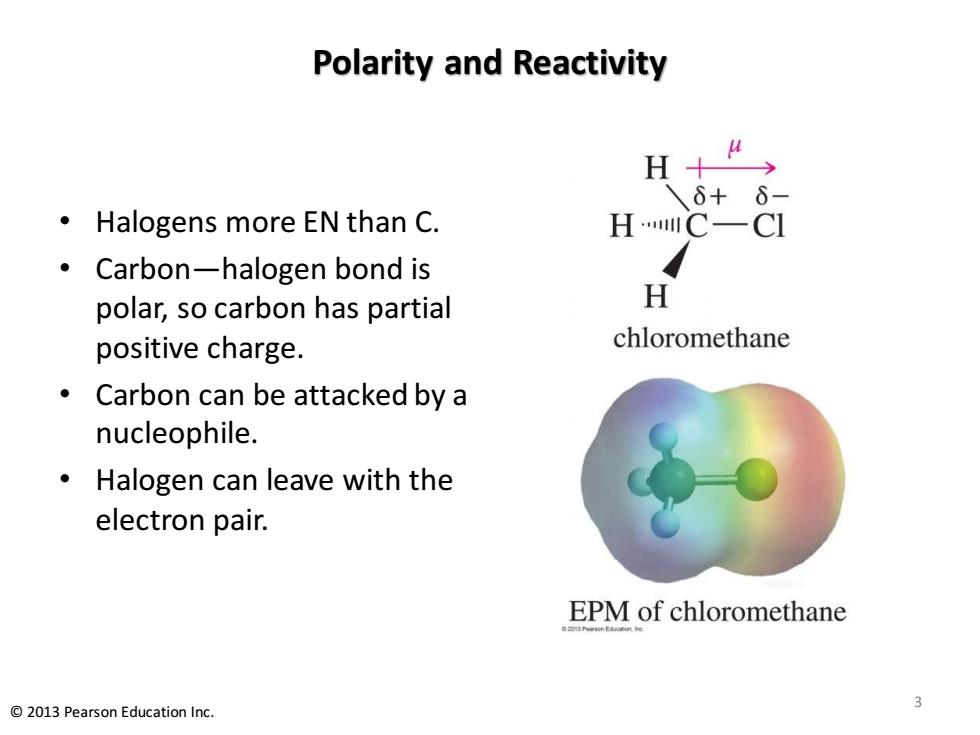
Polarity and Reactivity H+ 6+ 6 Halogens more EN than C. HC- CI Carbon-halogen bond is polar,so carbon has partial H positive charge. chloromethane Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. Halogen can leave with the electron pair. EPM of chloromethane 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Polarity and Reactivity • Halogens more EN than C. • Carbon—halogen bond is polar, so carbon has partial positive charge. • Carbon can be attacked by a nucleophile. • Halogen can leave with the electron pair. 3 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
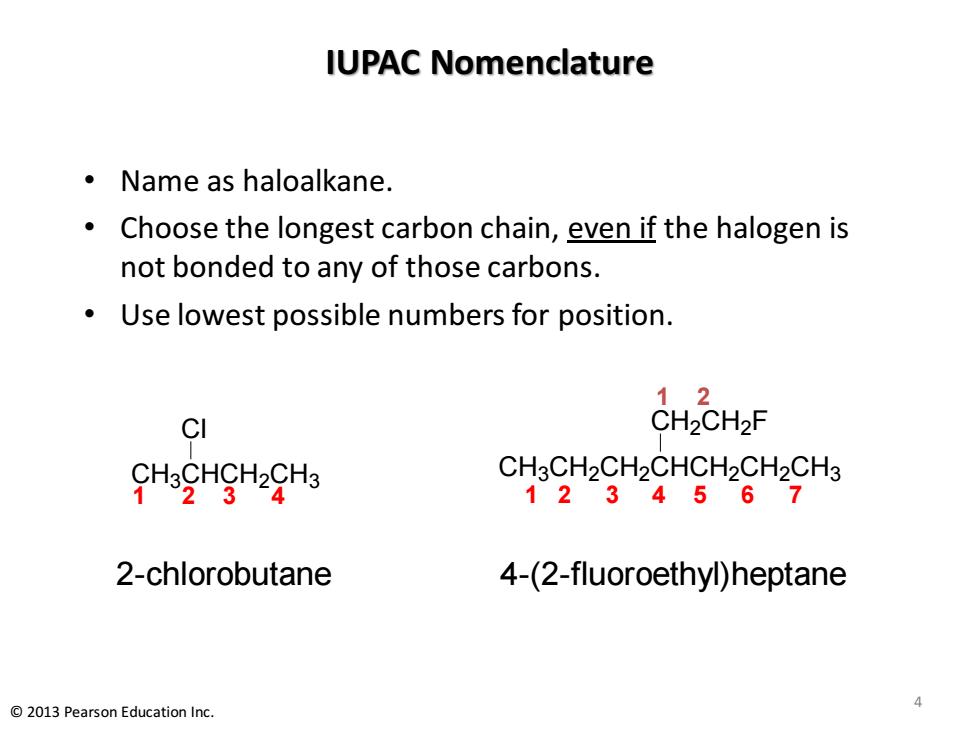
IUPAC Nomenclature ·Name as haloalkane. Choose the longest carbon chain,even if the halogen is not bonded to any of those carbons. Use lowest possible numbers for position. 12 CI CH2CH2F CHoCHgHgHa CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 1234567 2-chlorobutane 4-(2-fluoroethyl)heptane 2013 Pearson Education Inc
IUPAC Nomenclature • Name as haloalkane. • Choose the longest carbon chain, even if the halogen is not bonded to any of those carbons. • Use lowest possible numbers for position. CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 CH2CH2 F 1 2 3 4 2-chlorobutane 4-(2-fluoroethyl)heptane 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 CH3CHCH2CH3 Cl 4 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
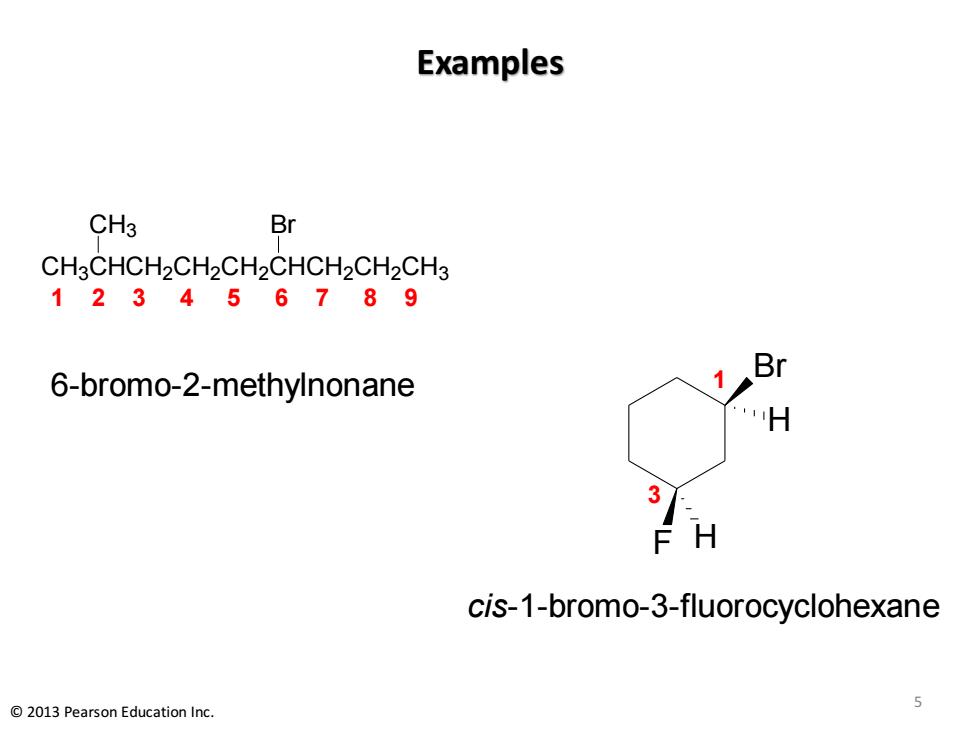
Examples CH3 Br CH3CHCH2CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 123456789 Br 6-bromo-2-methylnonane H 3 FH cis-1-bromo-3-fluorocyclohexane 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Examples CH3CHCH2CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 CH3 Br Br F H H 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6-bromo-2-methylnonane 1 3 cis-1-bromo-3-fluorocyclohexane 5 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
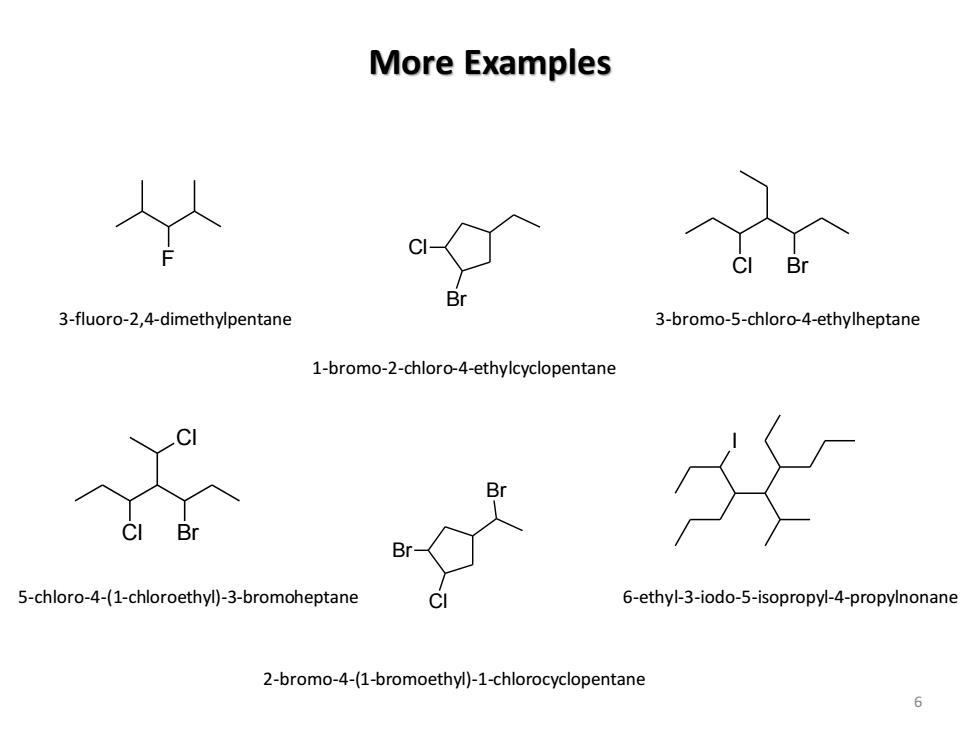
More Examples Br 3-fluoro-2,4-dimethylpentane 3-bromo-5-chloro-4-ethylheptane 1-bromo-2-chloro-4-ethylcyclopentane Bi B Br 5-chloro-4-(1-chloroethyl)-3-bromoheptane 6-ethyl-3-iodo-5-isopropyl-4-propylnonane 2-bromo-4-(1-bromoethyl)-1-chlorocyclopentane
More Examples 6 F Br Cl Cl Br Cl Cl Br Br Cl Br I 3-fluoro-2,4-dimethylpentane 1-bromo-2-chloro-4-ethylcyclopentane 3-bromo-5-chloro-4-ethylheptane 5-chloro-4-(1-chloroethyl)-3-bromoheptane 2-bromo-4-(1-bromoethyl)-1-chlorocyclopentane 6-ethyl-3-iodo-5-isopropyl-4-propylnonane
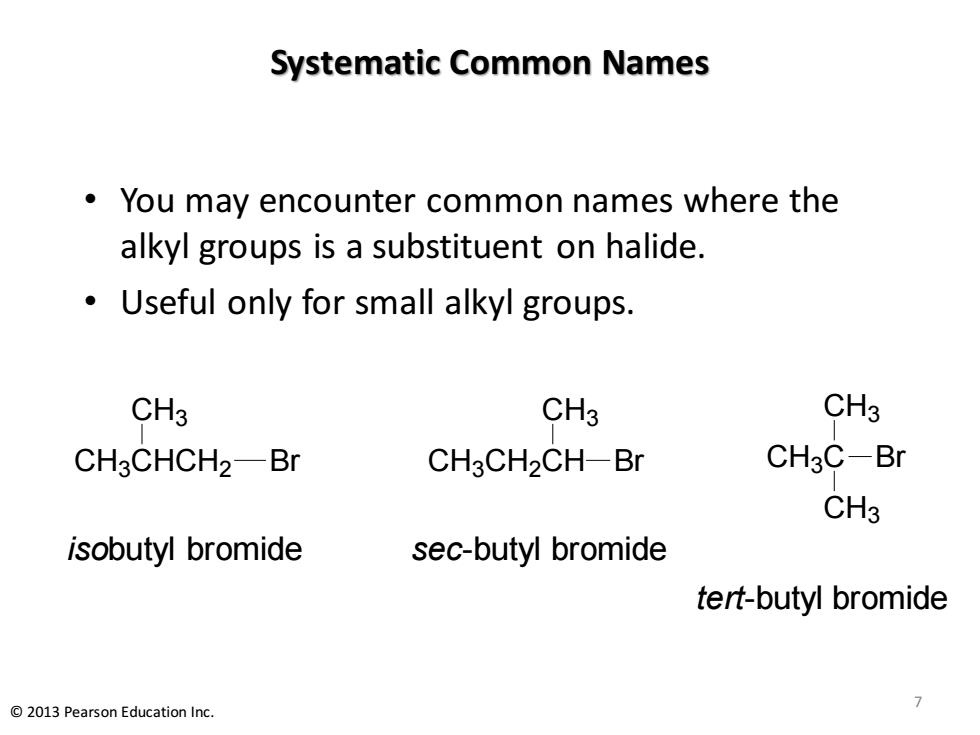
Systematic Common Names You may encounter common names where the alkyl groups is a substituent on halide. Useful only for small alkyl groups. CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3CHCH2-Br CH3CH2CH-Br CH3C-Br CH3 isobutyl bromide sec-butyl bromide tert-butyl bromide 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Systematic Common Names • You may encounter common names where the alkyl groups is a substituent on halide. • Useful only for small alkyl groups. CH3CHCH2 CH3 Br CH3CH2CH CH3 Br CH3C CH3 Br CH3 isobutyl bromide sec-butyl bromide tert-butyl bromide 7 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

Common Names of Halides CH2X2 is called methylene halide. 。CHX3 is a haloform. CX is carbon tetrahalide. Common halogenated solvents: CH,Cl,is methylene chloride. CHCl2 is chloroform. CCla is carbon tetrachloride. 8 2013 Pearson Education Inc
Common Names of Halides • CH2X2 is called methylene halide. • CHX3 is a haloform. • CX4 is carbon tetrahalide. • Common halogenated solvents: CH2Cl2 is methylene chloride. CHCl3 is chloroform. CCl4 is carbon tetrachloride. 8 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc

Alkyl Halides Classification Methyl halides:Halide is attached to a methyl group. Primary alkyl halide:Carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to only one other carbon. Secondary alkyl halide:Carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to two other carbons. Tertiary alkyl halide:Carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to three other carbons. 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 9
Alkyl Halides Classification • Methyl halides: Halide is attached to a methyl group. • Primary alkyl halide: Carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to only one other carbon. • Secondary alkyl halide: Carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to two other carbons. • Tertiary alkyl halide: Carbon to which halogen is bonded is attached to three other carbons. 9 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc
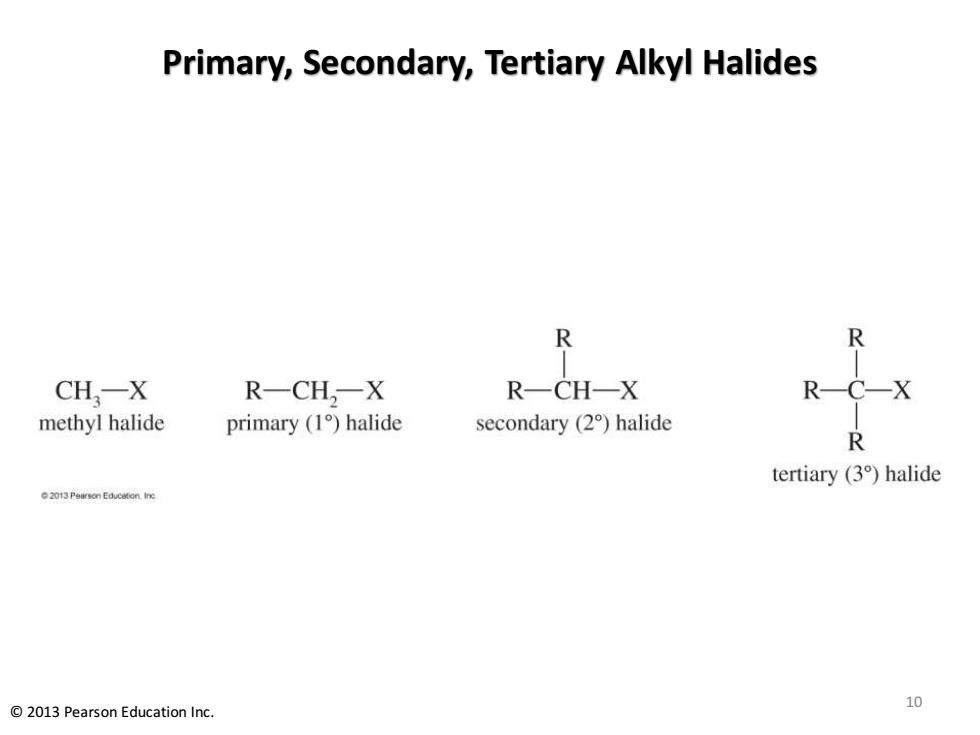
Primary,Secondary,Tertiary Alkyl Halides R CH,-X R一CH,一X R一CH-X methyl halide primary (1)halide secondary (2)halide R tertiary (3)halide 2013 Peurson Educaten.ine 2013 Pearson Education Inc. 10
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Alkyl Halides 10 © 2013 Pearson Education Inc