
Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 20 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Carboxylic Acids

Introduction The functional group of carboxylic acids consists of a C=O with-OH bonded to the same carbon. -Carboxyl group is usually written-COOH. -Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -COOH. -Aromatic acids have an aryl group. -Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. Chapter 20 2
Chapter 20 2 Introduction ▪ The functional group of carboxylic acids consists of a C═O with —OH bonded to the same carbon. ▪ Carboxyl group is usually written —COOH. ▪ Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to —COOH. ▪ Aromatic acids have an aryl group. ▪ Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids

Common Names es-ccc8om NH, CH CH3-CH-C-OH CH,一CH2一CH2一C-OH CH,一CH一CH2一C-OH B y B a-chloropropionic acid y-aminobutyric acid isovaleric acid (B-methylbutyric acid) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Many aliphatic acids have historical names. Positions of substituents on the chain are labeled with Greek letters starting at the carbon attached to the carboxylic carbon Chapter 20 3
Chapter 20 3 Common Names ▪ Many aliphatic acids have historical names. ▪ Positions of substituents on the chain are labeled with Greek letters starting at the carbon attached to the carboxylic carbon
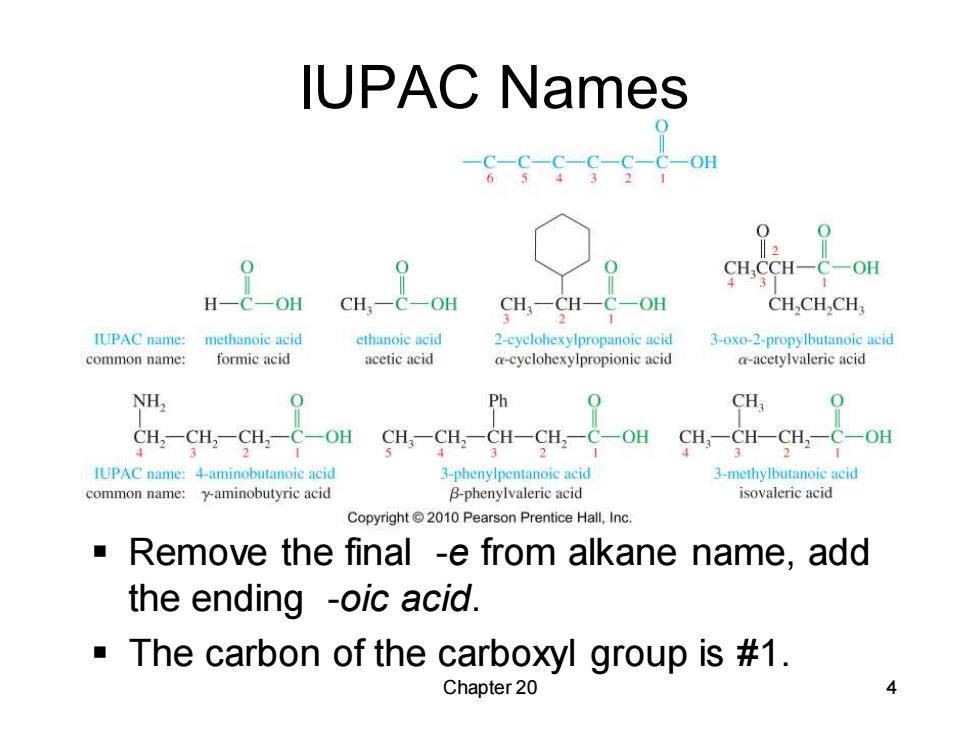
IUPAC Names C-OH ‖2 CHCCH-C-OH H-C-OH CHC一OH CH,-CH-C-OH CH,CH.CH; IUPAC name: methanoic acid ethanoie acid 2-cyelohexylpropanoic acid 3-oxo-2-propylbutanoic acid common name: formic acid acetic acid a-cyclohexylpropionic acid a-acetylvaleric acid NH, 0 Ph 0 CH CH,一CH,一CH,一C-OH CH,一CH,一CH-CH,一C-OH CH,-CH-CH,一C-OH IUPAC name:4-aminobutanoic acid 3-phenylpentanoic acid 3-methylbutanoie acid common name:y-aminobutyric acid B-phenylvaleric acid isovaleric acid Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Remove the final -e from alkane name,add the ending -oic acid. The carbon of the carboxyl group is #1. Chapter 20
Chapter 20 4 IUPAC Names ▪ Remove the final -e from alkane name, add the ending -oic acid. ▪ The carbon of the carboxyl group is #1
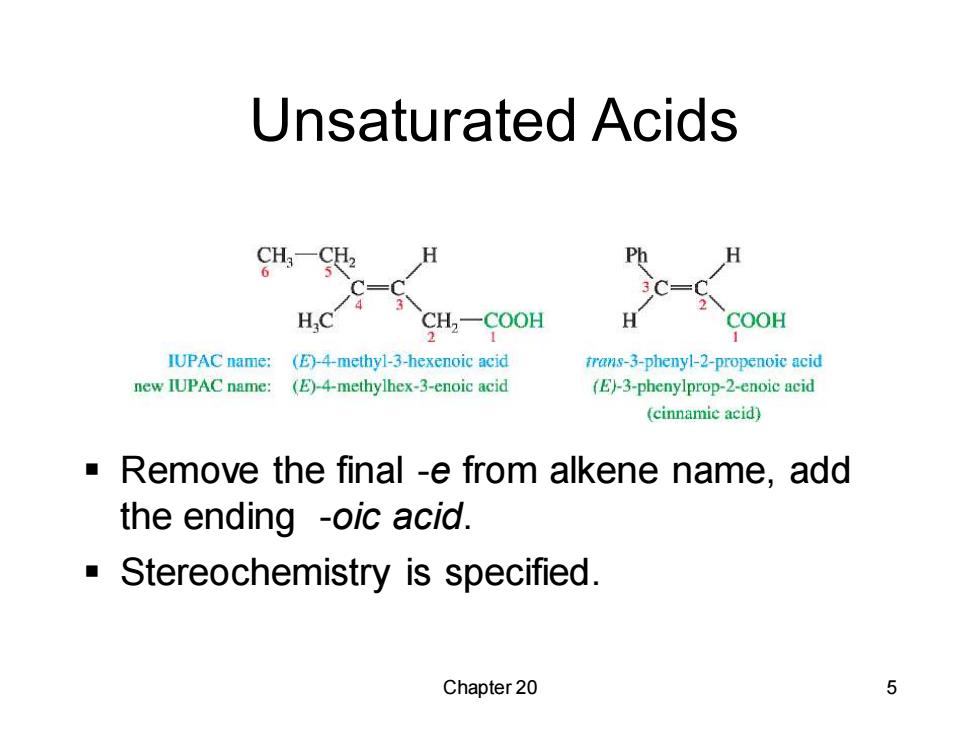
Unsaturated Acids Ph SH,一C0OH H COOH IUPAC name: (E)-4-methy1-3-hexenoic acid trans-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid new IUPAC name: (E)-4-methylhex-3-enoic acid (E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoic acid (cinnamic acid) Remove the final -e from alkene name,add the ending -oic acid. Stereochemistry is specified. Chapter 20 5
Chapter 20 5 Unsaturated Acids ▪ Remove the final -e from alkene name, add the ending -oic acid. ▪ Stereochemistry is specified
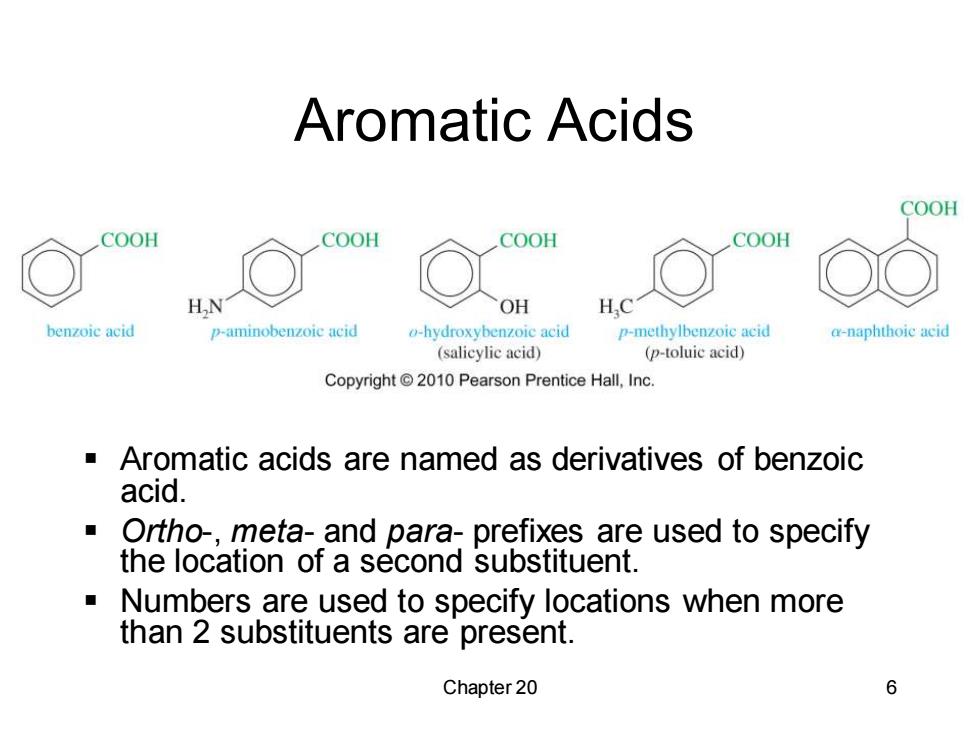
Aromatic Acids COOH COOH COOH COOH COOH HN OH H.C benzoic acid p-aminobenzoic acid o-hydroxybenzoic acid p-methylbenzoie aeid a-naphthoie acid (salicylic acid) (p-toluic acid) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Aromatic acids are named as derivatives of benzoic acid. ■ Ortho-,meta-and para-prefixes are used to specify the location of a second substituent. Numbers are used to specify locations when more than 2 substituents are present. Chapter 20 6
Chapter 20 6 Aromatic Acids ▪ Aromatic acids are named as derivatives of benzoic acid. ▪ Ortho-, meta- and para- prefixes are used to specify the location of a second substituent. ▪ Numbers are used to specify locations when more than 2 substituents are present

Dicarboxylic Acids Aliphatic diacids are usually called by their common names. For IUPAC name,number the chain from the end closest to a substituent. Br HOOCCH2CHCH2CH2COOH 3-bromohexanedioic acid B-bromoadipic acid Chapter 20 7
Chapter 20 7 Dicarboxylic Acids ▪ Aliphatic diacids are usually called by their common names. ▪ For IUPAC name, number the chain from the end closest to a substituent. 3-bromohexanedioic acid -bromoadipic acid HOOCCH2CHCH2CH2COOH Br
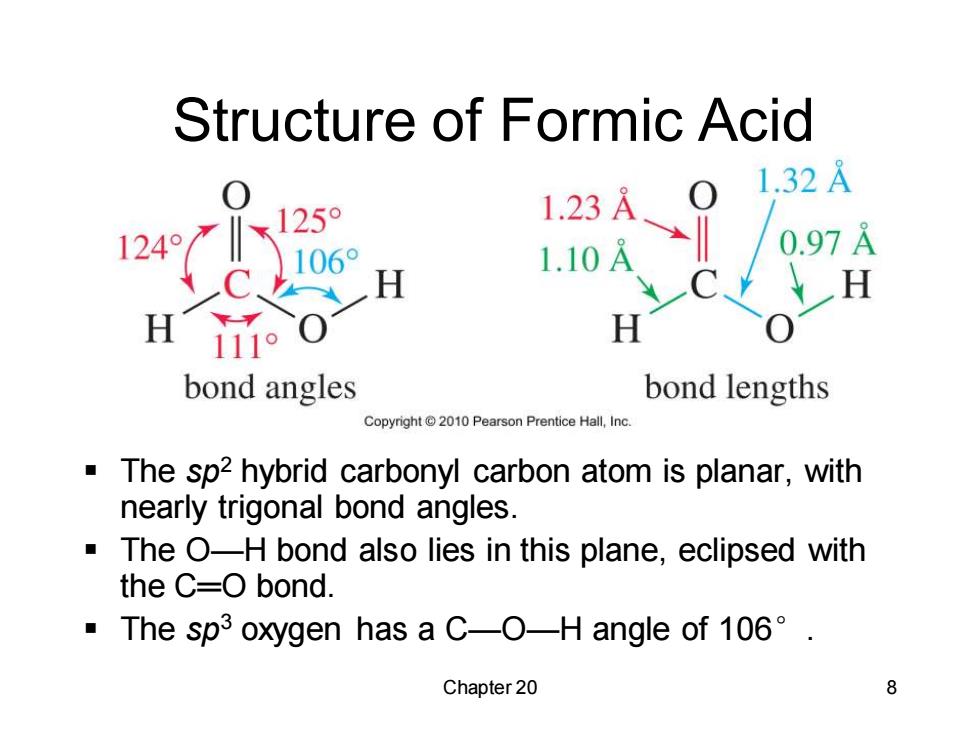
Structure of Formic Acid 1.32A 25° 1.23A 124° 1.10A 0.97A H H H 111o H bond angles bond lengths Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc The sp2 hybrid carbonyl carbon atom is planar,with nearly trigonal bond angles. The O-H bond also lies in this plane,eclipsed with the C=O bond. ·The spi3 oxygen has a C--O-H angle of106°. Chapter 20 8
Chapter 20 8 Structure of Formic Acid ▪ The sp2 hybrid carbonyl carbon atom is planar, with nearly trigonal bond angles. ▪ The O—H bond also lies in this plane, eclipsed with the C═O bond. ▪ The sp3 oxygen has a C—O—H angle of 106°
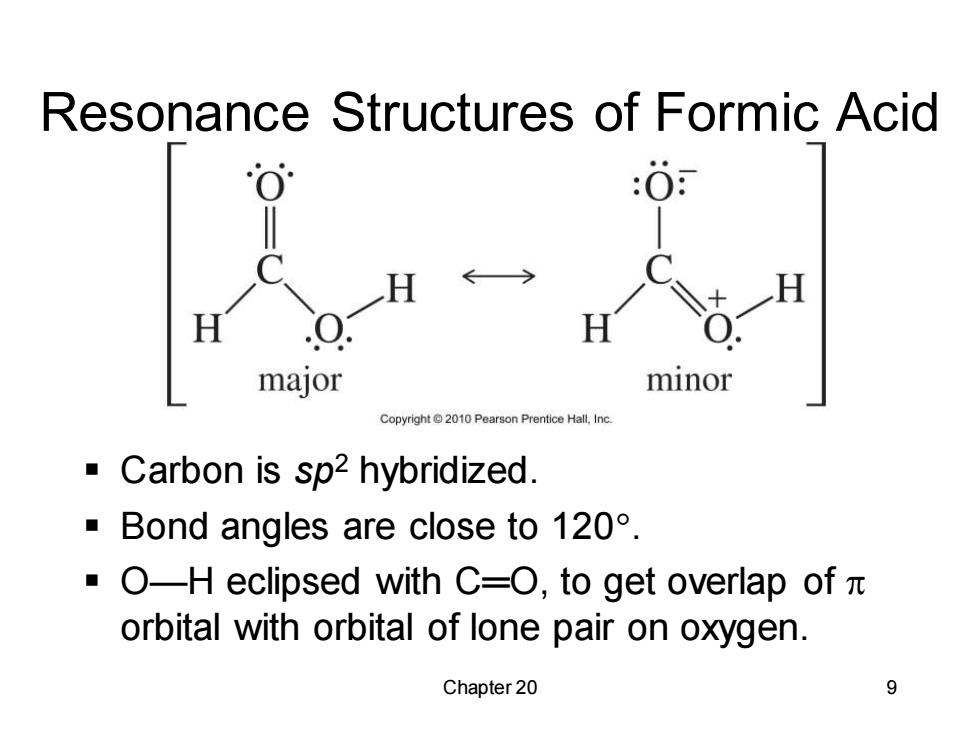
Resonance Structures of Formic Acid :0 H H major minor Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Carbon is sp2 hybridized. Bond angles are close to 120. ·O-H eclipsed with C=O,to get overlap ofπ orbital with orbital of lone pair on oxygen. Chapter 20 9
Chapter 20 9 Resonance Structures of Formic Acid ▪ Carbon is sp2 hybridized. ▪ Bond angles are close to 120. ▪ O—H eclipsed with C═O, to get overlap of orbital with orbital of lone pair on oxygen
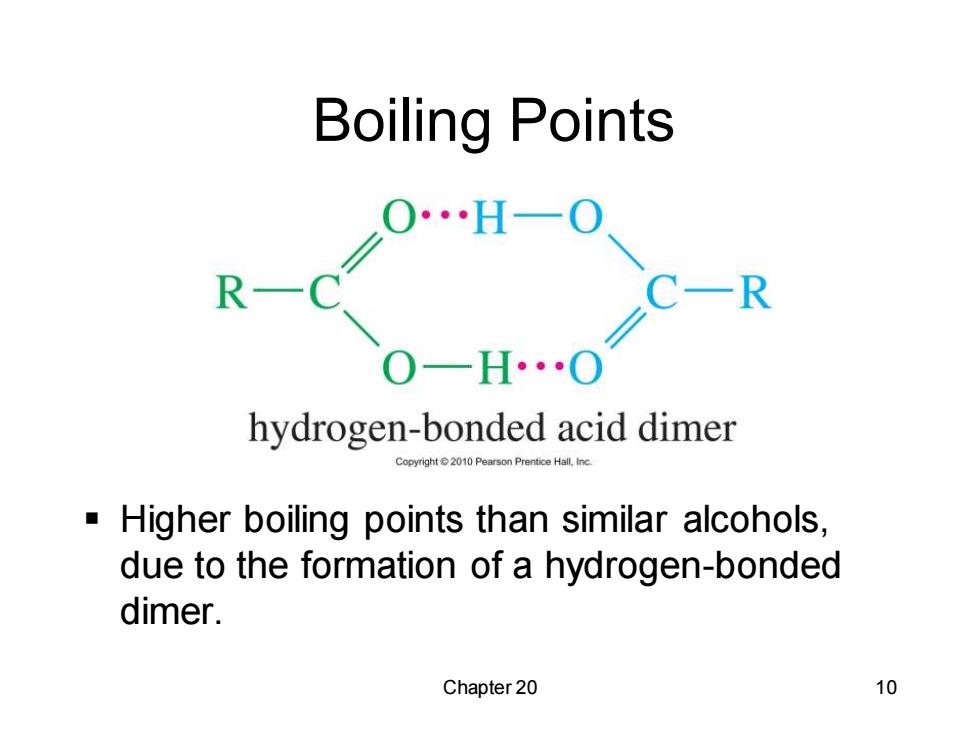
Boiling Points 20H-0 R C-R O-H..O hydrogen-bonded acid dimer Prentice Hall.Inc Higher boiling points than similar alcohols, due to the formation of a hydrogen-bonded dimer. Chapter 20 10
Chapter 20 10 Boiling Points ▪ Higher boiling points than similar alcohols, due to the formation of a hydrogen-bonded dimer