
CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 16 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
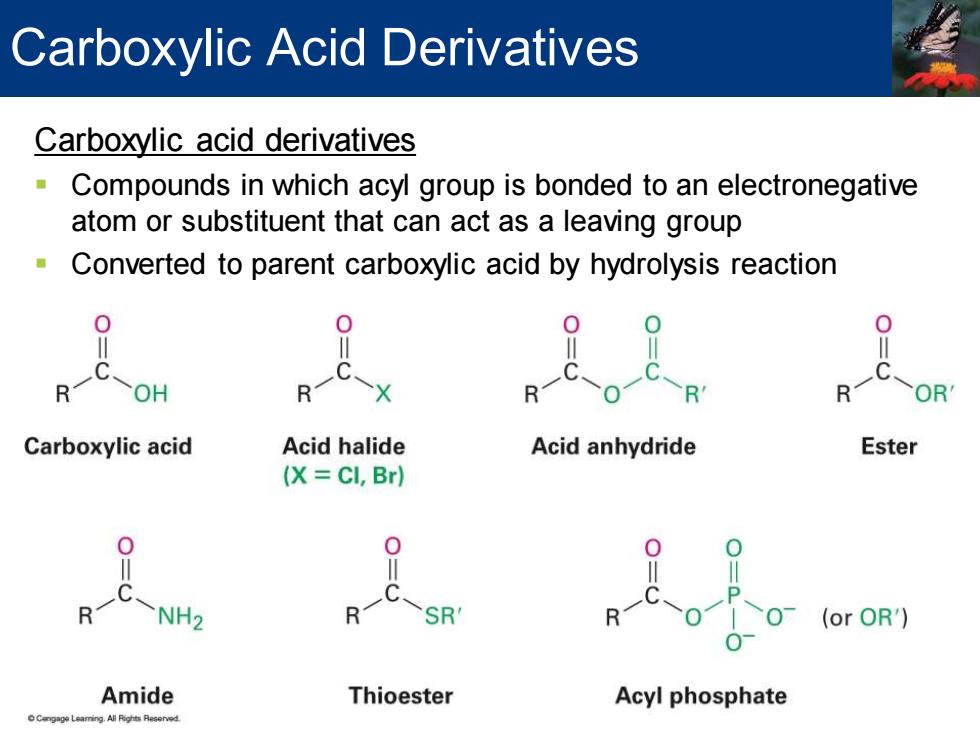
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives Compounds in which acyl group is bonded to an electronegative atom or substituent that can act as a leaving group Converted to parent carboxylic acid by hydrolysis reaction Carboxylic acid Acid halide Acid anhydride Ester (X=CI,Br) 0 R NH2 R -s8 0 (or OR') Amide Thioester Acyl phosphate
Carboxylic acid derivatives ▪ Compounds in which acyl group is bonded to an electronegative atom or substituent that can act as a leaving group ▪ Converted to parent carboxylic acid by hydrolysis reaction Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
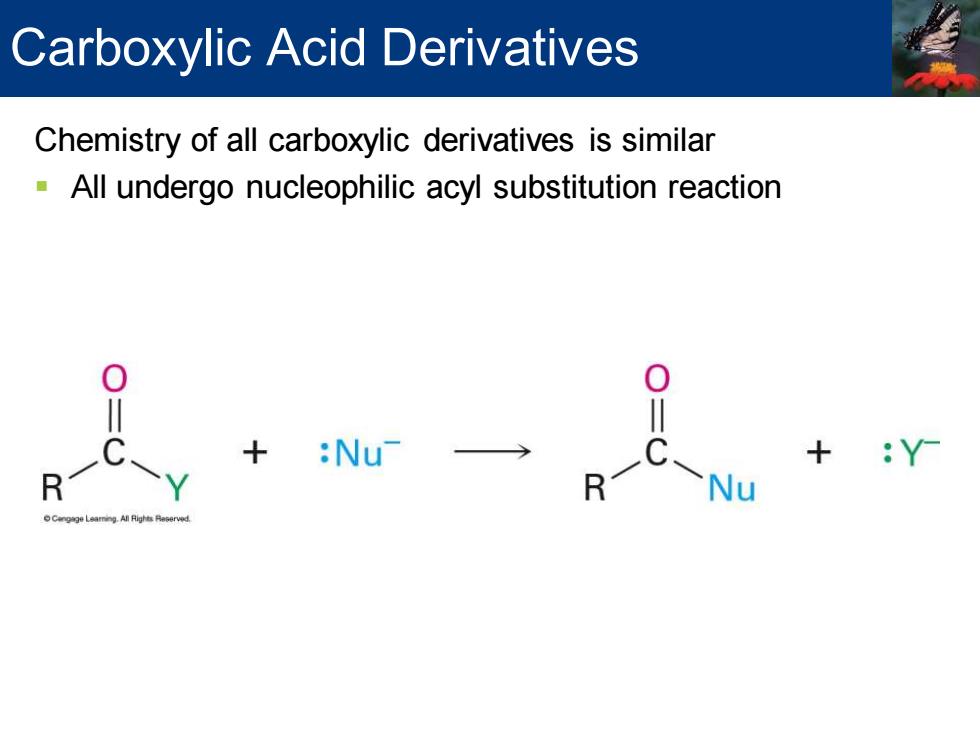
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Chemistry of all carboxylic derivatives is similar All undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction + → Y
Chemistry of all carboxylic derivatives is similar ▪ All undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
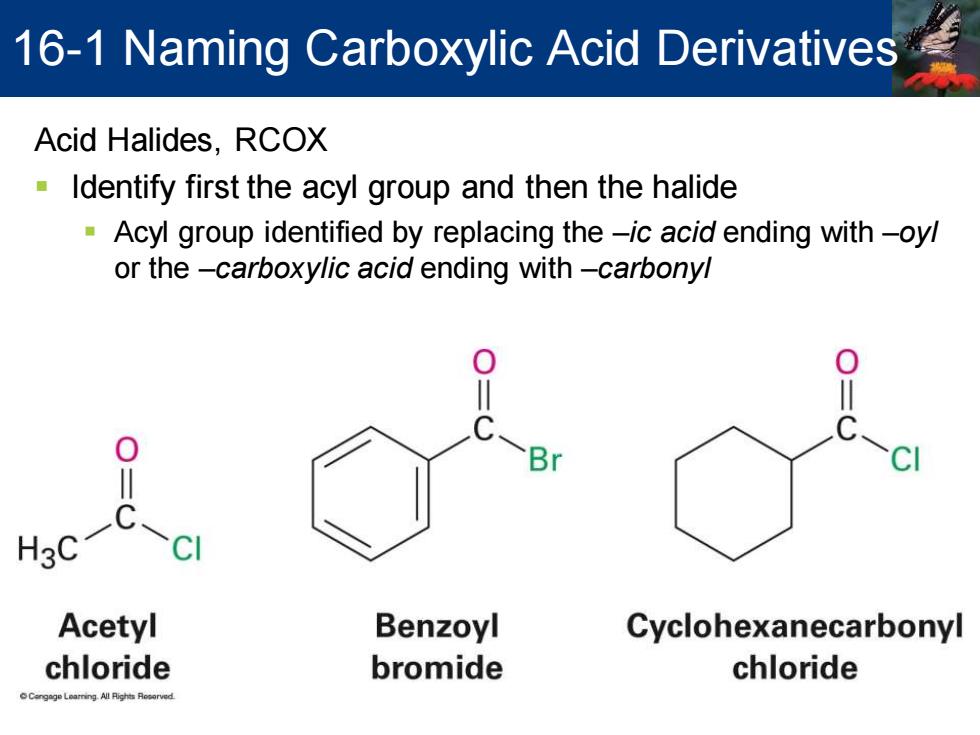
16-1 Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Acid Halides,RCOX Identify first the acyl group and then the halide Acyl group identified by replacing the-ic acid ending with-oyl or the -carboxylic acid ending with-carbonyl 0 H3C C-C Acetyl Benzoyl Cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride bromide chloride
Acid Halides, RCOX ▪ Identify first the acyl group and then the halide ▪ Acyl group identified by replacing the –ic acid ending with –oyl or the –carboxylic acid ending with –carbonyl 16-1 Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
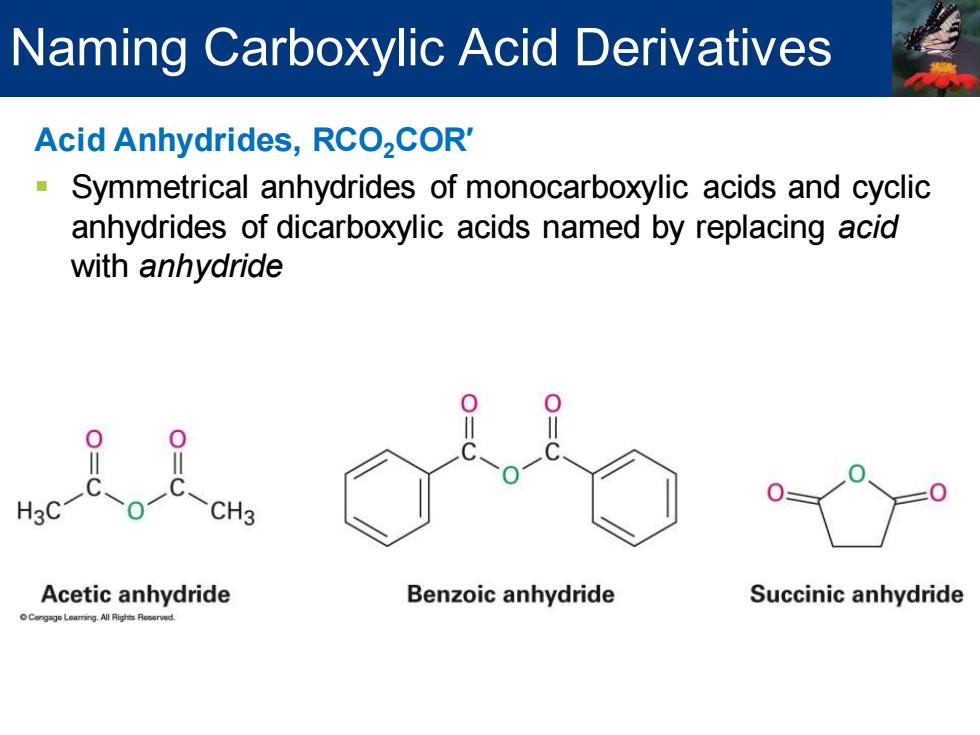
Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Acid Anhydrides,RCO2COR' Symmetrical anhydrides of monocarboxylic acids and cyclic anhydrides of dicarboxylic acids named by replacing acid with anhydride H3C CH3 Acetic anhydride Benzoic anhydride Succinic anhydride
Acid Anhydrides, RCO2COR′ ▪ Symmetrical anhydrides of monocarboxylic acids and cyclic anhydrides of dicarboxylic acids named by replacing acid with anhydride Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
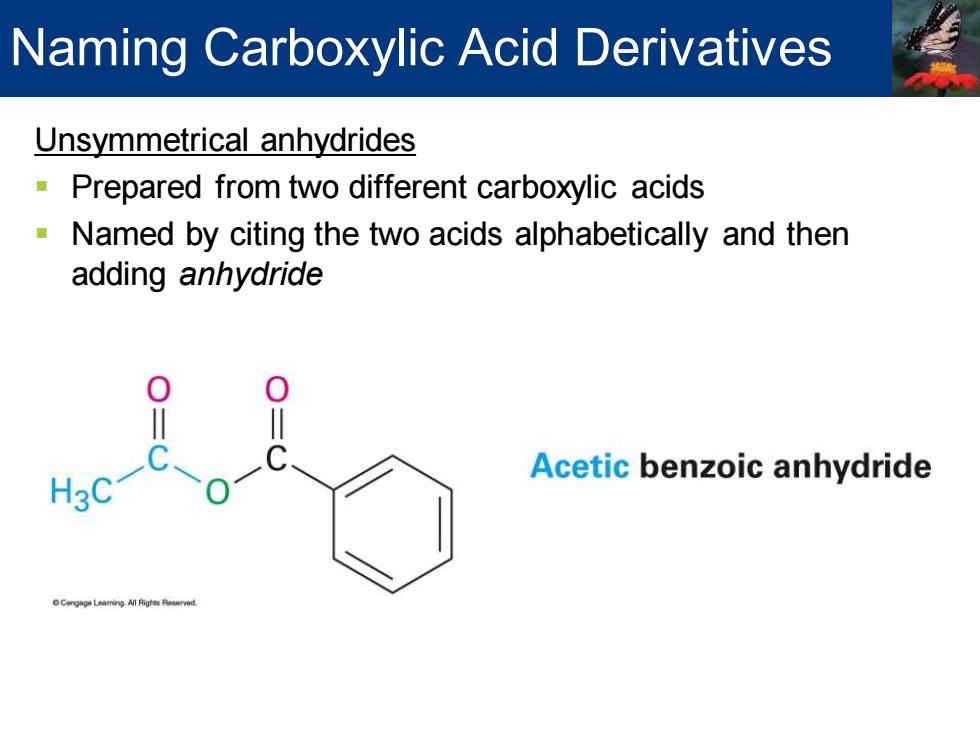
Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Unsymmetrical anhydrides Prepared from two different carboxylic acids Named by citing the two acids alphabetically and then adding anhydride Acetic benzoic anhydride Leamng All Righe Peerved
Unsymmetrical anhydrides ▪ Prepared from two different carboxylic acids ▪ Named by citing the two acids alphabetically and then adding anhydride Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
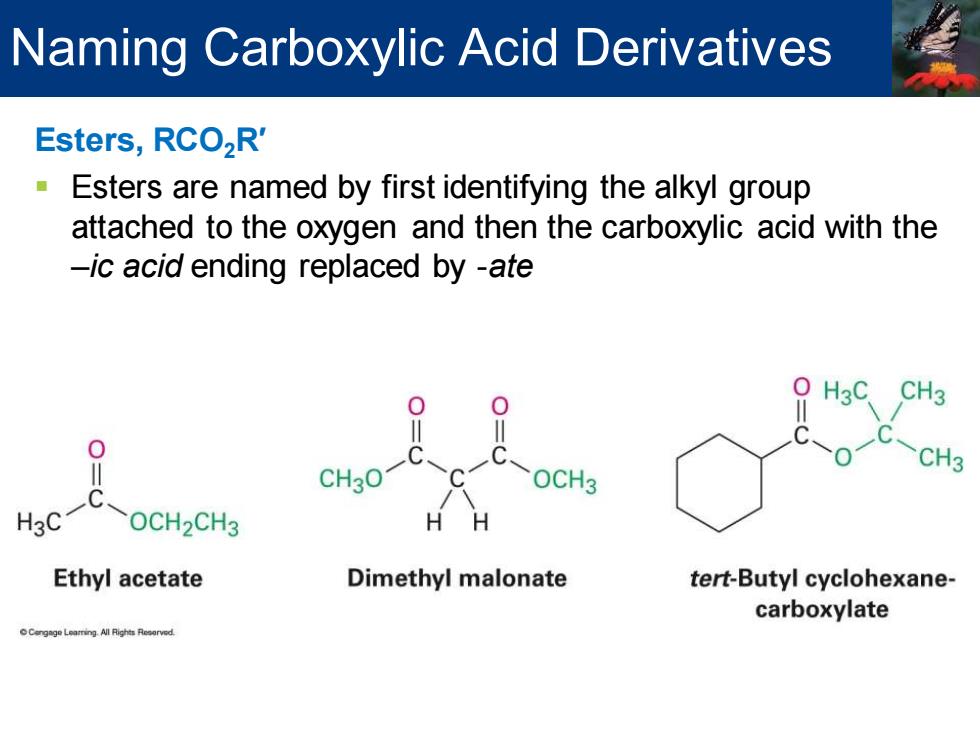
Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Esters,RCO,R' Esters are named by first identifying the alkyl group attached to the oxygen and then the carboxylic acid with the -ic acid ending replaced by -ate 0 CH3 0 OCH3 CH3 CH3O1 C H3C OCH2CH3 Ethyl acetate Dimethyl malonate tert-Butyl cyclohexane- carboxylate
Esters, RCO2R′ ▪ Esters are named by first identifying the alkyl group attached to the oxygen and then the carboxylic acid with the –ic acid ending replaced by -ate Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
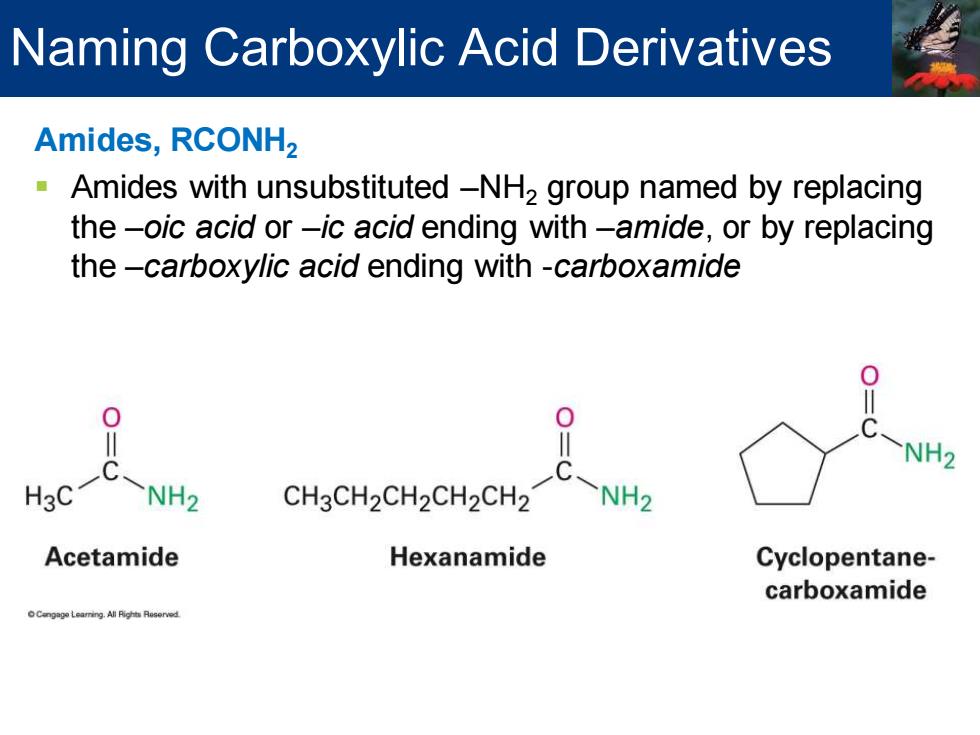
Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Amides,RCONH2 Amides with unsubstituted-NH2 group named by replacing the-oic acid or-ic acid ending with-amide,or by replacing the-carboxylic acid ending with -carboxamide 0 0 NH2 H3C NH2 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2 NH2 Acetamide Hexanamide Cyclopentane- carboxamide
Amides, RCONH2 ▪ Amides with unsubstituted –NH2 group named by replacing the –oic acid or –ic acid ending with –amide, or by replacing the –carboxylic acid ending with -carboxamide Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
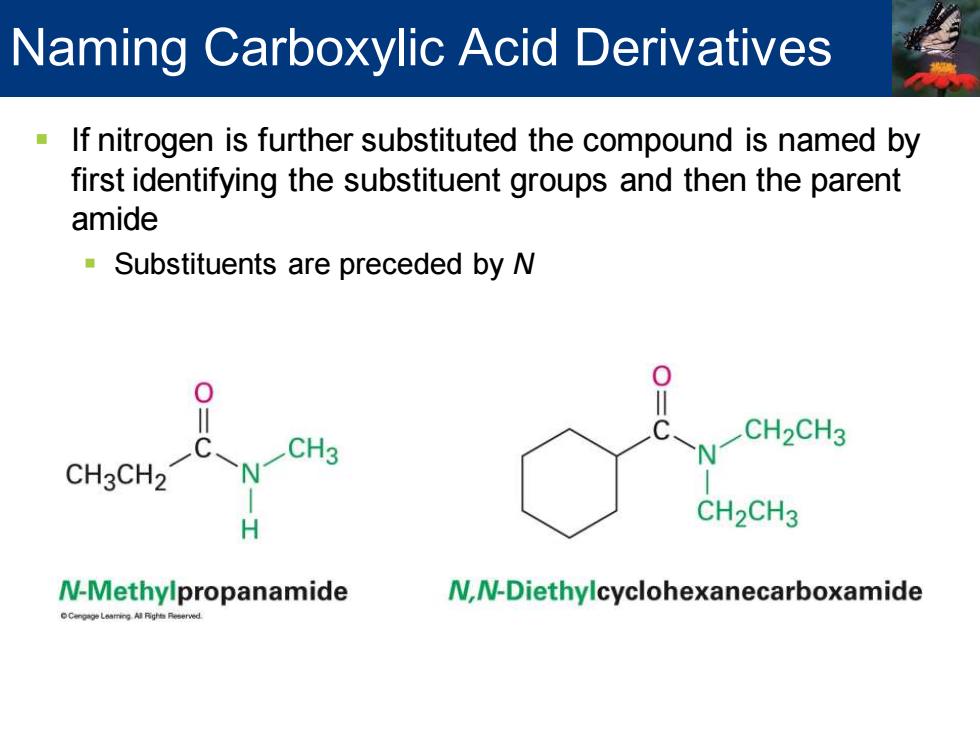
Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives If nitrogen is further substituted the compound is named by first identifying the substituent groups and then the parent amide Substituents are preceded by N CH3 CH2CH3 CH3CH2 H CH2CH3 N-Methylpropanamide N,N-Diethylcyclohexanecarboxamide
▪ If nitrogen is further substituted the compound is named by first identifying the substituent groups and then the parent amide ▪ Substituents are preceded by N Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
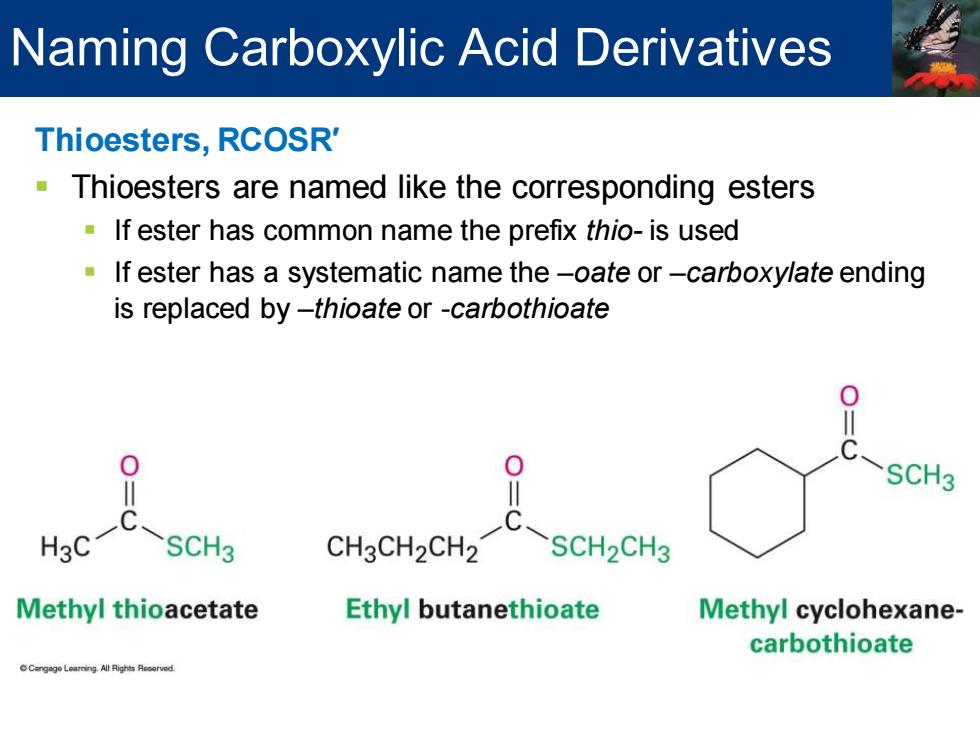
Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Thioesters,RCOSR' Thioesters are named like the corresponding esters If ester has common name the prefix thio-is used If ester has a systematic name the-oate or-carboxylate ending is replaced by-thioate or -carbothioate 0 SCH3 H3C SCH3 CH3CH2CH2 C-SCH2CH3 Methyl thioacetate Ethyl butanethioate Methyl cyclohexane- carbothioate
Thioesters, RCOSR′ ▪ Thioesters are named like the corresponding esters ▪ If ester has common name the prefix thio- is used ▪ If ester has a systematic name the –oate or –carboxylate ending is replaced by –thioate or -carbothioate Naming Carboxylic Acid Derivatives