
CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER9 Aromatic Compounds TH IRD EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 9 Aromatic Compounds
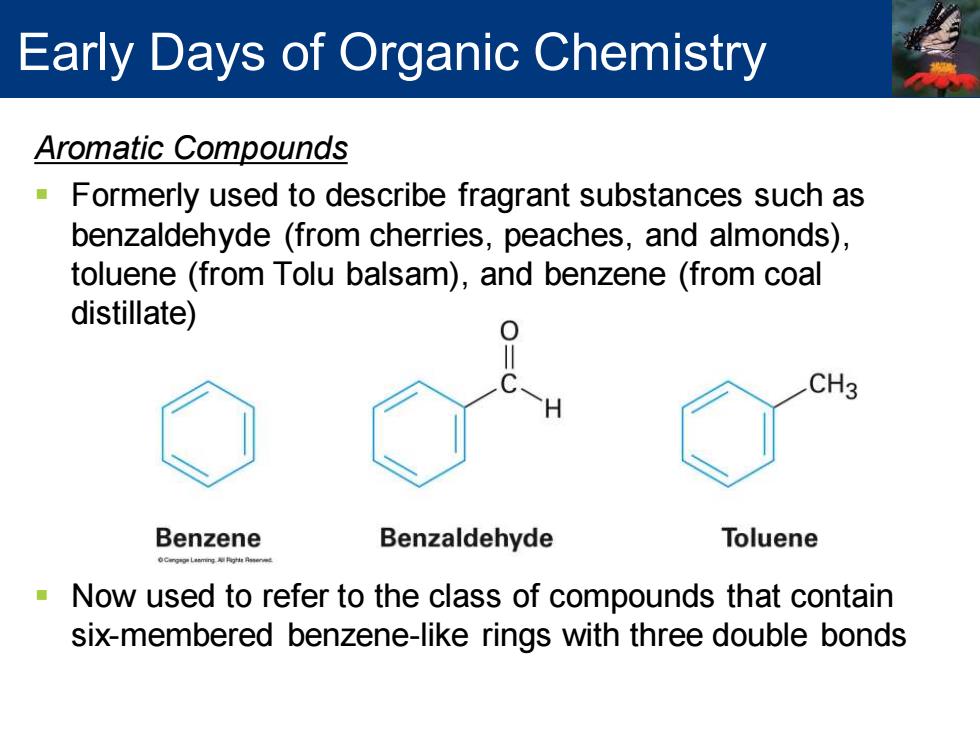
Early Days of Organic Chemistry Aromatic Compounds Formerly used to describe fragrant substances such as benzaldehyde (from cherries,peaches,and almonds), toluene (from Tolu balsam),and benzene (from coal distillate) CH3 Benzene Benzaldehyde Toluene Now used to refer to the class of compounds that contain six-membered benzene-like rings with three double bonds
Aromatic Compounds ▪ Formerly used to describe fragrant substances such as benzaldehyde (from cherries, peaches, and almonds), toluene (from Tolu balsam), and benzene (from coal distillate) ▪ Now used to refer to the class of compounds that contain six-membered benzene-like rings with three double bonds Early Days of Organic Chemistry
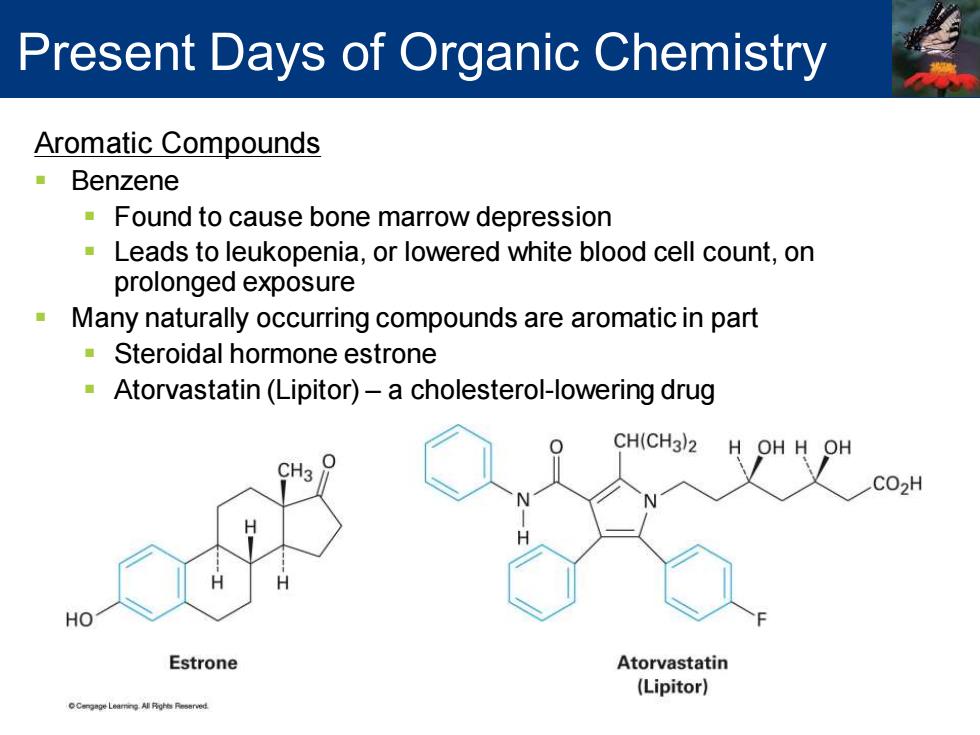
Present Days of Organic Chemistry Aromatic Compounds Benzene Found to cause bone marrow depression Leads to leukopenia,or lowered white blood cell count,on prolonged exposure Many naturally occurring compounds are aromatic in part Steroidal hormone estrone Atorvastatin(Lipitor)-a cholesterol-lowering drug CH(CH3)2 H OH H OH CH3 CO2H HO Estrone Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
Aromatic Compounds ▪ Benzene ▪ Found to cause bone marrow depression ▪ Leads to leukopenia, or lowered white blood cell count, on prolonged exposure ▪ Many naturally occurring compounds are aromatic in part ▪ Steroidal hormone estrone ▪ Atorvastatin (Lipitor) – a cholesterol-lowering drug Present Days of Organic Chemistry
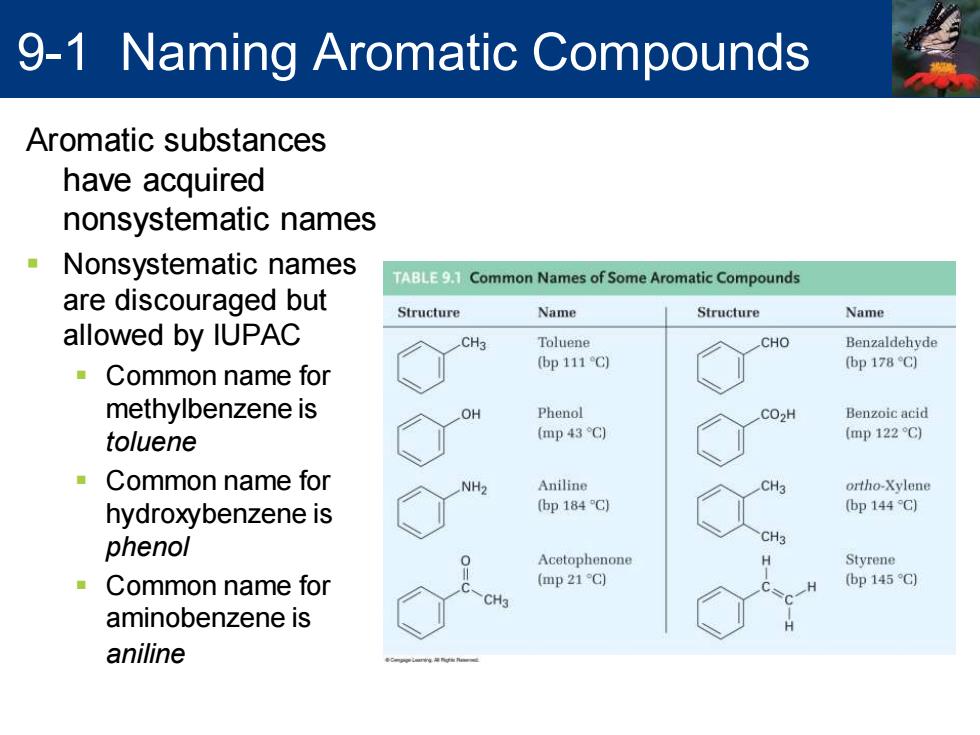
9-1 Naming Aromatic Compounds Aromatic substances have acquired nonsystematic names Nonsystematic names :EC Common Names of Some Aromatic Compounds are discouraged but Structure Name Structure Name allowed by IUPAC CH3 Toluene CHO Benzaldehyde (bp 111C) (bp 178C) Common name for methylbenzene is OH Phenol CO>H Benzoic acid toluene (mp 43C) (mp122C) Common name for NH2 Aniline ortho-Xylene hydroxybenzene is (bp184G) (bp 144C) phenol CH3 Acetophenone Styrene Common name for (mp 21C) (bp145C) CH3 aminobenzene is aniline
Aromatic substances have acquired nonsystematic names ▪ Nonsystematic names are discouraged but allowed by IUPAC ▪ Common name for methylbenzene is toluene ▪ Common name for hydroxybenzene is phenol ▪ Common name for aminobenzene is aniline 9-1 Naming Aromatic Compounds
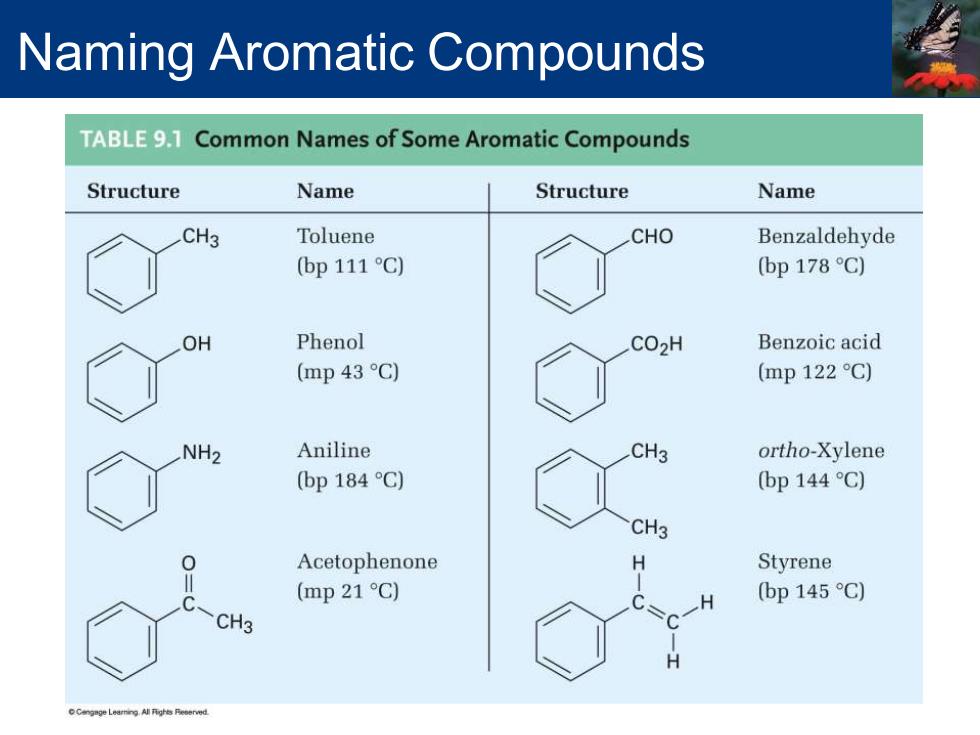
Naming Aromatic Compounds TABLE9.1 Common Names of Some Aromatic Compounds Structure Name Structure Name CH3 Toluene CHO Benzaldehyde (bp 111 C) (bp178C) OH Phenol CO2H Benzoic acid (mp 43C) (mp122C) NH2 Aniline CH3 ortho-Xylene (bp 184C) (bp 144 C) CH3 0 Acetophenone H Styrene C (mp 21 C) (bp 145C) CH3 H
Naming Aromatic Compounds
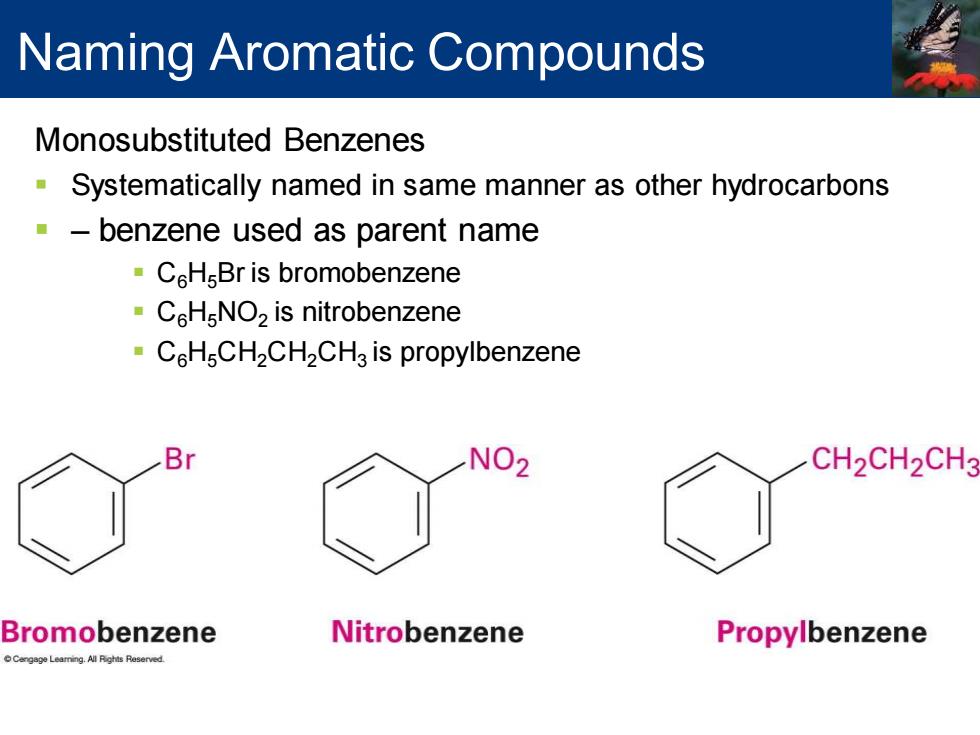
Naming Aromatic Compounds Monosubstituted Benzenes Systematically named in same manner as other hydrocarbons benzene used as parent name CHsBr is bromobenzene C6H NO2 is nitrobenzene CH CH2CH2CH3 is propylbenzene Br NO2 CH2CH2CH3 Bromobenzene Nitrobenzene Propylbenzene
Monosubstituted Benzenes ▪ Systematically named in same manner as other hydrocarbons ▪ – benzene used as parent name ▪ C6H5Br is bromobenzene ▪ C6H5NO2 is nitrobenzene ▪ C6H5CH2CH2CH3 is propylbenzene Naming Aromatic Compounds
Naming Aromatic Compounds Arenes Alkyl-substituted benzenes Named depending on the size of the alkyl group Alkyl substituent smaller than the ring(6 or fewer carbons),named as an alkyl substituted benzene Alkyl substituent larger than the ring(7 or more carbons),named as a phenyl-substituted alkane Phenyl Derived from the Greek pheno("I bear light") Michael Faraday discovered benzene in 1825 from the oily residue left by illuminating gas used in London street lamps Used for the-CeH5 unit when the benzene ring is considered as a substituent Abbreviated as Ph or (Greek phi) Benzyl Used for the C6H5CH2-group
Arenes ▪ Alkyl-substituted benzenes ▪ Named depending on the size of the alkyl group ▪ Alkyl substituent smaller than the ring (6 or fewer carbons), named as an alkyl substituted benzene ▪ Alkyl substituent larger than the ring (7 or more carbons), named as a phenyl-substituted alkane Phenyl ▪ Derived from the Greek pheno (“I bear light”) ▪ Michael Faraday discovered benzene in 1825 from the oily residue left by illuminating gas used in London street lamps ▪ Used for the –C6H5 unit when the benzene ring is considered as a substituent ▪ Abbreviated as Ph or F (Greek phi) Benzyl ▪ Used for the C6H5CH2– group Naming Aromatic Compounds
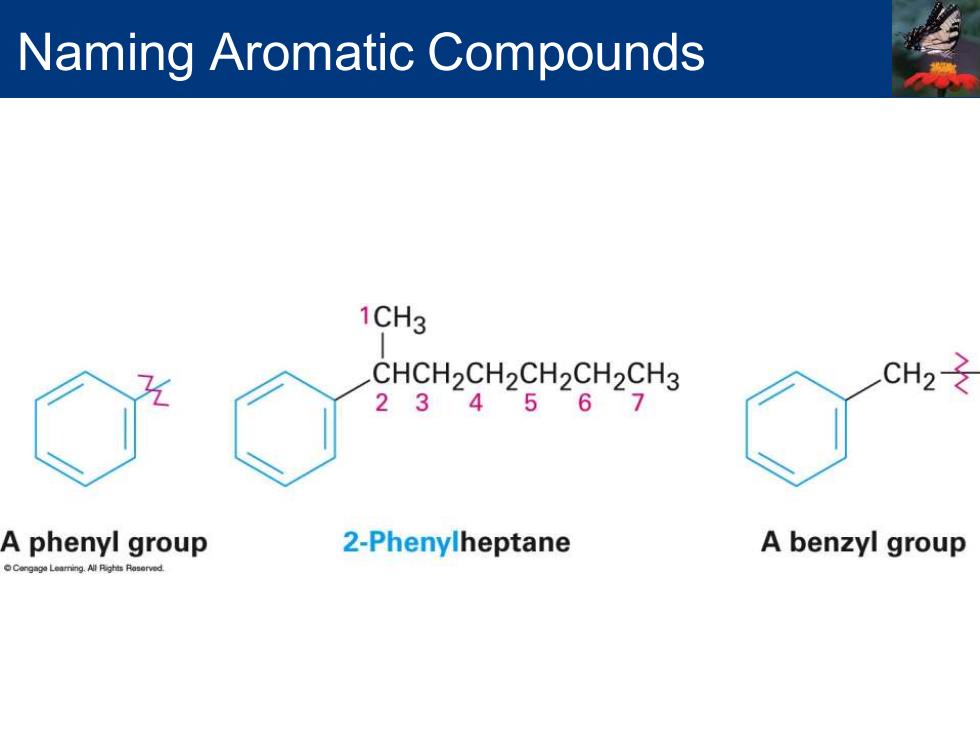
Naming Aromatic Compounds 1CH3 CHCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH2 234567 A phenyl group 2-Phenylheptane A benzyl group
Naming Aromatic Compounds
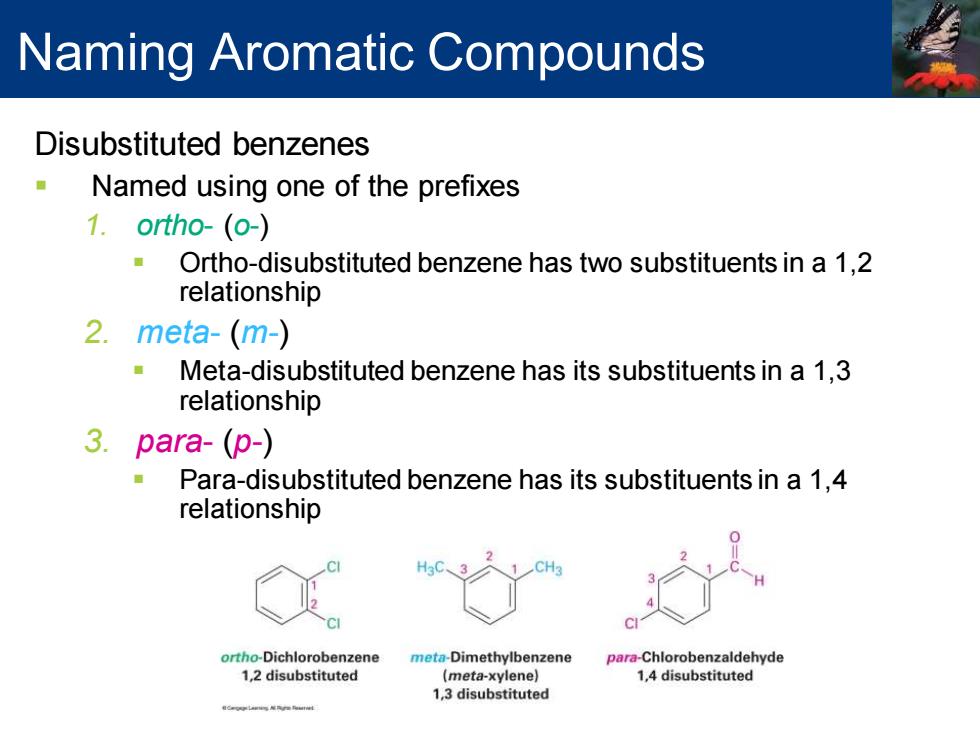
Naming Aromatic Compounds Disubstituted benzenes Named using one of the prefixes 1.ortho-(o-) Ortho-disubstituted benzene has two substituents in a 1,2 relationship 2.meta-(m-) ■ Meta-disubstituted benzene has its substituents in a 1,3 relationship 3.para-(p-) Para-disubstituted benzene has its substituents in a 1,4 relationship ortho-Dichlorobenzene meta-Dimethylbenzene para-Chlorobenzaldehyde 1,2 disubstituted (meta-xylene) 1,4 disubstituted 1,3 disubstituted
Disubstituted benzenes ▪ Named using one of the prefixes 1. ortho- (o-) ▪ Ortho-disubstituted benzene has two substituents in a 1,2 relationship 2. meta- (m-) ▪ Meta-disubstituted benzene has its substituents in a 1,3 relationship 3. para- (p-) ▪ Para-disubstituted benzene has its substituents in a 1,4 relationship Naming Aromatic Compounds
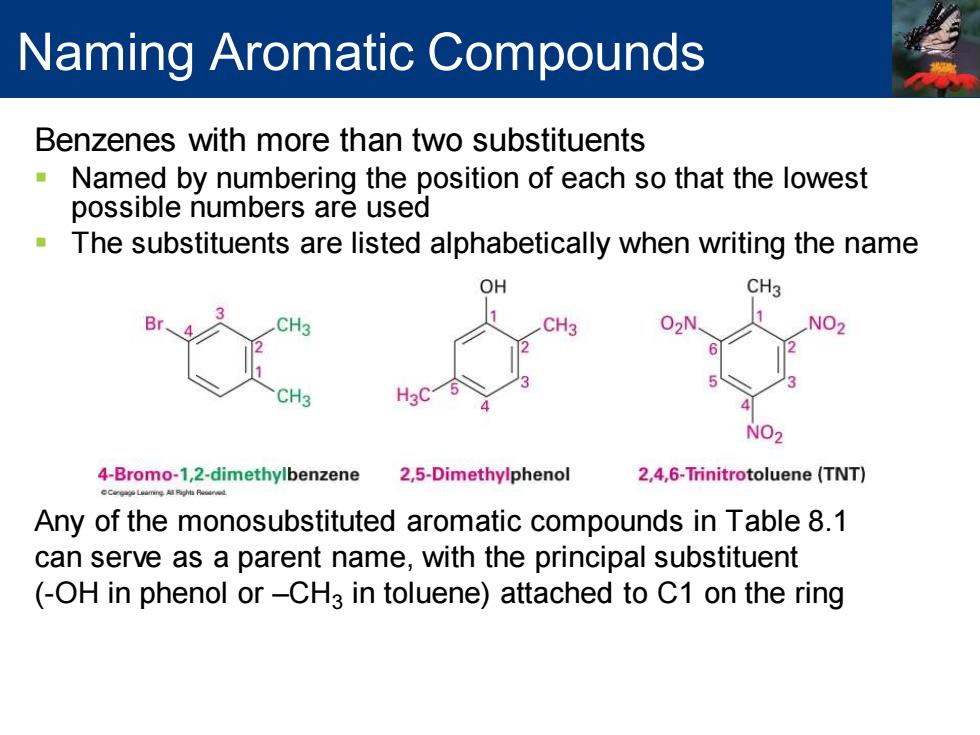
Naming Aromatic Compounds Benzenes with more than two substituents Named by numbering the position of each so that the lowest possible numbers are used The substituents are listed alphabetically when writing the name OH CH3 02N 1 CH3 CH3 NO2 6 CH3 H3C NO2 4-Bromo-1,2-dimethylbenzene 2,5-Dimethylphenol 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene(TNT) Any of the monosubstituted aromatic compounds in Table 8.1 can serve as a parent name,with the principal substituent (-OH in phenol or-CH3 in toluene)attached to C1 on the ring
Benzenes with more than two substituents ▪ Named by numbering the position of each so that the lowest possible numbers are used ▪ The substituents are listed alphabetically when writing the name Any of the monosubstituted aromatic compounds in Table 8.1 can serve as a parent name, with the principal substituent (-OH in phenol or –CH3 in toluene) attached to C1 on the ring Naming Aromatic Compounds