
CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 15 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
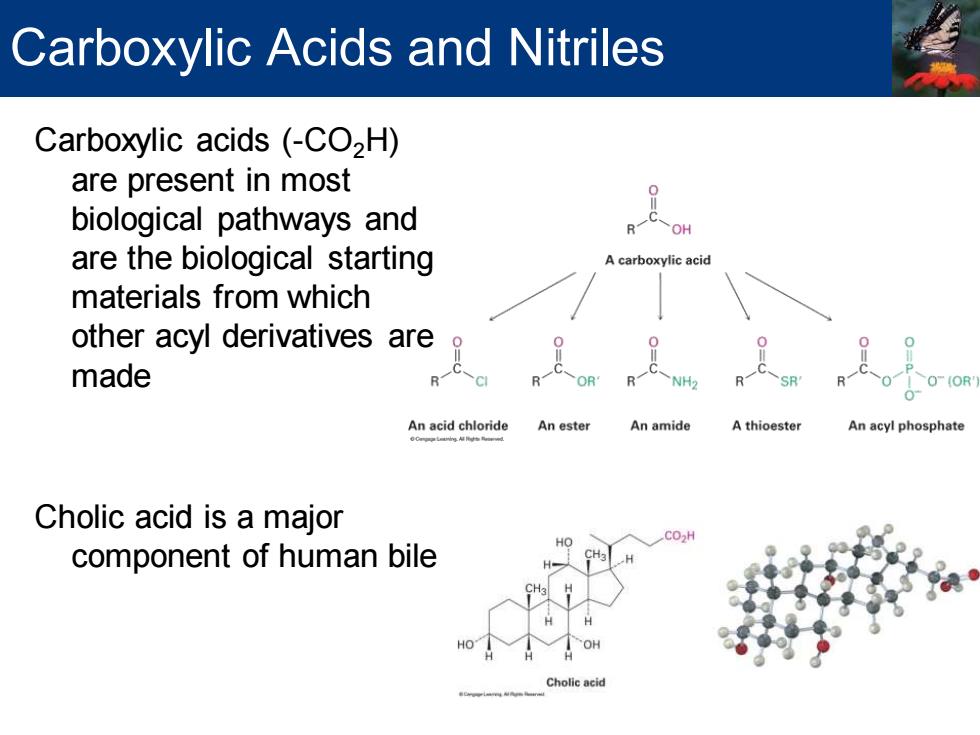
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Carboxylic acids (-CO2H) are present in most biological pathways and are the biological starting A carboxylic acid materials from which other acyl derivatives are made 。 0 O(OR' An acid chloride An ester An amide A thioester An acyl phosphate Cholic acid is a major component of human bile HO HO OH Cholic acid
Carboxylic acids (-CO2H) are present in most biological pathways and are the biological starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are made Cholic acid is a major component of human bile Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles

15-1 Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Carboxylic acids named by replacing -e of the corresponding alkane name with -oic acid -CO,H carbon atom is numbered C1 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3CH2COH CH3CHCH2CH2COH HOCCH2CHCH2CH2CHCH2COH 5432 12345678 Propanoic acid 4-Methylpentanoic acid 3-Ethyl-6-methyloctanedioic acid
Carboxylic acids named by replacing –e of the corresponding alkane name with –oic acid ▪ –CO2H carbon atom is numbered C1 15-1Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles

Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Name compounds with-CO2H group bonded to a ring using the suffix-carboxylic acid 6 CO2H HO trans-4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid Cyclopent-1-enecarboxylic acid
▪ Name compounds with –CO2H group bonded to a ring using the suffix –carboxylic acid Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
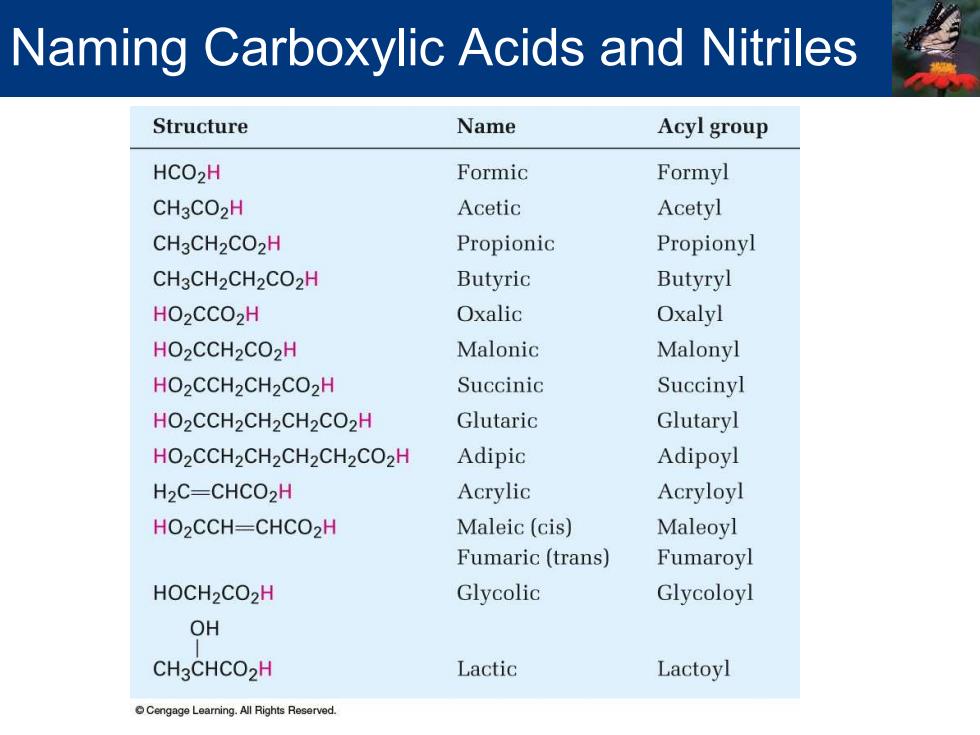
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Structure Name Acyl group HCO2H Formic Formyl CH3CO2H Acetic Acetyl CH3CH2CO2H Propionic Propionyl CH3CH2CH2CO2H Butyric Butyryl HO2CCO2H Oxalic Oxalyl HO2CCH2CO2H Malonic Malonyl HO2CCH2CH2CO2H Succinic Succinyl HO2CCH2CH2CH2CO2H Glutaric Glutaryl HO2CCH2CH2CH2CH2CO2H Adipic Adipoyl H2C-CHCO2H Acrylic Acryloyl HO2CCH-CHCO2H Maleic(cis) Maleoyl Fumaric (trans) Fumaroyl HOCH2CO2H Glycolic Glycoloyl OH CH3CHCO2H Lactic Lactoyl Cengage Learning.All Rights Reserved
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles

Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Structure Name Acyl group 0 CH3CCO2H Pyruvic Pyruvoyl OH HOCH2CHCO2H Glyceric Glyceroyl OH HO2CCHCH2CO2H Malic Maloyl 0 HO2CCCH2CO2H Oxaloacetic Oxaloacetyl CO2H Benzoic Benzoyl CO2H Phthalic Phthaloyl CO2H
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles

Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Nitriles,RCEN Compounds containing -C=N functional group are called nitriles Named by adding -nitrile as a suffix to the alkane name Nitrile carbon numbered C1 CH3 CH3CHCH2CH2CN 4-Methylpentanenitrile 54321
Nitriles, RC≡N Compounds containing -C≡N functional group are called nitriles ▪ Named by adding –nitrile as a suffix to the alkane name ▪ Nitrile carbon numbered C1 Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
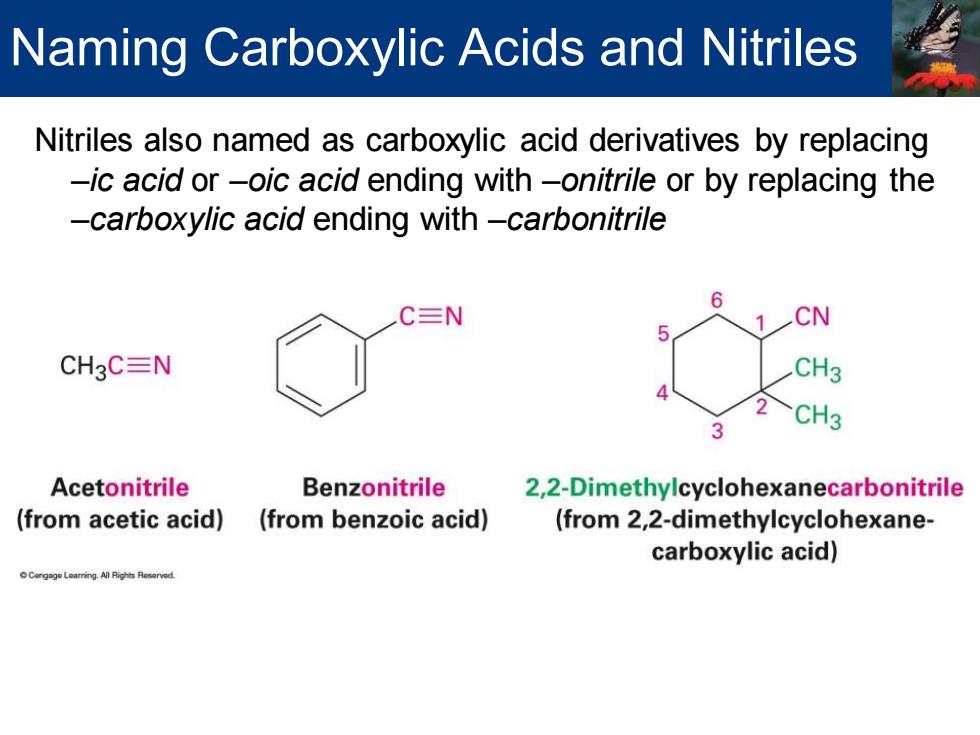
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Nitriles also named as carboxylic acid derivatives by replacing -ic acid or-oic acid ending with-onitrile or by replacing the -carboxylic acid ending with-carbonitrile C三N CN CH3C=N CH3 Acetonitrile Benzonitrile 2,2-Dimethylcyclohexanecarbonitrile (from acetic acid) (from benzoic acid) (from 2,2-dimethylcyclohexane- carboxylic acid)
Nitriles also named as carboxylic acid derivatives by replacing –ic acid or –oic acid ending with –onitrile or by replacing the –carboxylic acid ending with –carbonitrile Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
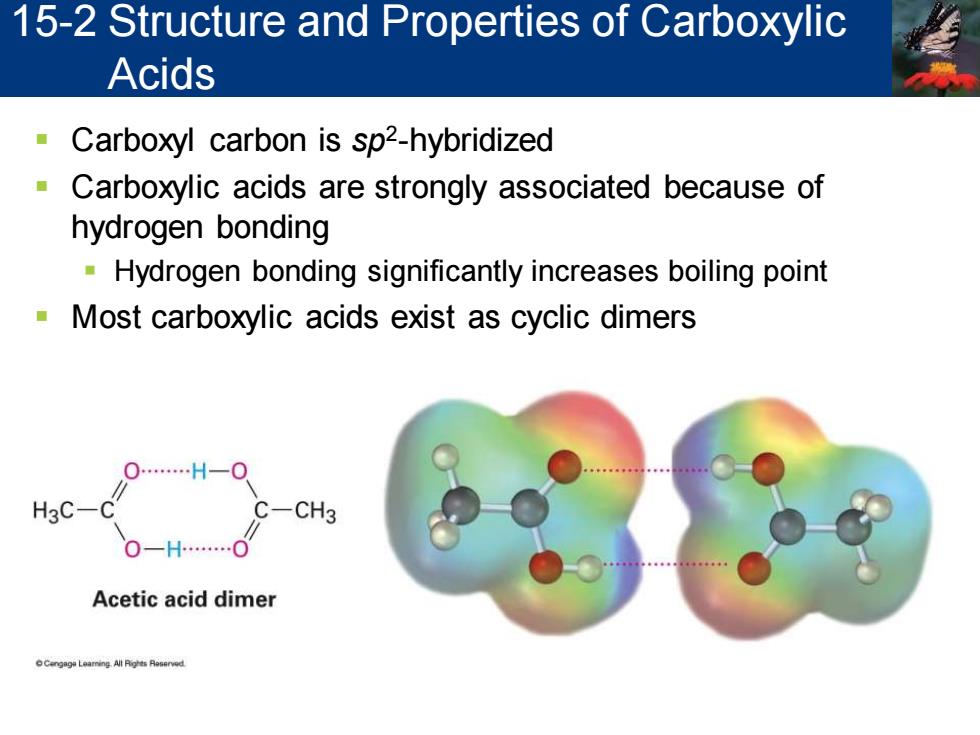
15-2 Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids Carboxyl carbon is sp2-hybridized a Carboxylic acids are strongly associated because of hydrogen bonding Hydrogen bonding significantly increases boiling point Most carboxylic acids exist as cyclic dimers O…H-O H3C-C C- CH3 Acetic acid dimer
▪ Carboxyl carbon is sp2 -hybridized ▪ Carboxylic acids are strongly associated because of hydrogen bonding ▪ Hydrogen bonding significantly increases boiling point ▪ Most carboxylic acids exist as cyclic dimers 15-2 Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids
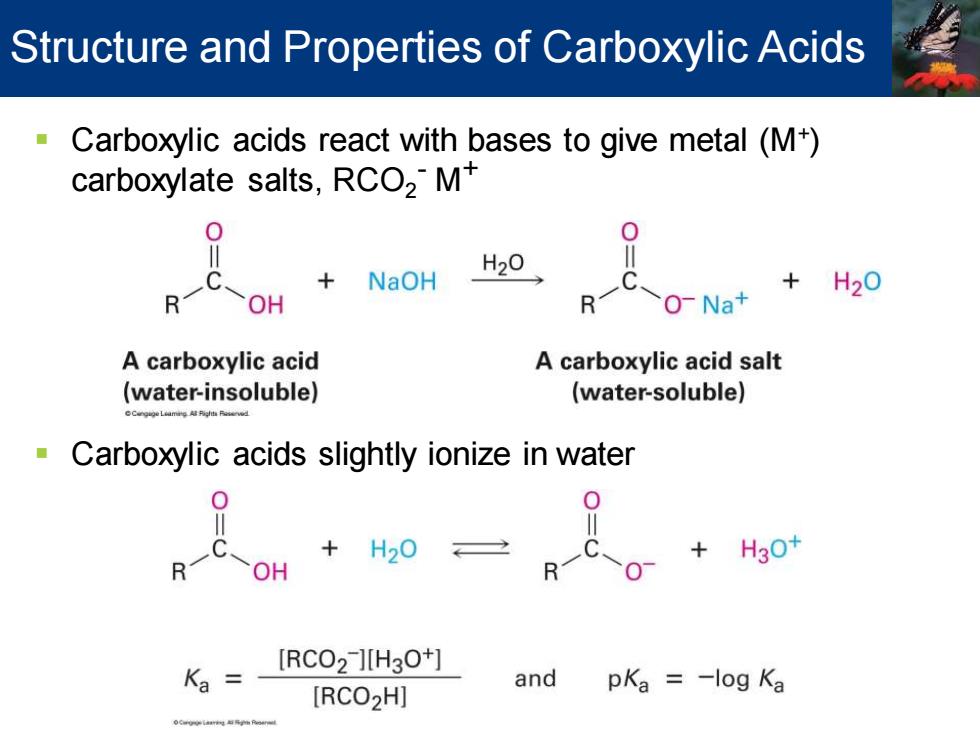
Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids react with bases to give metal(M+) carboxylate salts,RCO2M NaOH H20 +H20 OH R O-Na+ A carboxylic acid A carboxylic acid salt (water-insoluble) (water-soluble) Carboxylic acids slightly ionize in water R一 +H30 OH [RCO2 ][H3O+] Ka and pKa =-log Ka [RCO2H]
▪ Carboxylic acids react with bases to give metal (M+ ) carboxylate salts, RCO2 - M+ ▪ Carboxylic acids slightly ionize in water Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids