
Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems,Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 15 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
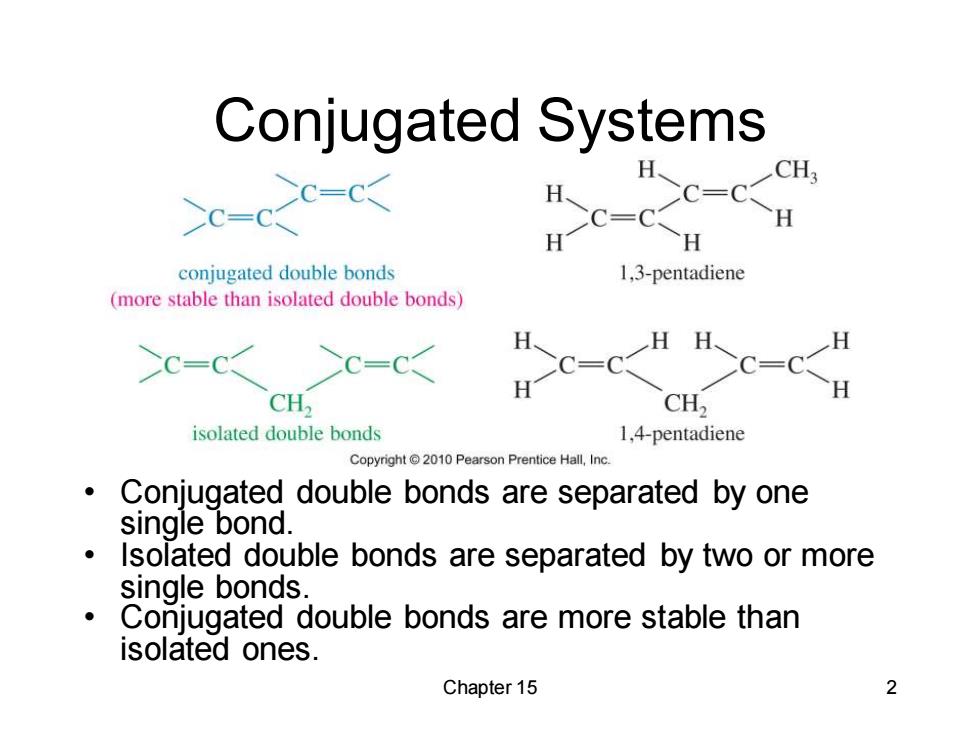
Conjugated Systems C-CH 3 uc-c H conjugated double bonds 1,3-pentadiene (more stable than isolated double bonds) HH、 H C-C C=C >C= C=C CH, CH2 isolated double bonds 1,4-pentadiene Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Conjugated double bonds are separated by one single bond. Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds Conjugated double bonds are more stable than isolated ones. Chapter 15 2
Chapter 15 2 Conjugated Systems • Conjugated double bonds are separated by one single bond. • Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds. • Conjugated double bonds are more stable than isolated ones
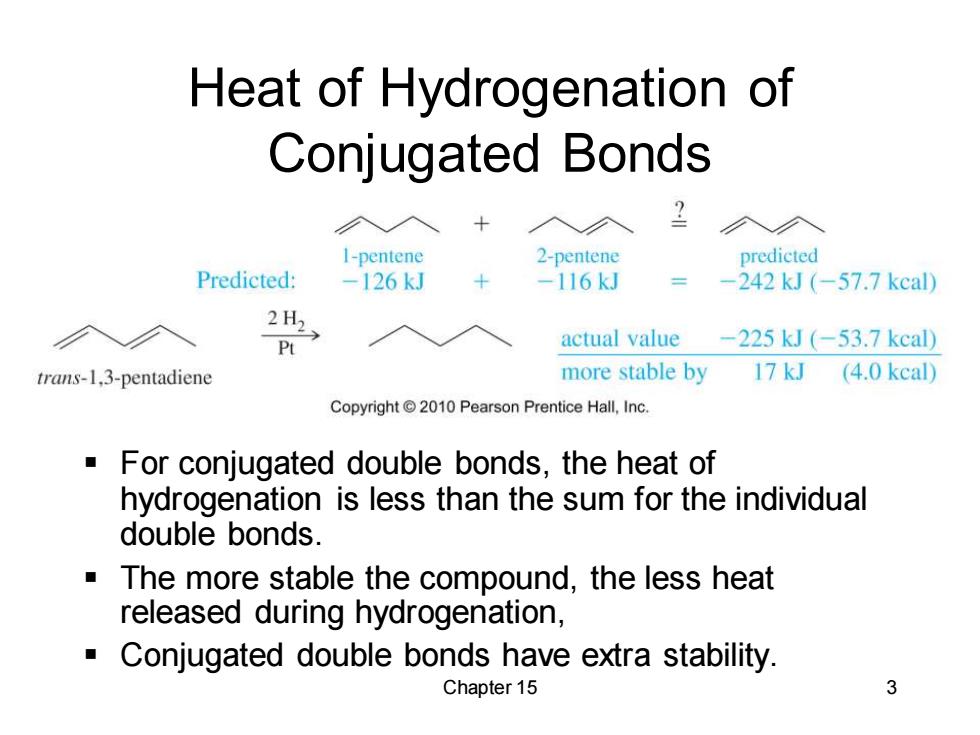
Heat of Hydrogenation of Conjugated Bonds I-pentene 2-pentene predicted Predicted: -126kJ -116kJ -242kJ(-57.7kcal) 2H2 actual value -225kJ(-53.7kcal) trans-1,3-pentadiene more stable by 17 kJ (4.0 kcal) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. For conjugated double bonds,the heat of hydrogenation is less than the sum for the individual double bonds. The more stable the compound,the less heat released during hydrogenation, Conjugated double bonds have extra stability. Chapter 15 3
Chapter 15 3 Heat of Hydrogenation of Conjugated Bonds ▪ For conjugated double bonds, the heat of hydrogenation is less than the sum for the individual double bonds. ▪ The more stable the compound, the less heat released during hydrogenation, ▪ Conjugated double bonds have extra stability

Relative Stabilities cumulated terminal diene alkyne C- twice 1-pentene 1.2-pentadiene I-pentyne internal alkyne 292kJ 2-pentyne more substituted (69.8 kcal) isolated 291kJ diene (69.5 keal) isolated 275kJ 1.4-pentadiene diene (65.8kcl trans-1.4-hexadiene conjugated 252kJ diene (60.2 keal) 242kJ trans-1,3-pentadiene (57.7 kcal) 225kJ (53.7kcal) alkane (pentane or hexane) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 15 4
Chapter 15 4 Relative Stabilities twice 1-pentene more substituted
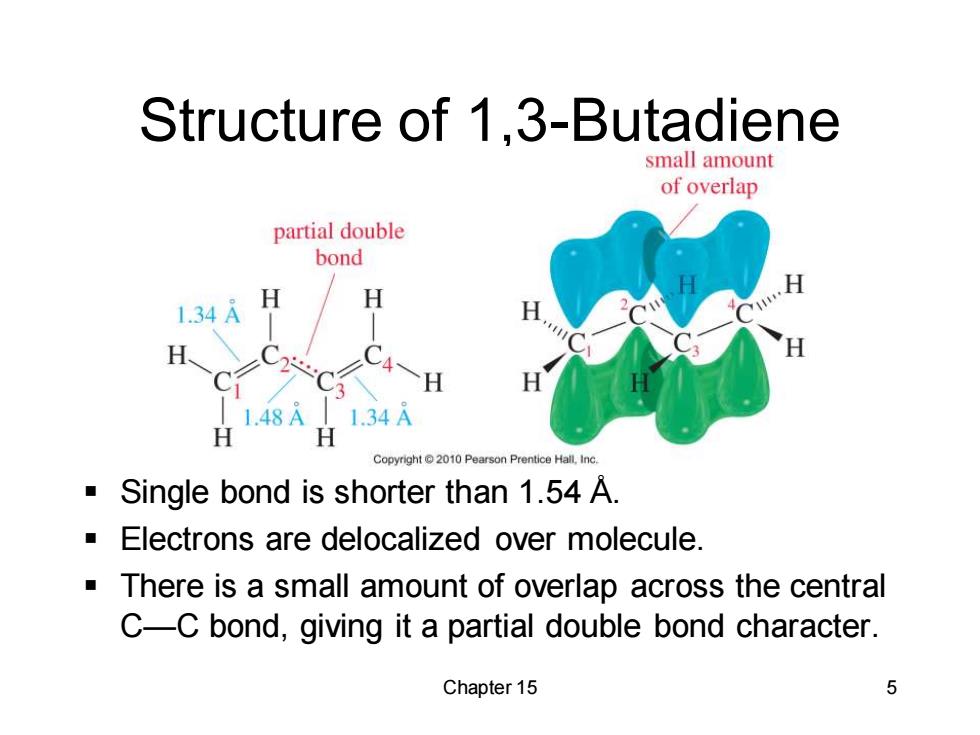
Structure of 1,3-Butadiene small amount of overlap partial double bond 1.34A H H H H 1.48A 1.34A H Copyright10 Pearson Prentice Hall,inc. a Single bond is shorter than 1.54 A. Electrons are delocalized over molecule There is a small amount of overlap across the central C-C bond,giving it a partial double bond character. Chapter 15 5
Chapter 15 5 Structure of 1,3-Butadiene ▪ Single bond is shorter than 1.54 Å. ▪ Electrons are delocalized over molecule. ▪ There is a small amount of overlap across the central C—C bond, giving it a partial double bond character

Molecular Orbitals(MOs) Pi molecular orbitals are the sideways overlap of p orbitals. -p orbitals have two lobes.Plus (+)and minus (-)indicate the opposite phases of the wave function,not electrical charges. When lobes overlap constructively (and + or-and-),a bonding MO is formed. When and lobes overlap,waves cancel out and a node forms;antibonding MO. Chapter 15 6
Chapter 15 6 Molecular Orbitals (MOs) ▪ Pi molecular orbitals are the sideways overlap of p orbitals. ▪ p orbitals have two lobes. Plus (+) and minus (-) indicate the opposite phases of the wave function, not electrical charges. ▪ When lobes overlap constructively (+ and +, or - and -), a bonding MO is formed. ▪ When + and - lobes overlap, waves cancel out and a node forms; antibonding MO

Ethylene Pi MOs (antibonding) destructive energy (bonding)= Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc The combination of two p orbitals must give two molecular orbitals. Constructive overlap is a bonding MO. Destructive overlap is an antibonding MO. Chapter 15 7
Chapter 15 7 Ethylene Pi MOs ▪ The combination of two p orbitals must give two molecular orbitals. ▪ Constructive overlap is a bonding MO. ▪ Destructive overlap is an antibonding MO

MO for 1,3-Butadiene Lowest energy. bondingbonding bonding ·All bonding interactions. -Electrons are delocalized over four nuclei. Copyright 2010 Pearn Prentice Hall,Inc Chapter 15 8
Chapter 15 8 1 MO for 1,3-Butadiene ▪ Lowest energy. ▪ All bonding interactions. ▪ Electrons are delocalized over four nuclei

2 MO for 1,3-Butadiene Two bonding antibonding bonding interactions. bonding One antibonding interaction. ■A bonding MO. Higher energy than 元1 MO and not as node strong. Chapter 15 9
Chapter 15 9 2 MO for 1,3-Butadiene ▪ Two bonding interactions. ▪ One antibonding interaction. ▪ A bonding MO. ▪ Higher energy than 1 MO and not as strong
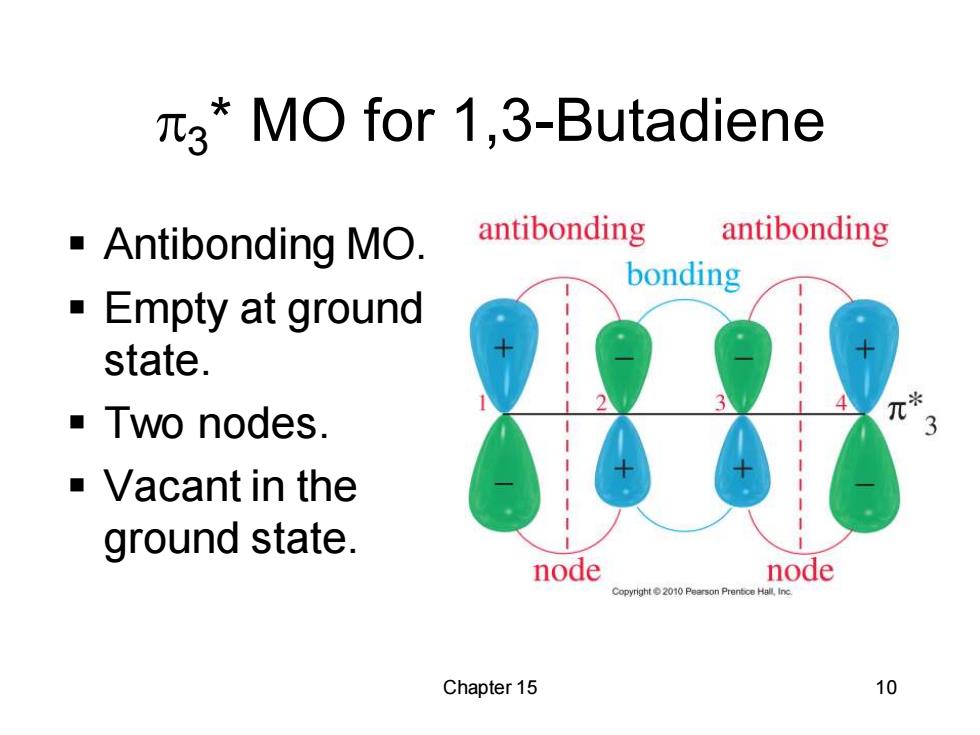
3*MO for 1,3-Butadiene Antibonding MO antibonding antibonding bonding Empty at ground state. Two nodes. Vacant in the ground state. node node Chapter 15 10
Chapter 15 10 3 * MO for 1,3-Butadiene ▪ Antibonding MO. ▪ Empty at ground state. ▪ Two nodes. ▪ Vacant in the ground state