
Organic Chemistry, ORGANIC 8th Edition CHEMISTRY L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 4 Lecture The Study of Chemical Reactions G.WADE,JR Rizalia Klausmeyer Baylor University Waco,TX 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. ALWAYS LEARNING PEARSON
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 4 Lecture Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. The Study of Chemical Reactions © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Rizalia Klausmeyer Baylor University Waco, TX
Introduction ·Overall reaction:reactants→products To learn more about a reaction: Thermodynamics is the study of the energy changes that accompany chemical and physical transformations. Kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Mechanism:Step-by-step description of how the reaction happens. 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 4 2
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Introduction • Overall reaction: reactants → products • To learn more about a reaction: ▪ Thermodynamics is the study of the energy changes that accompany chemical and physical transformations. ▪ Kinetics is the study of reaction rates. • Mechanism: Step-by-step description of how the reaction happens. Chapter 4 2
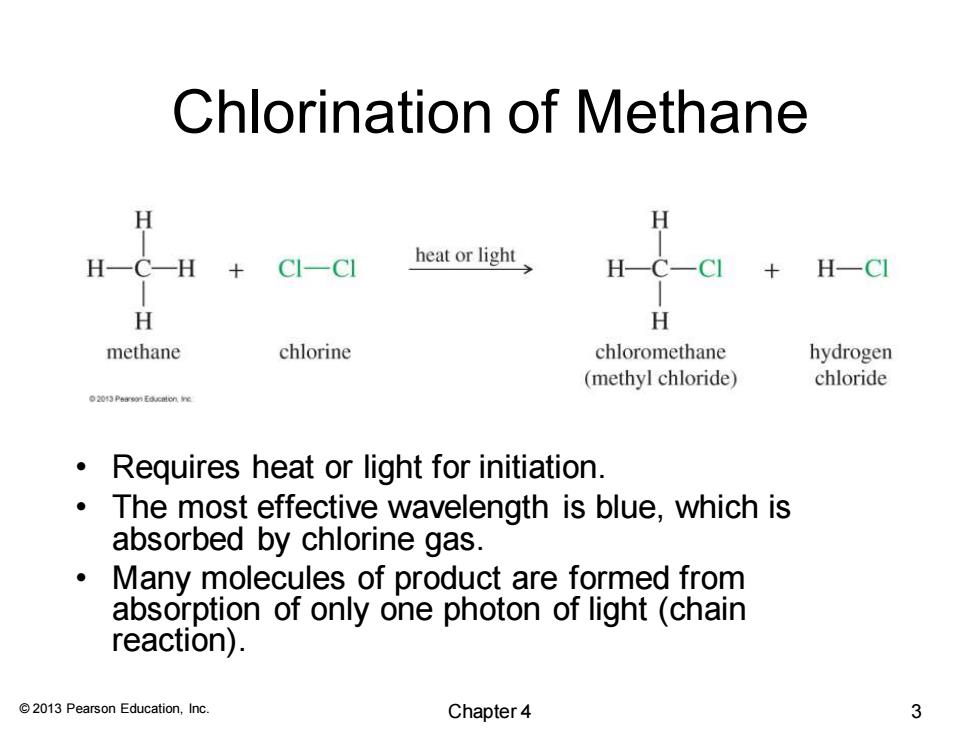
Chlorination of Methane H H一C-H CI-CI heat or light H- H-CI H H methane chlorine chloromethane hydrogen (methyl chloride) chloride 201 Peasn Eamon re Requires heat or light for initiation. The most effective wavelength is blue,which is absorbed by chlorine gas. Many molecules of product are formed from absorption of only one photon of light(chain reaction). 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 4 3
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Chlorination of Methane • Requires heat or light for initiation. • The most effective wavelength is blue, which is absorbed by chlorine gas. • Many molecules of product are formed from absorption of only one photon of light (chain reaction). Chapter 4 3

The Free-Radical Chain Reaction Initiation:Generates a radical intermediate. Propagation:The intermediate reacts with a stable molecule to produce another reactive intermediate(and a product molecule). Termination:Side reactions that destroy the reactive intermediate. 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 4 4
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. The Free-Radical Chain Reaction • Initiation: Generates a radical intermediate. • Propagation: The intermediate reacts with a stable molecule to produce another reactive intermediate (and a product molecule). • Termination: Side reactions that destroy the reactive intermediate. Chapter 4 4
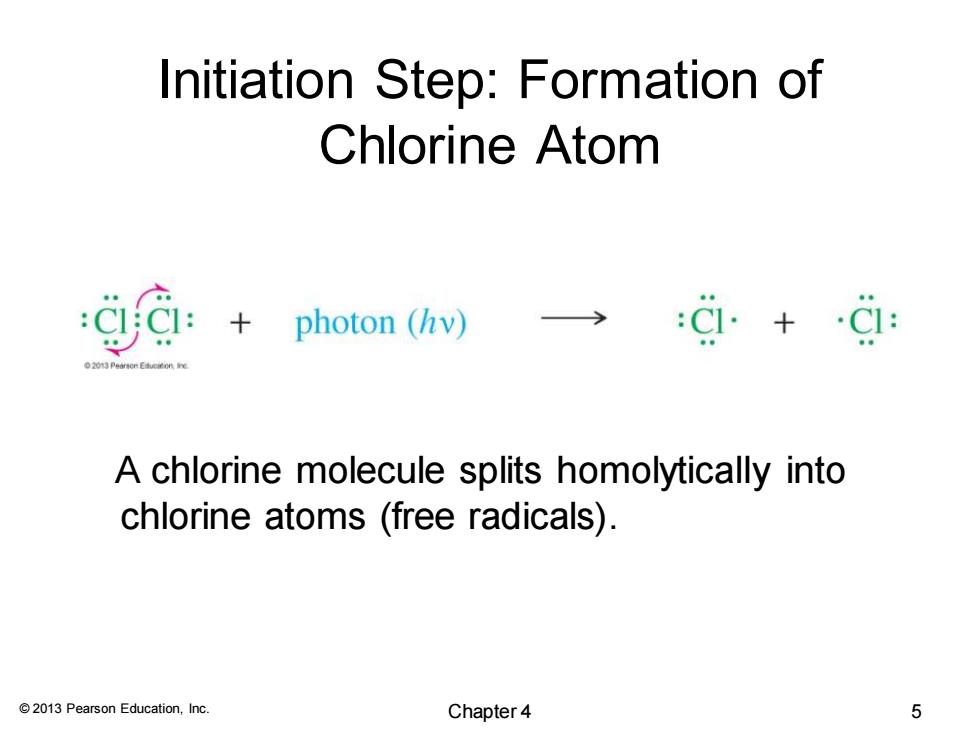
Initiation Step:Formation of Chlorine Atom ga: :+photon (hv)) A chlorine molecule splits homolytically into chlorine atoms (free radicals). 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter4 5
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Initiation Step: Formation of Chlorine Atom A chlorine molecule splits homolytically into chlorine atoms (free radicals). Chapter 4 5
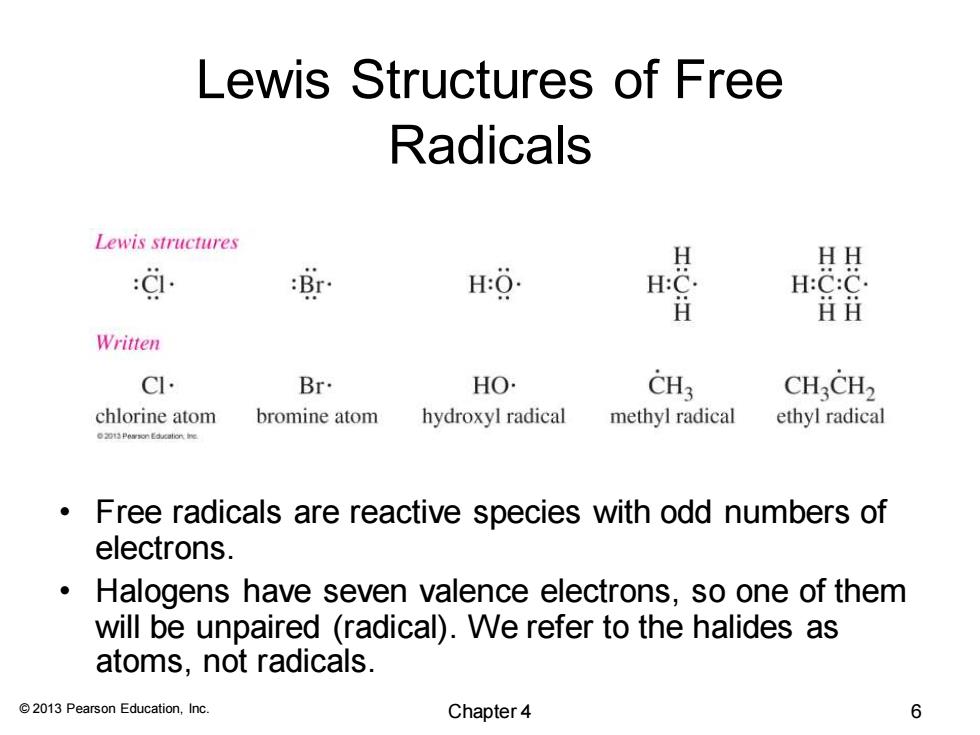
Lewis Structures of Free Radicals Lewis structures 效 H HH H H:C:C ⅱ丑 Written CI. Br. HO. CH3 CHCH2 chlorine atom bromine atom hydroxyl radical methyl radical ethyl radical Free radicals are reactive species with odd numbers of electrons. Halogens have seven valence electrons,so one of them will be unpaired (radical).We refer to the halides as atoms,not radicals. 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 4 6
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Lewis Structures of Free Radicals • Free radicals are reactive species with odd numbers of electrons. • Halogens have seven valence electrons, so one of them will be unpaired (radical). We refer to the halides as atoms, not radicals. Chapter 4 6
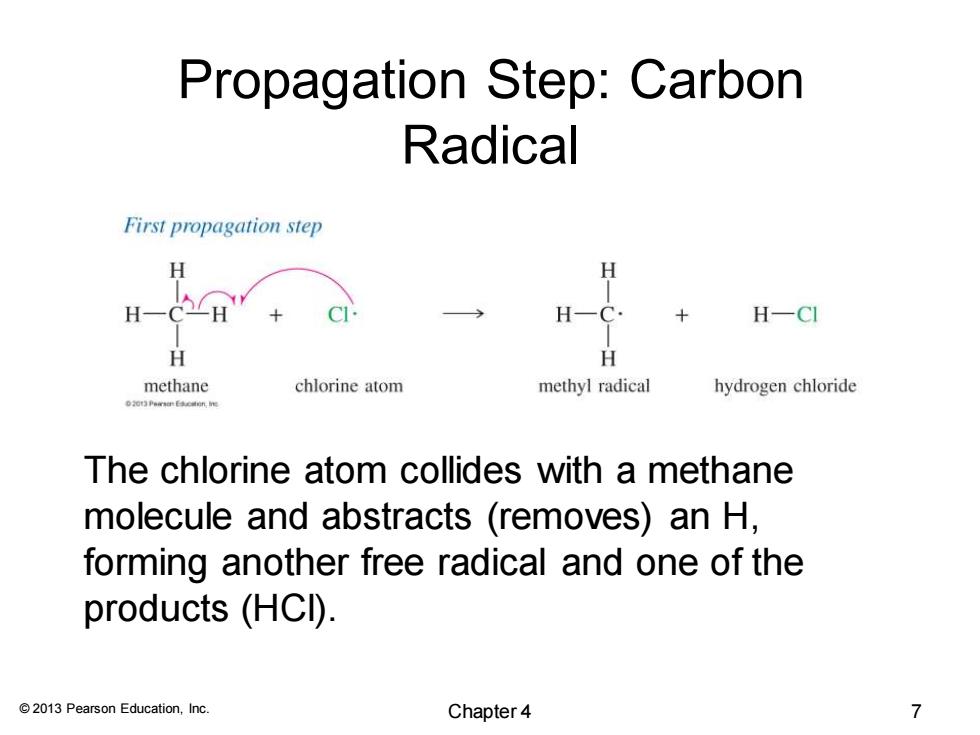
Propagation Step:Carbon Radical First propagation step H H H-日 H H-CI H methane chlorine atom methyl radical hydrogen chloride The chlorine atom collides with a methane molecule and abstracts (removes)an H, forming another free radical and one of the products (HCI). 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter4 7
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Propagation Step: Carbon Radical The chlorine atom collides with a methane molecule and abstracts (removes) an H, forming another free radical and one of the products (HCl). Chapter 4 7
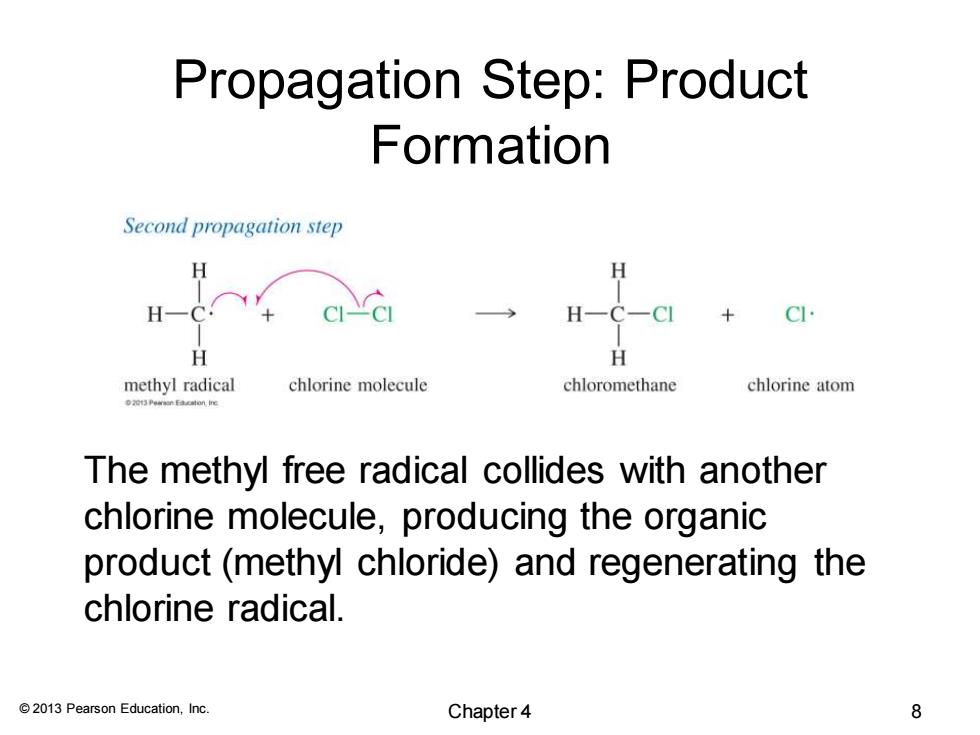
Propagation Step:Product Formation Second propagation step H H H H CI. H H methyl radical chlorine molecule chloromethane chlorine atom The methyl free radical collides with another chlorine molecule,producing the organic product(methyl chloride)and regenerating the chlorine radical. 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 4 8
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Propagation Step: Product Formation The methyl free radical collides with another chlorine molecule, producing the organic product (methyl chloride) and regenerating the chlorine radical. Chapter 4 8
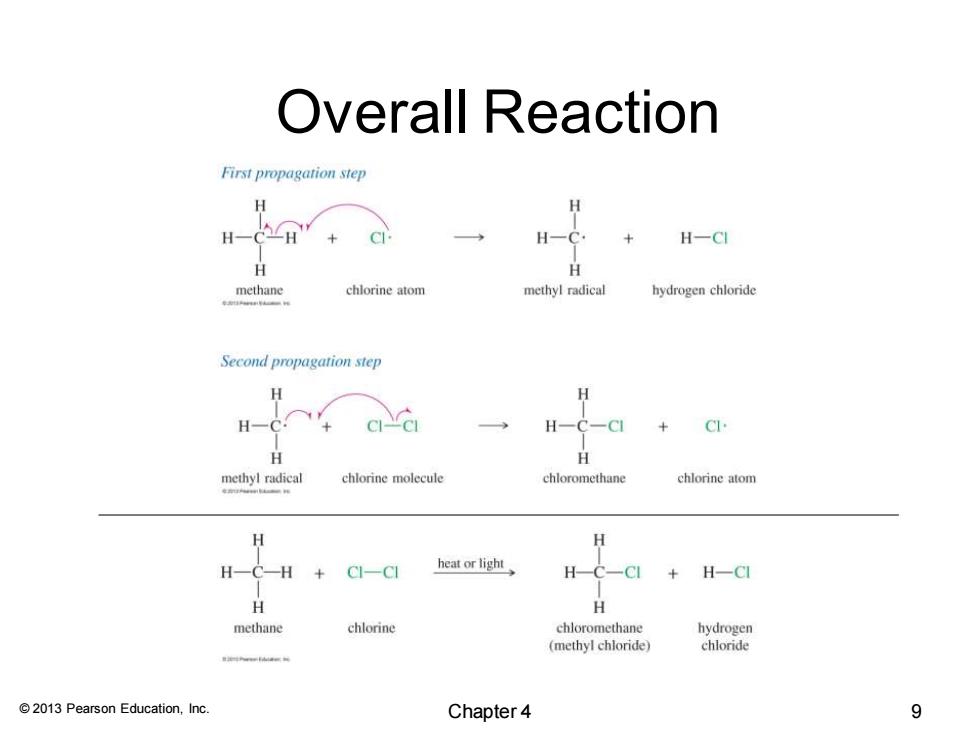
Overall Reaction First propagation step H H-CCH H-CI chlorine atom methyl radical hydrogen chloride Second propagation step H H H-C. H-C-CI H H methyl radical chlorine molecule chloromethane chlorine atom H-C—H+CI-C heat or light H-CI H H methane chlorine chloromethane hydrogen (methyl chloride) chloride n 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 4 9
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Overall Reaction Chapter 4 9
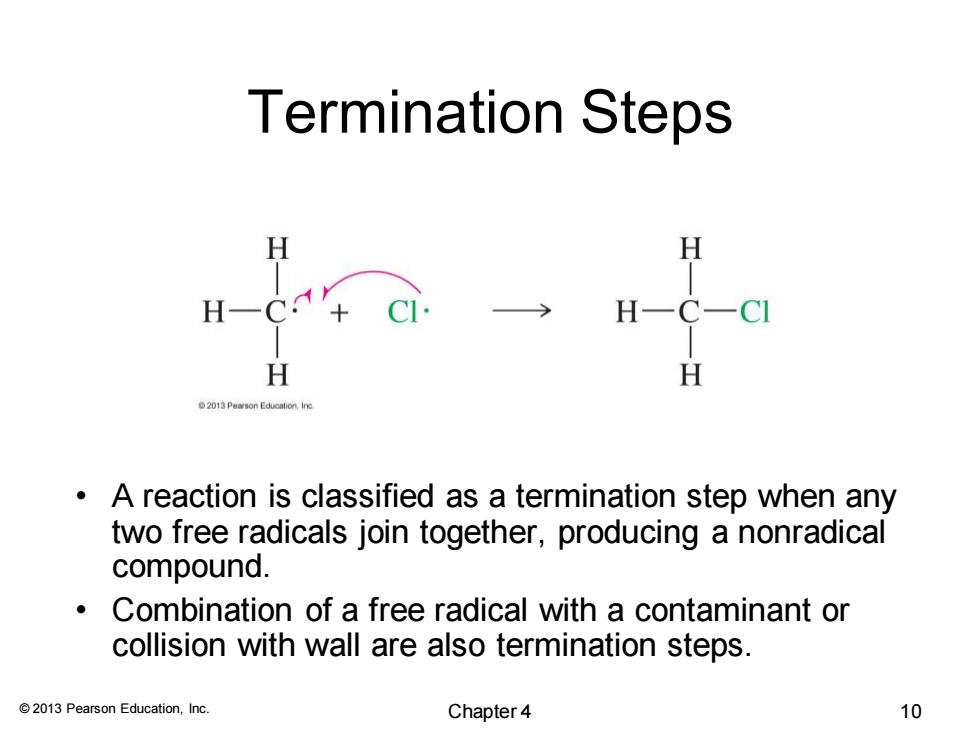
Termination Steps H H一C H H H 013 Pearson Educalion,ine A reaction is classified as a termination step when any two free radicals join together,producing a nonradical compound. 。 Combination of a free radical with a contaminant or collision with wall are also termination steps. 2013 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 4 10
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Termination Steps • A reaction is classified as a termination step when any two free radicals join together, producing a nonradical compound. • Combination of a free radical with a contaminant or collision with wall are also termination steps. Chapter 4 10