
CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry
3-1 Functional Groups Functional group A group of atoms within a molecule that has a characteristic chemical behavior These structural features allow compounds to be classified into families
Functional group ▪ A group of atoms within a molecule that has a characteristic chemical behavior ▪ These structural features allow compounds to be classified into families 3-1 Functional Groups
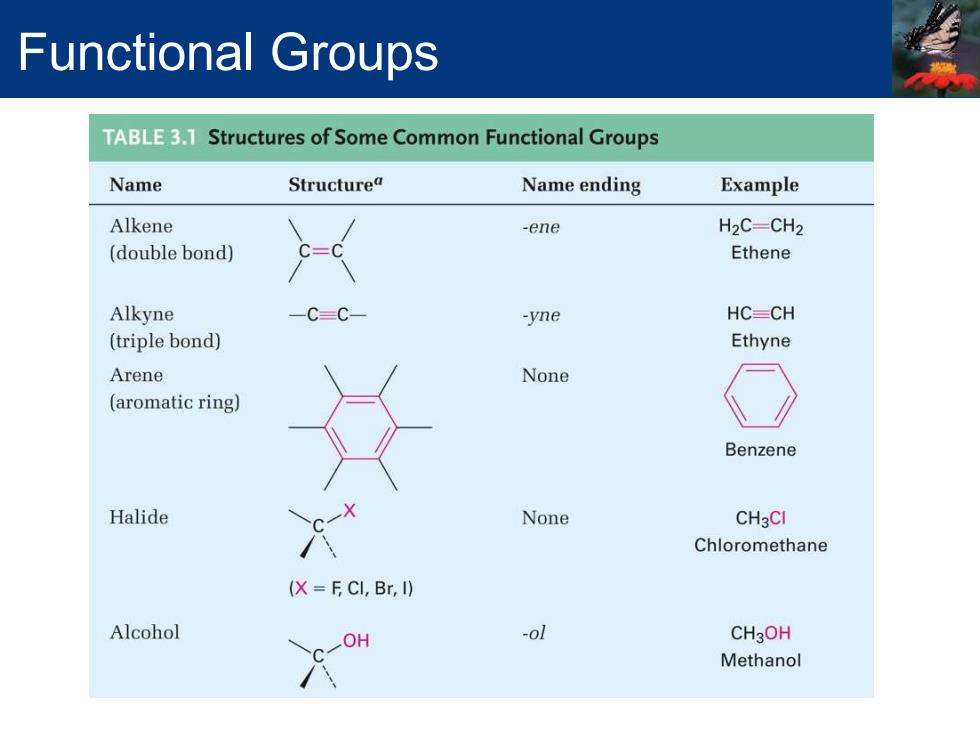
Functional Groups TABLE3.1 Structures of Some Common Functional Groups Name Structurea Name ending Example Alkene -ene H2C-CH2 (double bond) Ethene Alkyne C=C- -yne HC=CH (triple bond) Ethyne Arene None (aromatic ring) Benzene Halide None CH3CI Chloromethane (X F CI,Br,I) Alcohol OH -ol CH3OH Methanol
Functional Groups
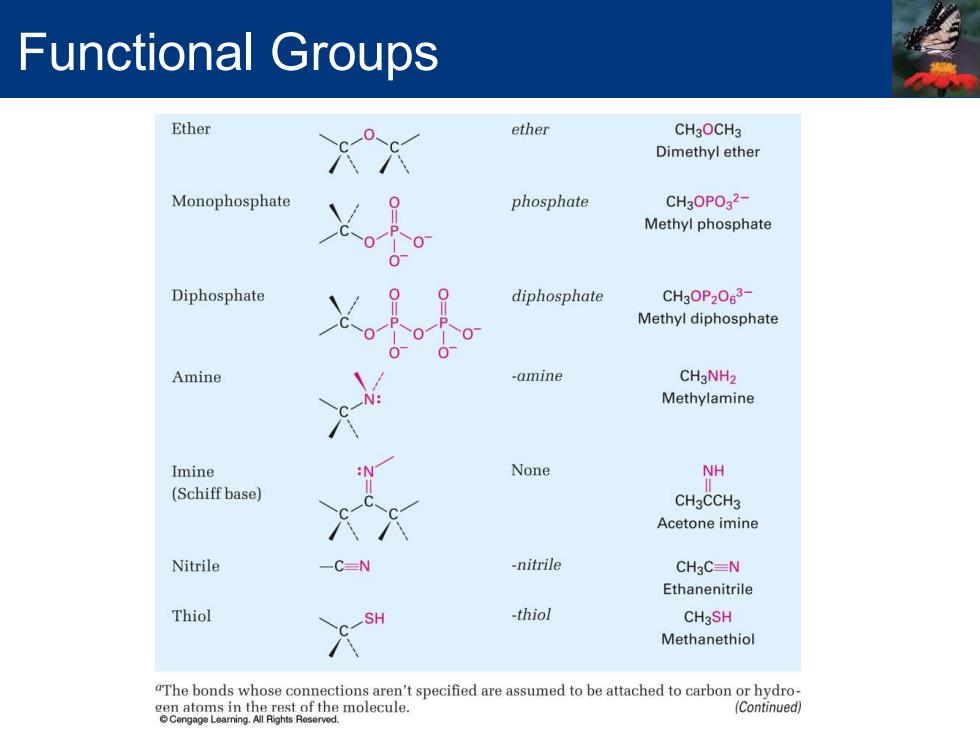
Functional Groups Ether ether CH30CH3 Dimethyl ether Monophosphate phosphate CH3OPO32- Methyl phosphate Diphosphate diphosphate CH3OP2063- Methyl diphosphate Amine -amine CH3NH2 Methylamine Imine None NH (Schiff base) CH3CCH3 Acetone imine Nitrile -C=N -nitrile CH3C=N Ethanenitrile Thiol SH thiol CH3SH Methanethiol "The bonds whose connections aren't specified are assumed to be attached to carbon or hydro- molecule. (Continued)
Functional Groups
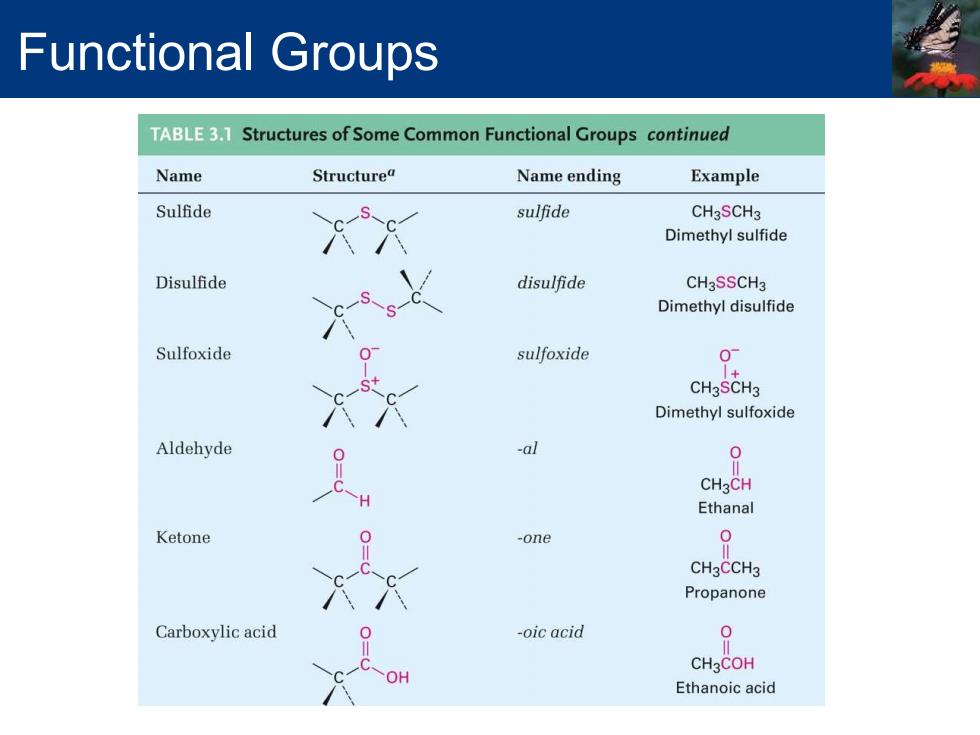
Functional Groups TABLE3.1 Structures of Some Common Functional Groups continued Name Structurea Name ending Example Sulfide sulfide CH3SCH3 Dimethyl sulfide Disulfide disulfide CHaSSCHa Dimethyl disulfide Sulfoxide sulfoxide 0 CH3SCH3 Dimethyl sulfoxide Aldehyde -al CH3CH Ethanal Ketone -one 0 CH3CCH3 Propanone Carboxylic acid -oic acid 0 CH3COH OH Ethanoic acid
Functional Groups
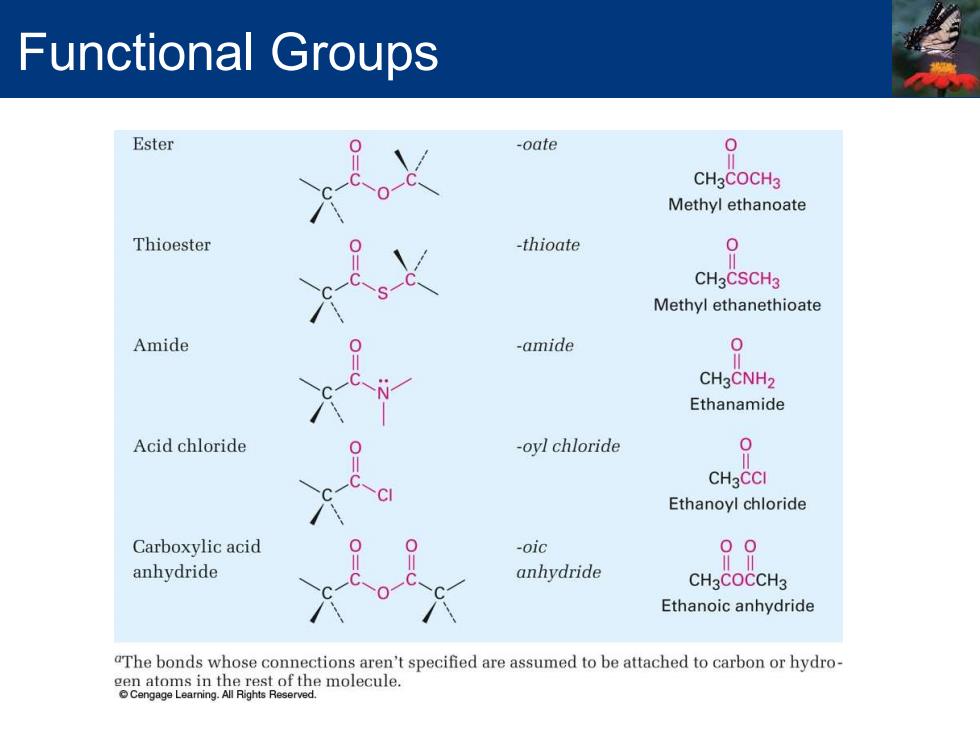
Functional Groups Ester -oate 0 CH3COCH3 Methyl ethanoate Thioester -thioate 0 CH3CSCH3 Methyl ethanethioate Amide -amide CH3CNH2 Ethanamide Acid chloride oyl chloride 0 CH3CCI Ethanoyl chloride Carboxylic acid -oic 00 anhydride anhydride CH3COCCH3 Ethanoic anhydride "The bonds whose connections aren't specified are assumed to be attached to carbon or hydro- molecule
Functional Groups
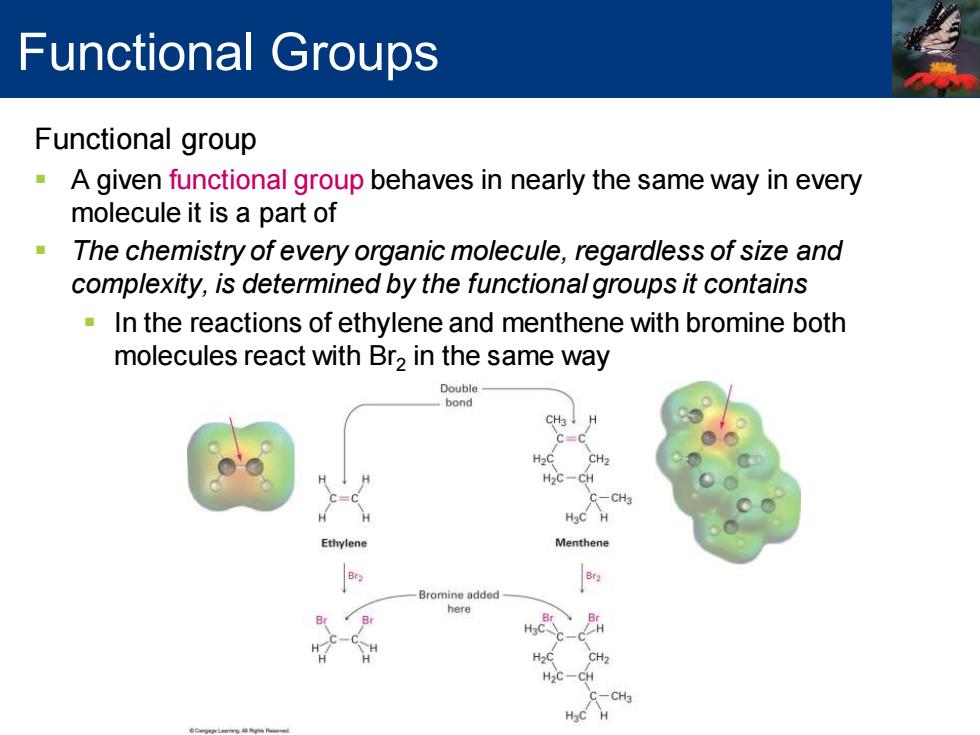
Functional Groups Functional group A given functional group behaves in nearly the same way in every molecule it is a part of The chemistry of every organic molecule,regardless of size and complexity,is determined by the functional groups it contains In the reactions of ethylene and menthene with bromine both molecules react with Br2 in the same way Double bond CH H2C H2C-CH C-CH3 Ethylene Menthene Bromine added here CH2 H2C-CH C-CH3
Functional group ▪ A given functional group behaves in nearly the same way in every molecule it is a part of ▪ The chemistry of every organic molecule, regardless of size and complexity, is determined by the functional groups it contains ▪ In the reactions of ethylene and menthene with bromine both molecules react with Br2 in the same way Functional Groups
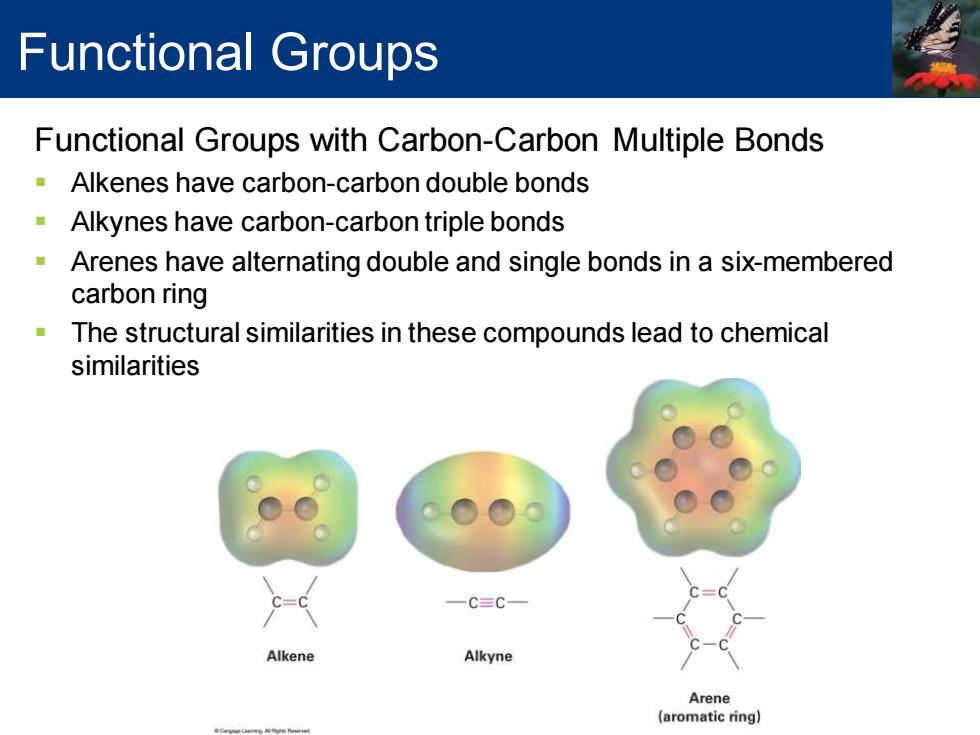
Functional Groups Functional Groups with Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds Alkenes have carbon-carbon double bonds -Alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds Arenes have alternating double and single bonds in a six-membered carbon ring The structural similarities in these compounds lead to chemical similarities 一C=C一 Alkene Alkyne Arene (aromatic ring)
Functional Groups with Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds ▪ Alkenes have carbon-carbon double bonds ▪ Alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds ▪ Arenes have alternating double and single bonds in a six-membered carbon ring ▪ The structural similarities in these compounds lead to chemical similarities Functional Groups
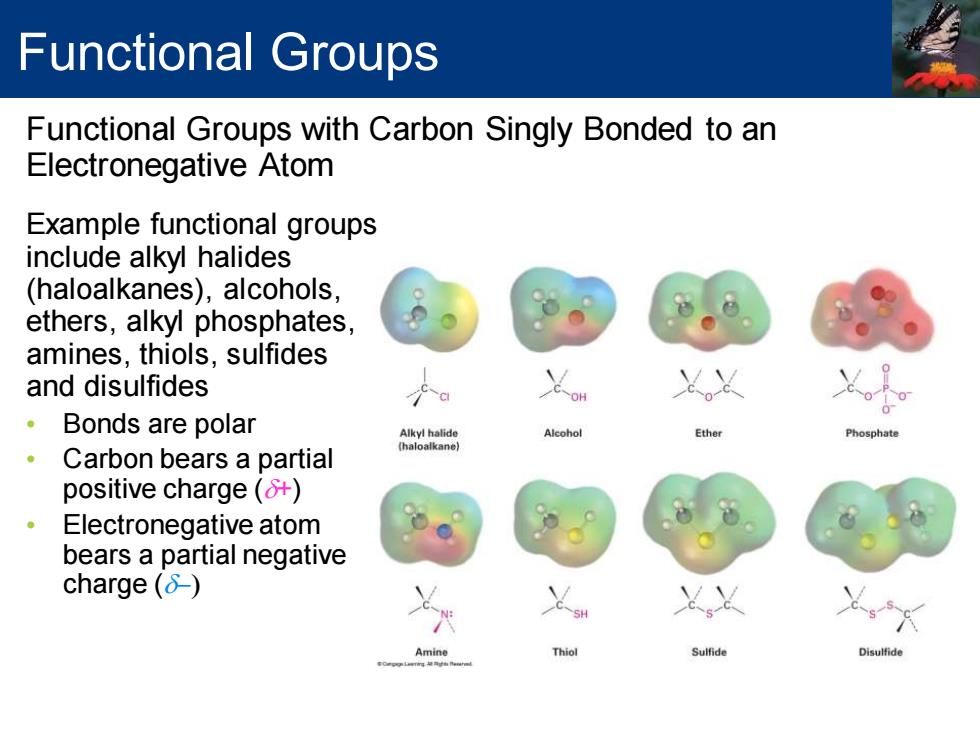
Functional Groups Functional Groups with Carbon Singly Bonded to an Electronegative Atom Example functional groups include alkyl halides (haloalkanes),alcohols, ethers,alkyl phosphates, amines,thiols,sulfides and disulfides C-O 。 Bonds are polar Alcohol Ether Phosphat Carbon bears a partial positive charge(+) Electronegative atom bears a partial negative charge() Amine Thiol Sulfide Disulfide
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly Bonded to an Electronegative Atom Functional Groups Example functional groups include alkyl halides (haloalkanes), alcohols, ethers, alkyl phosphates, amines, thiols, sulfides and disulfides • Bonds are polar • Carbon bears a partial positive charge (d+) • Electronegative atom bears a partial negative charge (d-)
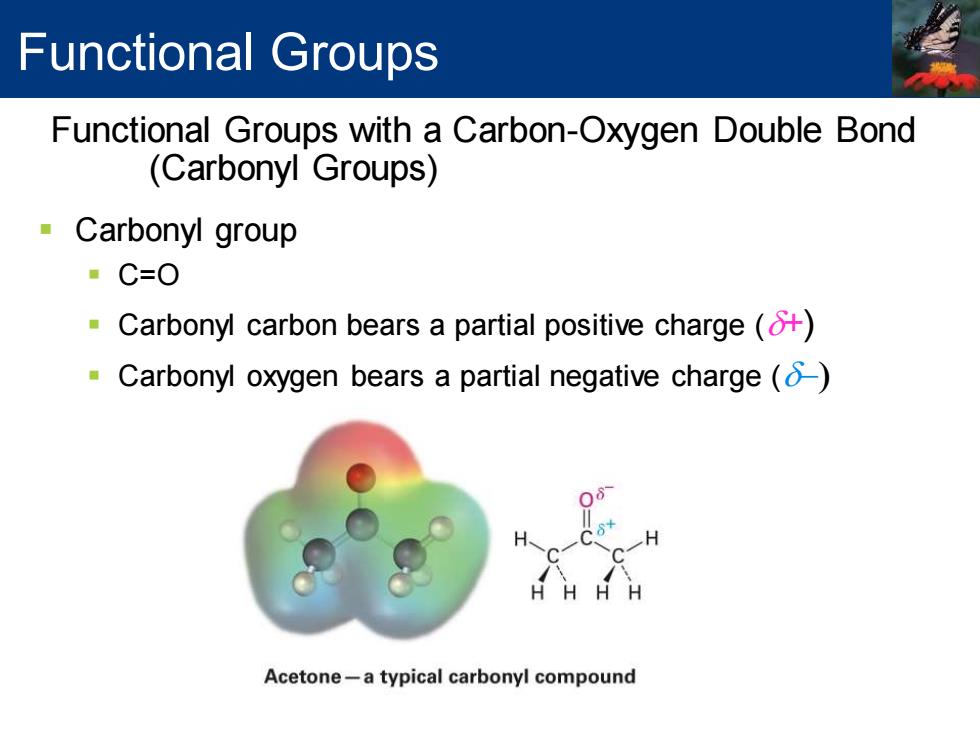
Functional Groups Functional Groups with a Carbon-Oxygen Double Bond (Carbonyl Groups) Carbonyl group ·C=O -Carbonyl carbon bears a partial positive charge() Carbonyl oxygen bears a partial negative charge() Acetone-a typical carbonyl compound
▪ Carbonyl group ▪ C=O ▪ Carbonyl carbon bears a partial positive charge (d+) ▪ Carbonyl oxygen bears a partial negative charge (d-) Functional Groups with a Carbon-Oxygen Double Bond (Carbonyl Groups) Functional Groups