
REACTION MECHANISM and SYNTHESIS REVIEW
REACTION MECHANISM and SYNTHESIS REVIEW
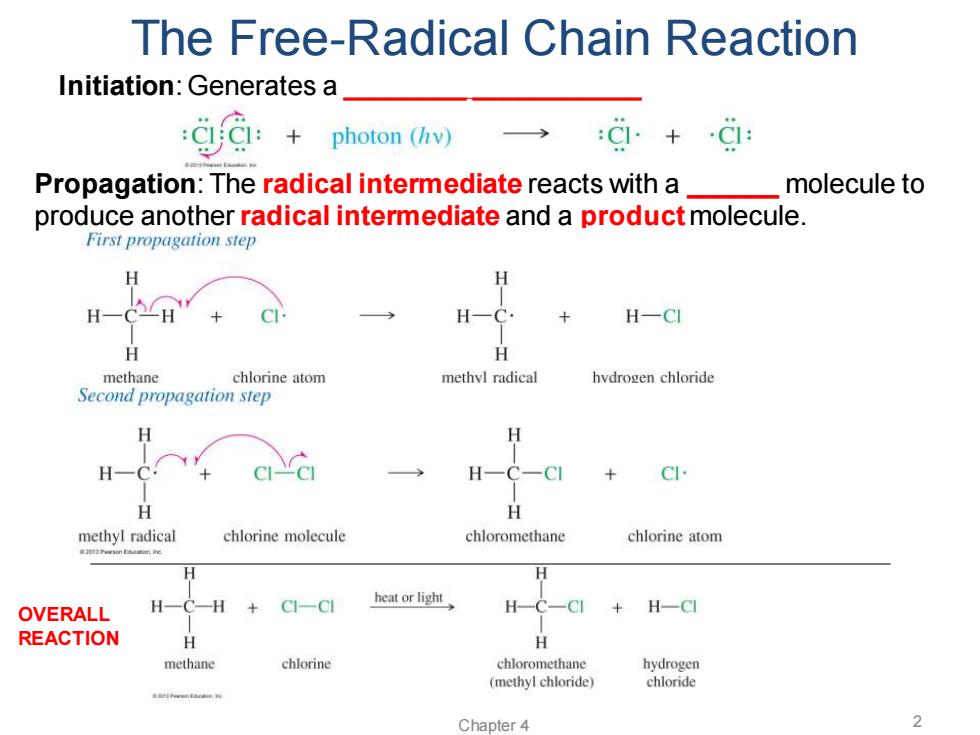
The Free-Radical Chain Reaction Initiation:Generates a CIC:+ photon(hv)→ Propagation:The radical intermediate reacts with a molecule to produce another radical intermediate and a product molecule. First propagation step H H-CI H methane chlorine atom methvl radical hvdrogen chloride Second propagation step H H H H + H H methyl radical chlorine molecule chloromethane chlorine atom OVERALL H- H CI-CI heat or light H H-CI REACTION H methane chlorine chloromethane hydrogen (methyl chloride) chloride smieenlacam he Chapter 4 2
Chapter 4 2 The Free-Radical Chain Reaction Initiation: Generates a ________ ___________ Propagation: The radical intermediate reacts with a ______ molecule to produce another radical intermediate and a product molecule. OVERALL REACTION
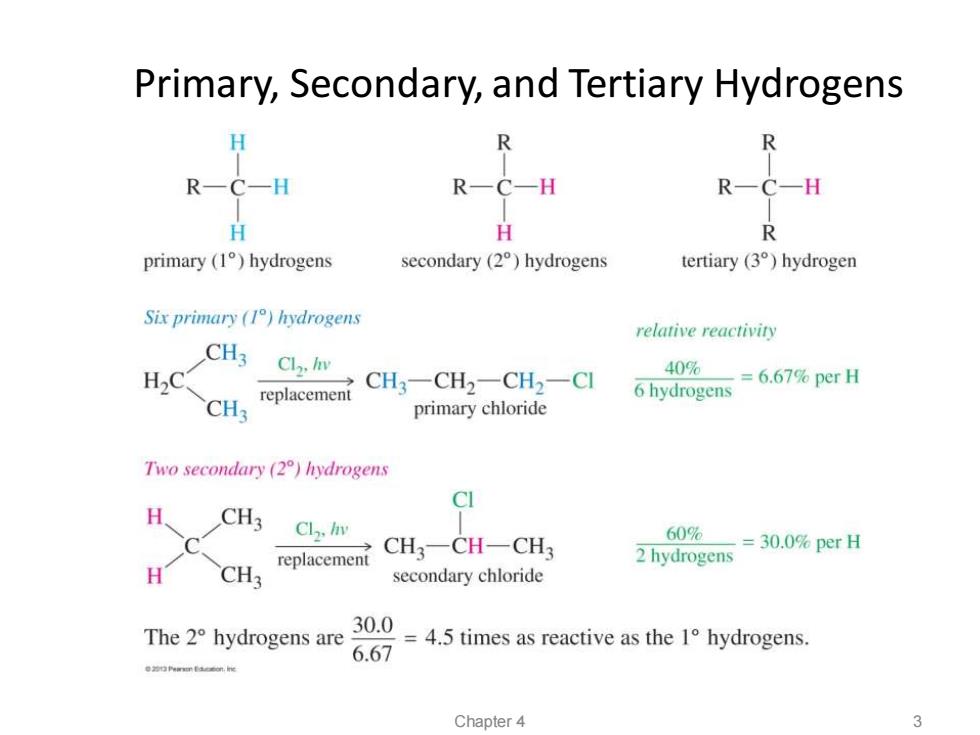
Primary,Secondary,and Tertiary Hydrogens H R RCH R一C-H R一C-H H H R primary (1)hydrogens secondary(2)hydrogens tertiary (3)hydrogen Six primary (I)hydrogens relative reactiviry CH3 Cl,lnv 40% H2C CH3一CH2一CH2-CI 6 hydrogens =6.67%perH CH3 replacement primary chloride Two secondary (2)hydrogens CI H CH3 Cl./n 60% CH3一CH一CH3 -=30.0%per日 replacement 2 hydrogens H CH3 secondary chloride The2°hydrogens are 30.0 6.67 =4.5 times as reactive as the 1 hydrogens. Chapter 4 3
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Hydrogens Chapter 4 3
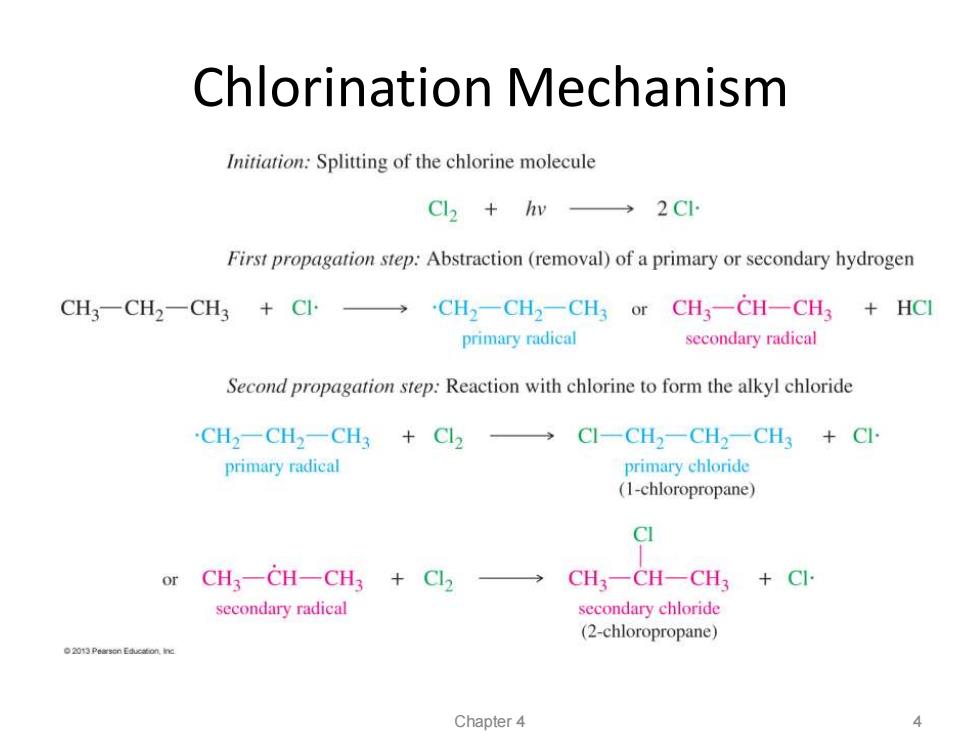
Chlorination Mechanism Initiation:Splitting of the chlorine molecule Cl2+hv→2C First propagation step:Abstraction(removal)of a primary or secondary hydrogen CH3-CH2-CH3+CI→·CH2一CH2-CH3 or CH3-CH-CH3+HC primary radical secondary radical Second propagation step:Reaction with chlorine to form the alkyl chloride CH2一CH2-CH3+C2 →C1-CH2-CH2-CH3+C primary radical primary chloride (1-chloropropane) CI or CH3-CH-CH3 Cl2 → CH3-CH-CH3 Cl. secondary radical secondary chloride (2-chloropropane) 2013 Pearsen Education ine Chapter 4
Chlorination Mechanism Chapter 4 4
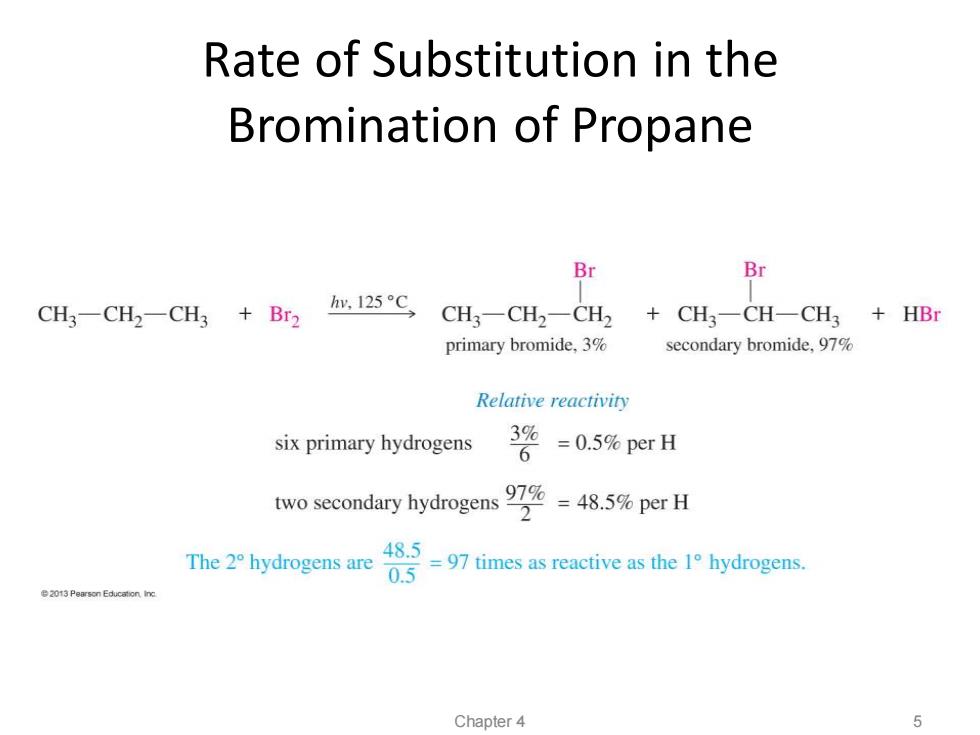
Rate of Substitution in the Bromination of Propane Br Br CH3-CH2-CH3 +Br2 hy.125C CH3-CH2一CH2 +CH3-CH-CH3 +HBr primary bromide,3% secondary bromide,97% Relative reactivity six primary hydrogens 3% 6 =0.5%per H two secondary hydrogens48.%per H 2 The 2 hydrogens are 48.5 0.5 =97 times as reactive as the 1 hydrogens. Chapter 4 5
Rate of Substitution in the Bromination of Propane Chapter 4 5
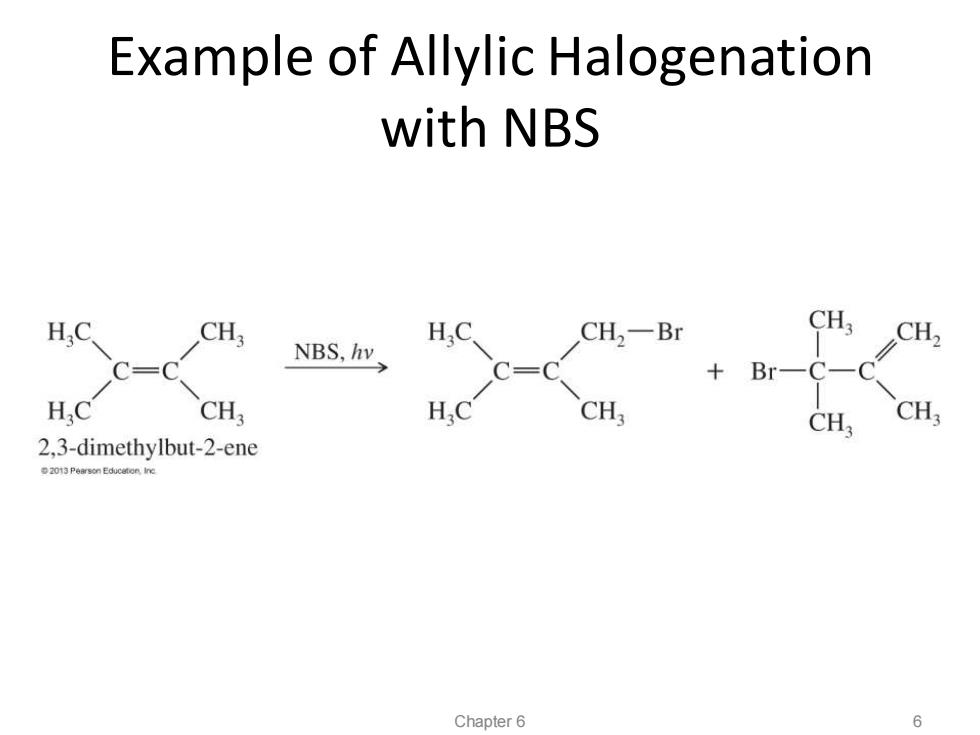
Example of Allylic Halogenation with NBS H.C CH. CH2一Br CH3 CH2 NBS,hv C=C Br- HC CH; H.C CH CH, 2.3-dimethylbut-2-ene 2013 Pearson Educeton.Iine Chapter 6 6
Example of Allylic Halogenation with NBS File Name: AAAKWEA0 Chapter 6 6
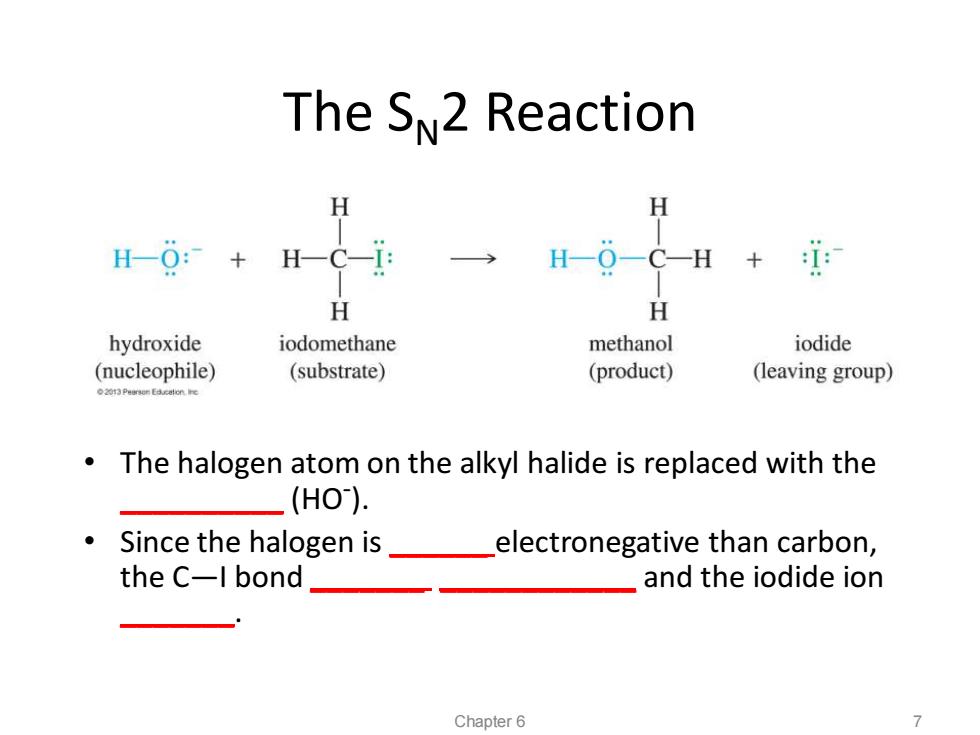
The SN2 Reaction H H H-0:+ H-0-C-H + H H hydroxide iodomethane methanol iodide (nucleophile) (substrate) (product) (leaving group) The halogen atom on the alkyl halide is replaced with the (HO). Since the halogen is_ electronegative than carbon, the C-l bond and the iodide ion Chapter 6 7
The SN2 Reaction • The halogen atom on the alkyl halide is replaced with the __________ (HO- ). • Since the halogen is ______ electronegative than carbon, the C—I bond _______ ____________ and the iodide ion _______. Chapter 6 7
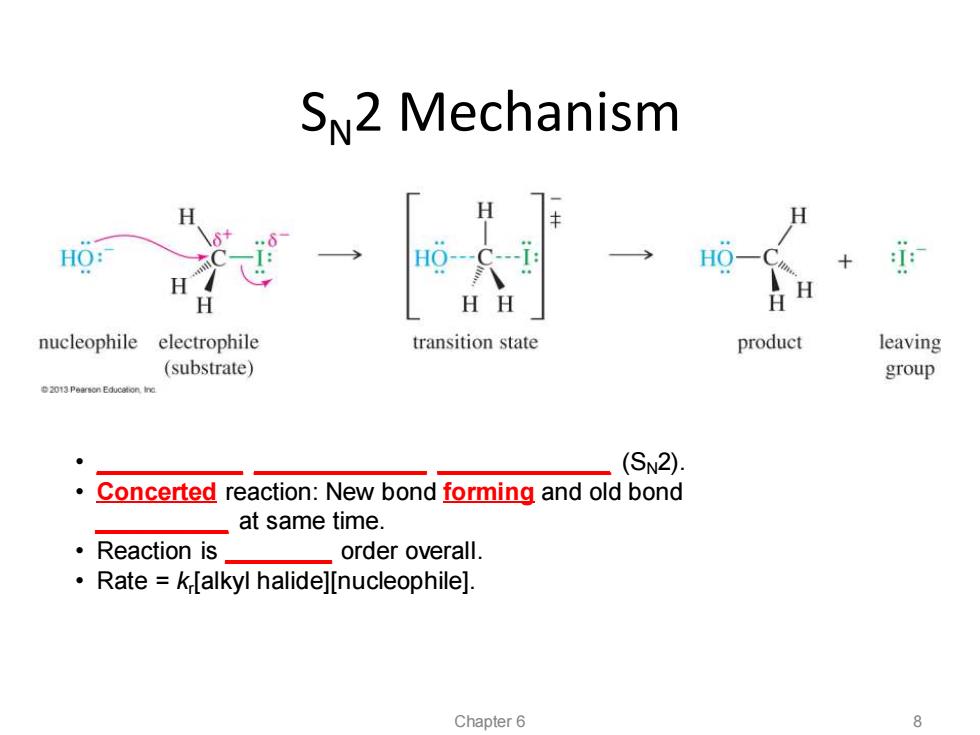
SN2 Mechanism H HO: HO- H H HH H nucleophile electrophile transition state product leaving (substrate) group (SN2). Concerted reaction:New bond forming and old bond at same time. ·Reaction is order overall. Rate k[alkyl halide][nucleophile]. Chapter 6
SN2 Mechanism • ___________ _____________ _____________ (SN2). • Concerted reaction: New bond forming and old bond __________ at same time. • Reaction is ________ order overall. • Rate = kr [alkyl halide][nucleophile]. Chapter 6 8
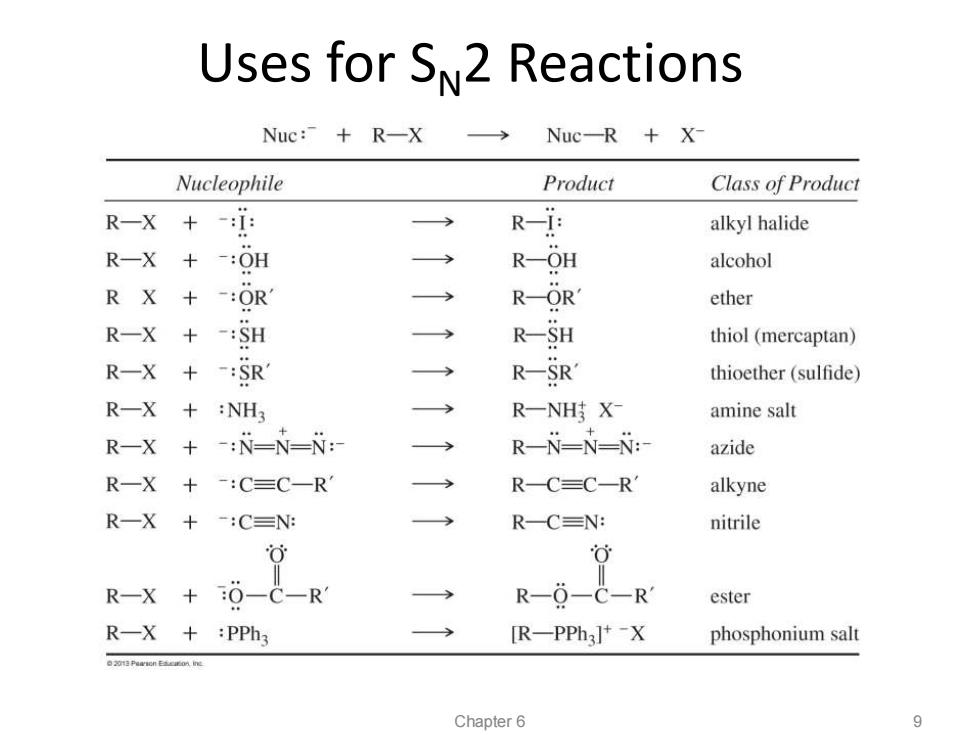
Uses for SN2 Reactions Nuc:”+R-X Nuc-R X- Nucleophile Product Class of Product R-X +-:i: > R-i: alkyl halide R-X+-:OH → R-OH alcohol R X+-:OR R-OR' ether R-X +-:SH R-SH thiol(mercaptan) R-X+-:SR R-SR' thioether(sulfide) R-X+ :NH3 R一NHX amine salt R-X +-:N=N=: R-N-N-N:- azide R-X+-:C=C-R R-C=C-R alkyne R-X+ -:C≡Ng R-C=N: nitrile 0 可 R-X +6--R R-0-C-R ester R-X +:PPh3 [R-PPh3]+-X phosphonium salt nE Chapter 6 9
Uses for SN2 Reactions Chapter 6 9
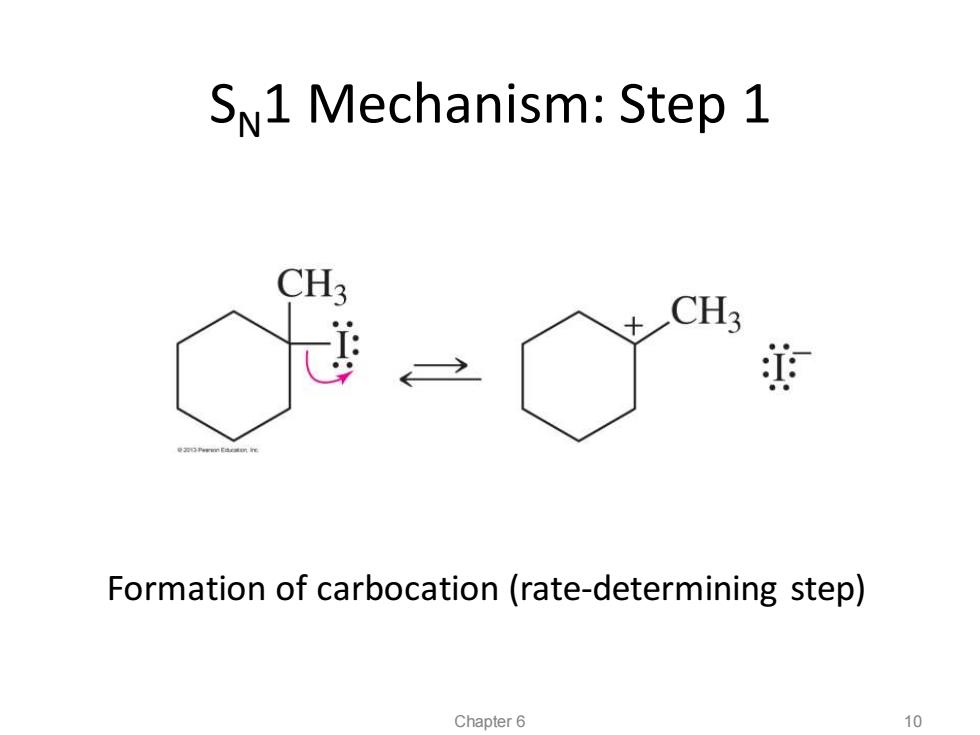
SN1 Mechanism:Step 1 CH3 +CH3 迫 Formation of carbocation(rate-determining step) Chapter 6 10
Formation of carbocation (rate-determining step) SN1 Mechanism: Step 1 Chapter 6 10