
CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 19 Biomolecules: Amino Acids,Peptides, and Proteins T H I R D E DI TION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 19 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
Amino Acids,Peptides,and Proteins Proteins Occur in every living organism Are of many different types Have many different biological functions Keratin of skin and fingernails -Fibroin of silk and spider webs Estimated 50,000 to 70,000 enzymes that catalyze the biological functions of the human body Made up of many amino acids linked together
Proteins ▪ Occur in every living organism ▪ Are of many different types ▪ Have many different biological functions ▪ Keratin of skin and fingernails ▪ Fibroin of silk and spider webs ▪ Estimated 50,000 to 70,000 enzymes that catalyze the biological functions of the human body ▪ Made up of many amino acids linked together Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
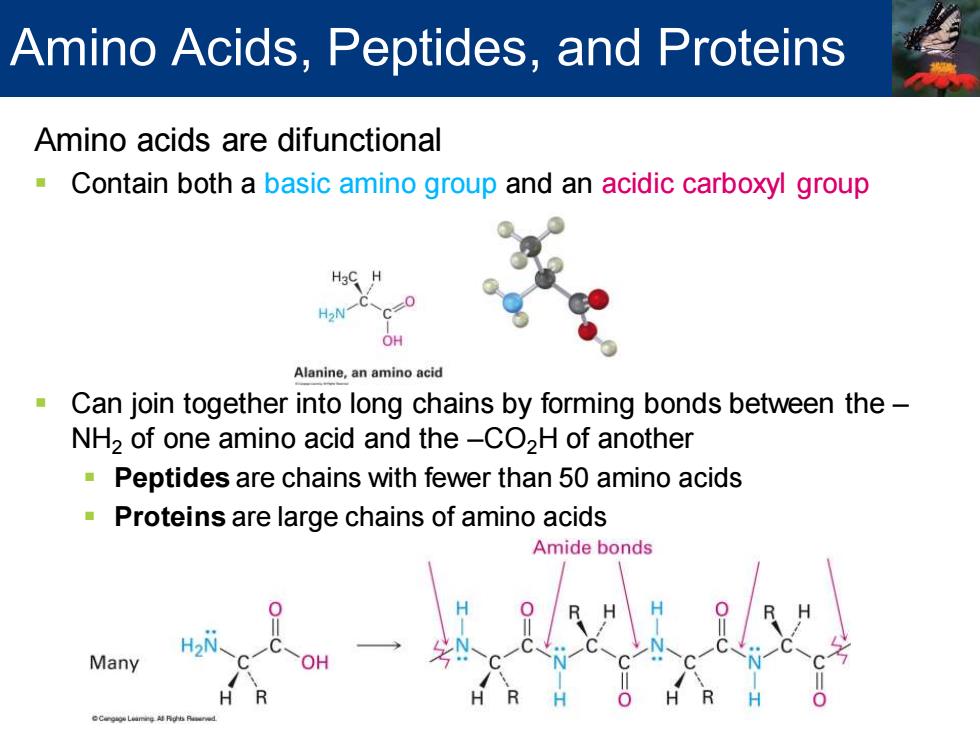
Amino Acids,Peptides,and Proteins Amino acids are difunctional Contain both a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl group H2N c=0 OH Alanine,an amino acid Can join together into long chains by forming bonds between the- NH2 of one amino acid and the-CO2H of another Peptides are chains with fewer than 50 amino acids Proteins are large chains of amino acids Amide bonds Many
Amino acids are difunctional ▪ Contain both a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl group ▪ Can join together into long chains by forming bonds between the – NH2 of one amino acid and the –CO2H of another ▪ Peptides are chains with fewer than 50 amino acids ▪ Proteins are large chains of amino acids Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
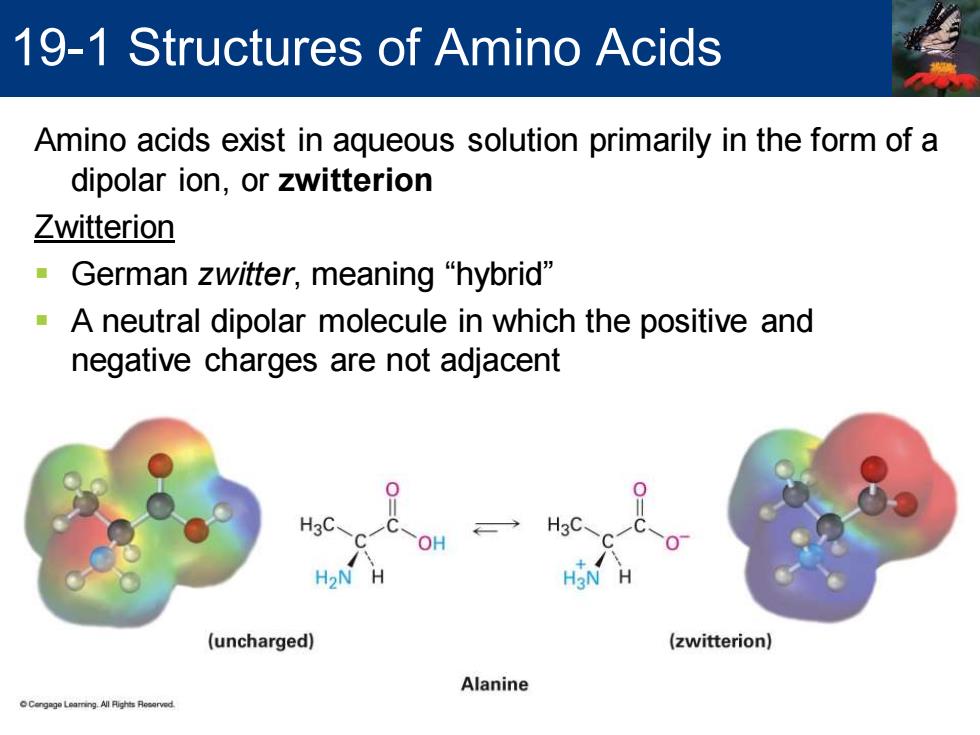
19-1 Structures of Amino Acids Amino acids exist in aqueous solution primarily in the form of a dipolar ion,or zwitterion Zwitterion German zwitter,,meaning“hybrid” A neutral dipolar molecule in which the positive and negative charges are not adjacent H3C. → H3C OH H2>N H H3N (uncharged) (zwitterion) Alanine
Amino acids exist in aqueous solution primarily in the form of a dipolar ion, or zwitterion Zwitterion ▪ German zwitter, meaning “hybrid” ▪ A neutral dipolar molecule in which the positive and negative charges are not adjacent 19-1 Structures of Amino Acids
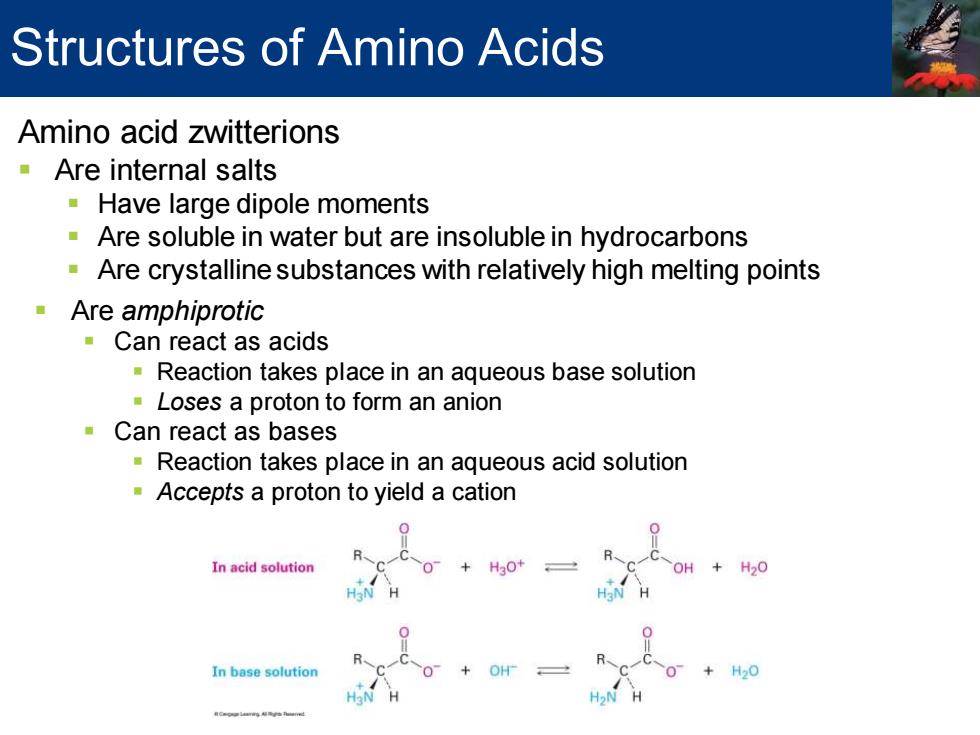
Structures of Amino Acids Amino acid zwitterions Are internal salts Have large dipole moments Are soluble in water but are insoluble in hydrocarbons Are crystalline substances with relatively high melting points Are amphiprotic Can react as acids Reaction takes place in an aqueous base solution Loses a proton to form an anion Can react as bases Reaction takes place in an aqueous acid solution Accepts a proton to yield a cation 0 In acid solution +H20 In base solution H20
Amino acid zwitterions ▪ Are internal salts ▪ Have large dipole moments ▪ Are soluble in water but are insoluble in hydrocarbons ▪ Are crystalline substances with relatively high melting points ▪ Are amphiprotic ▪ Can react as acids ▪ Reaction takes place in an aqueous base solution ▪ Loses a proton to form an anion ▪ Can react as bases ▪ Reaction takes place in an aqueous acid solution ▪ Accepts a proton to yield a cation Structures of Amino Acids
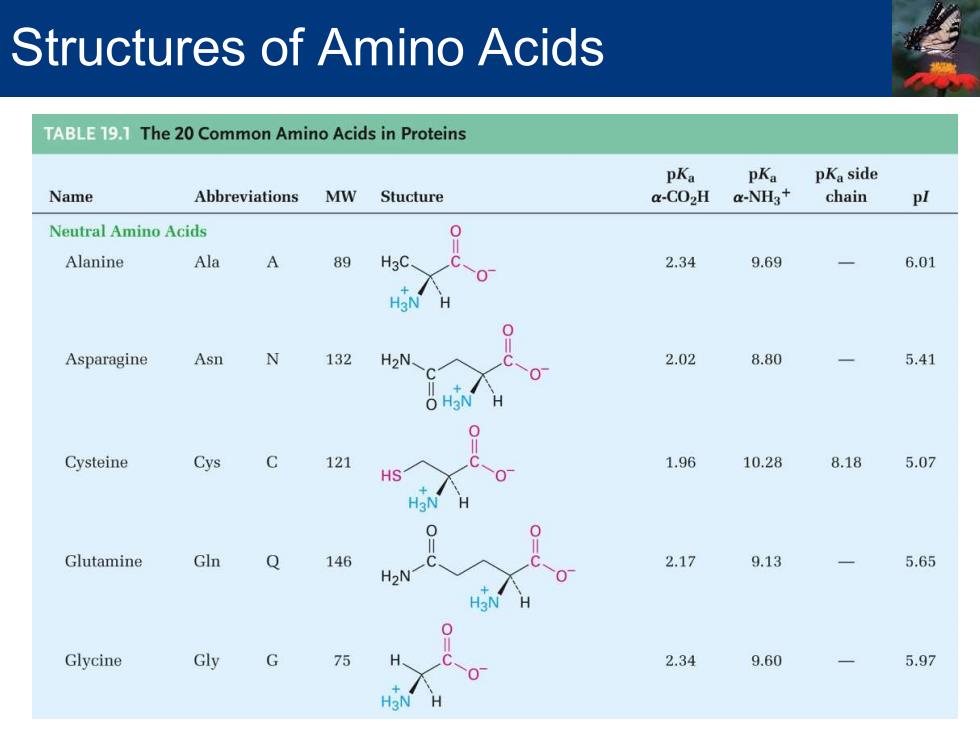
Structures of Amino Acids TABLE19.1 The 20 Common Amino Acids in Proteins pKa pKa pKa side Name Abbreviations MW Stucture a-CO2H a-NH3+ chain pl Neutral Amino Acids 0 Alanine Ala A 89 H3C、 2.34 9.69 6.01 0 H3N H O Asparagine Asn N 132 H2N 2.02 8.80 5.41 O H3N 0 Cysteine Cys C 121 1.96 10.28 8.18 5.07 HS 0 Glutamine Gln Q 146 2.17 9.13 5.65 H2N Glycine Gly G 75 2.34 9.60 5.97 0
Structures of Amino Acids

Structures of Amino Acids Isoleucine 131 2.36 9.60 6.02 0 0 Leucine Leu 131 HgC 2.36 9.60 一 5.98 Methionine Met M 149 2.28 9.21 一 5.74 H3C Phenylalanine Phe 165 1.83 9.13 一 5.48 Proline Pro 115 1.99 10.60 6.30 Cengage Learning.All Rights Reserved
Structures of Amino Acids

Structures of Amino Acids TABLE 19.1 The 20 Common Amino Acids in Proteins continued pKa pKa pKa side Name Abbreviations MW Stucture a-CO2H a-NH3+ chain Neutral Amino Acids continued Serine Ser 105 2.21 9.15 5.68 HO H HO H Threonine Thr 119 2.09 9.10 5.60 H3C H3 Tryptophan Trp 2 204 2.83 9.39 5.89 Tyrosine Tyr 181 2.20 9.11 10.07 5.66 HO CH3 Valine Val 117 2.32 9.62 5.96 H3C 0
Structures of Amino Acids
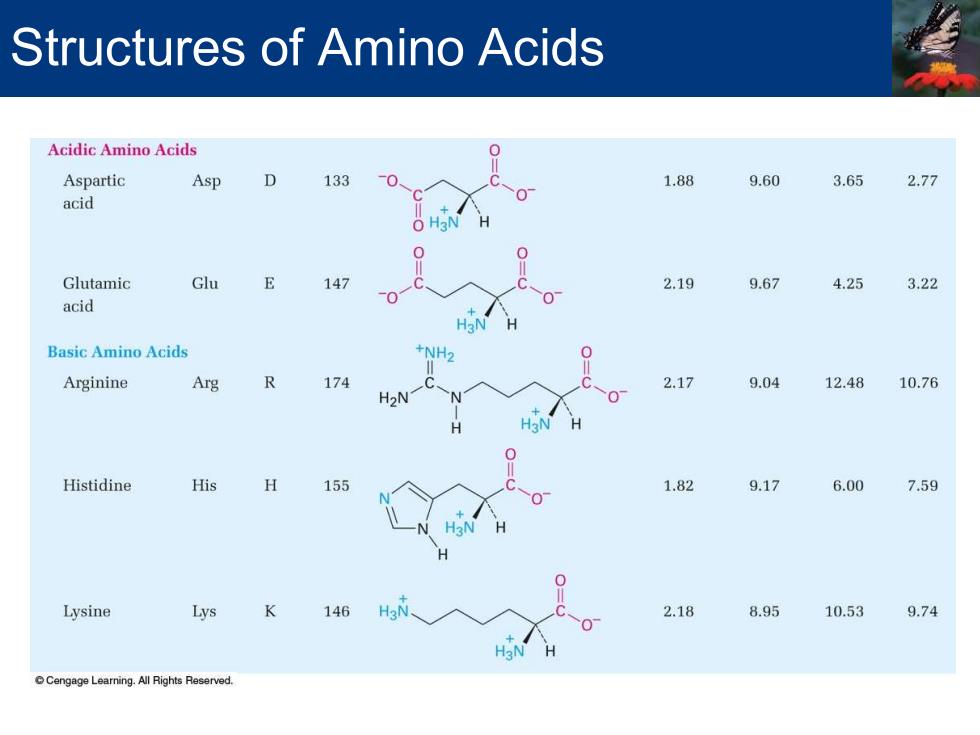
Structures of Amino Acids Acidic Amino Acids Aspartic Asp 0 133 0 1.88 9.60 3.65 2.77 acid O H3N Glutamic Glu E 147 2.19 9.67 4.25 3.22 acid H3N Basic Amino Acids +NH2 Arginine Arg R 174 2.17 9.04 12.48 10.76 H>N Histidine His H 155 1.82 9.17 6.00 7.59 H3 Lysine Lys 146 H3 2.18 8.95 10.53 9.74 Cengage Learning.All Rights Reserved
Structures of Amino Acids
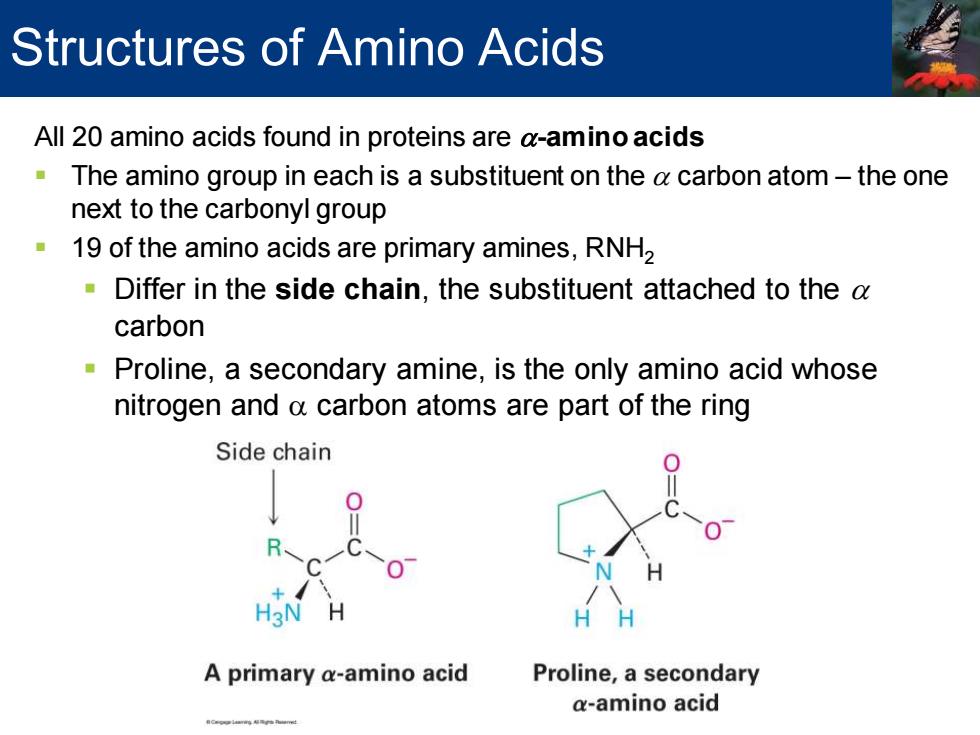
Structures of Amino Acids All 20 amino acids found in proteins are a-amino acids The amino group in each is a substituent on the a carbon atom-the one next to the carbonyl group 19 of the amino acids are primary amines,RNH2 Differ in the side chain,the substituent attached to the a carbon Proline,a secondary amine,is the only amino acid whose nitrogen and a carbon atoms are part of the ring Side chain H3N H HH A primary a-amino acid Proline,a secondary a-amino acid
All 20 amino acids found in proteins are a-amino acids ▪ The amino group in each is a substituent on the a carbon atom – the one next to the carbonyl group ▪ 19 of the amino acids are primary amines, RNH2 ▪ Differ in the side chain, the substituent attached to the a carbon ▪ Proline, a secondary amine, is the only amino acid whose nitrogen and a carbon atoms are part of the ring Structures of Amino Acids