
Organic Chemistry,5th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate lons Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,C=O. Step 1:Deprotonation Step 2:Attack on electrophile H enolate ion Chapter 22
Chapter 22 2 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl, C=O. enolate ion =>
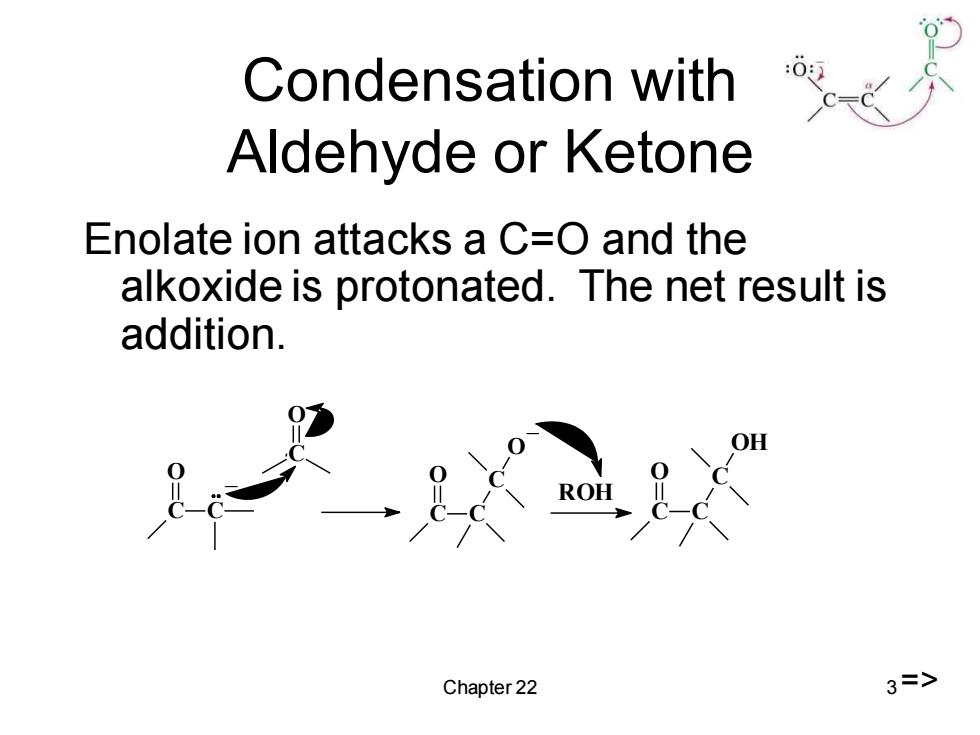
Condensation with Aldehyde or Ketone Enolate ion attacks a C=O and the alkoxide is protonated.The net result is addition. ROH Chapter 22 3=>
Chapter 22 3 Condensation with Aldehyde or Ketone Enolate ion attacks a C=O and the alkoxide is protonated. The net result is addition. C O C _ C O C O C C O _ ROH C O C C OH =>

Condensation with Esters Loss of alkoxide ion results in nucleophilic acyl substitution. Step 1:Addition of the enolate Step 2:Elimination of the alkoxide C=0 COR- +RO- enolate ester substitution product Chapter 22 4
Chapter 22 4 Condensation with Esters Loss of alkoxide ion results in nucleophilic acyl substitution. =>
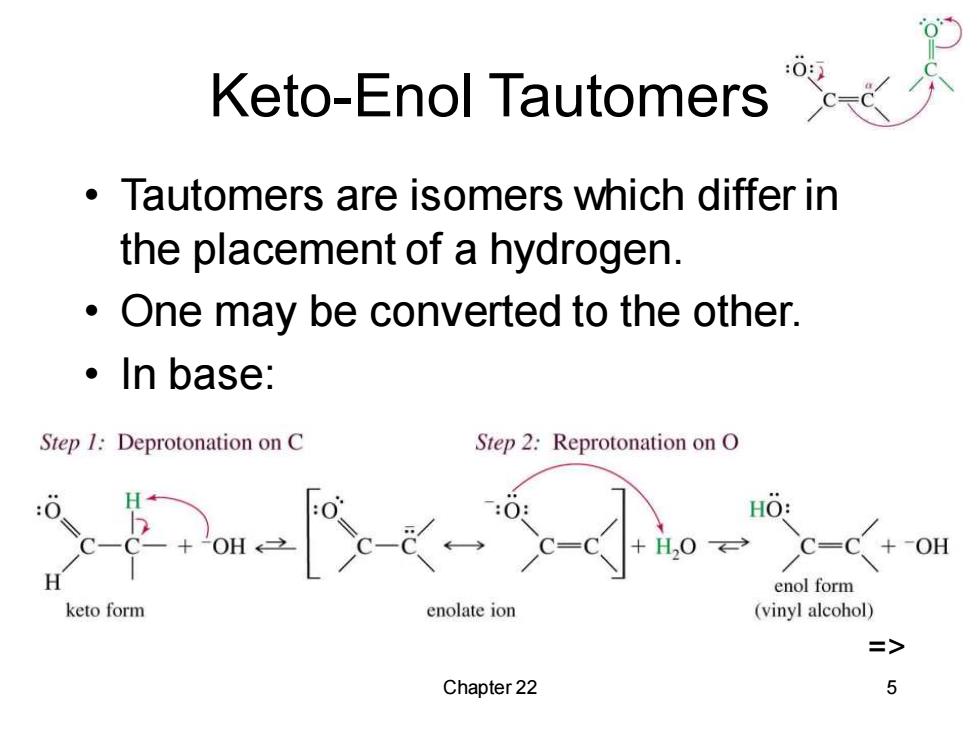
Keto-Enol Tautomers Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of a hydrogen. One may be converted to the other. 。In base: Step 1:Deprotonation on C Step 2:Reprotonation on O HO: C=( enol form keto form enolate ion (vinyl alcohol) Chapter 22 5
Chapter 22 5 Keto-Enol Tautomers • Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of a hydrogen. • One may be converted to the other. • In base: =>
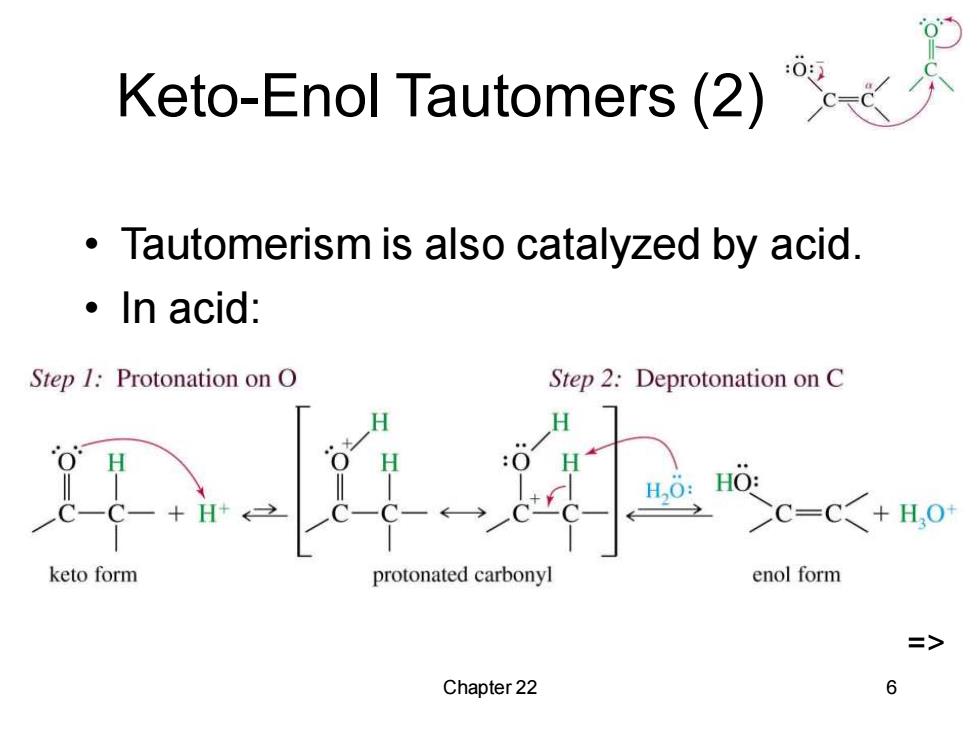
Keto-Enol Tautomers(2) Tautomerism is also catalyzed by acid. 。In acid: Step /Protonation on O Step 2:Deprotonation on C H HO: >C=C+H,0 keto form protonated carbonyl enol form => Chapter 22 6
Chapter 22 6 Keto-Enol Tautomers (2) • Tautomerism is also catalyzed by acid. • In acid: =>
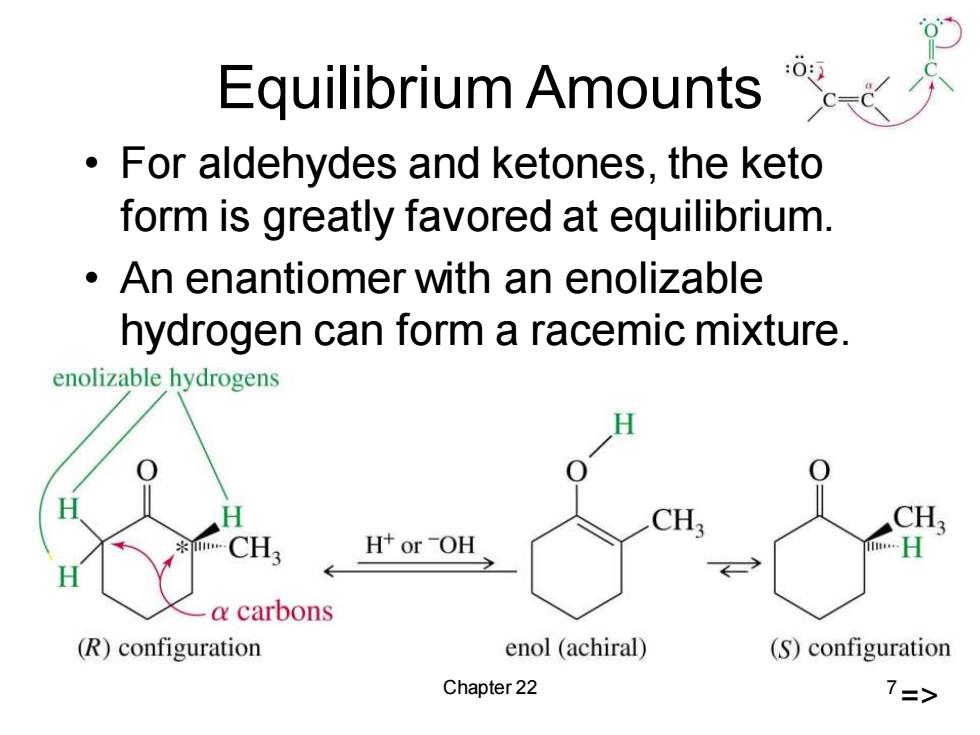
Equilibrium Amounts For aldehydes and ketones,the keto form is greatly favored at equilibrium. An enantiomer with an enolizable hydrogen can form a racemic mixture. enolizable hydrogens CH3 CH3 H+orOH H a carbons (R)configuration enol (achiral) (S)configuration Chapter 22 7=>
Chapter 22 7 Equilibrium Amounts • For aldehydes and ketones, the keto form is greatly favored at equilibrium. • An enantiomer with an enolizable hydrogen can form a racemic mixture. =>

D Acidity of a-Hydrogens pKa for a-H of aldehyde or ketone~20. Much more acidic than alkane or alkene (pKa 40)or alkyne (pKa 25). Less acidic than water (pKa=15.7)or alcohol (pKa 16-19). In the presence of hydroxide or alkoxide ions,only a small amount of enolate ion is present at equilibrium. => Chapter 22 8
Chapter 22 8 Acidity of -Hydrogens • pKa for -H of aldehyde or ketone ~20. • Much more acidic than alkane or alkene (pKa > 40) or alkyne (pKa = 25). • Less acidic than water (pKa = 15.7) or alcohol (pKa = 16-19). • In the presence of hydroxide or alkoxide ions, only a small amount of enolate ion is present at equilibrium. =>
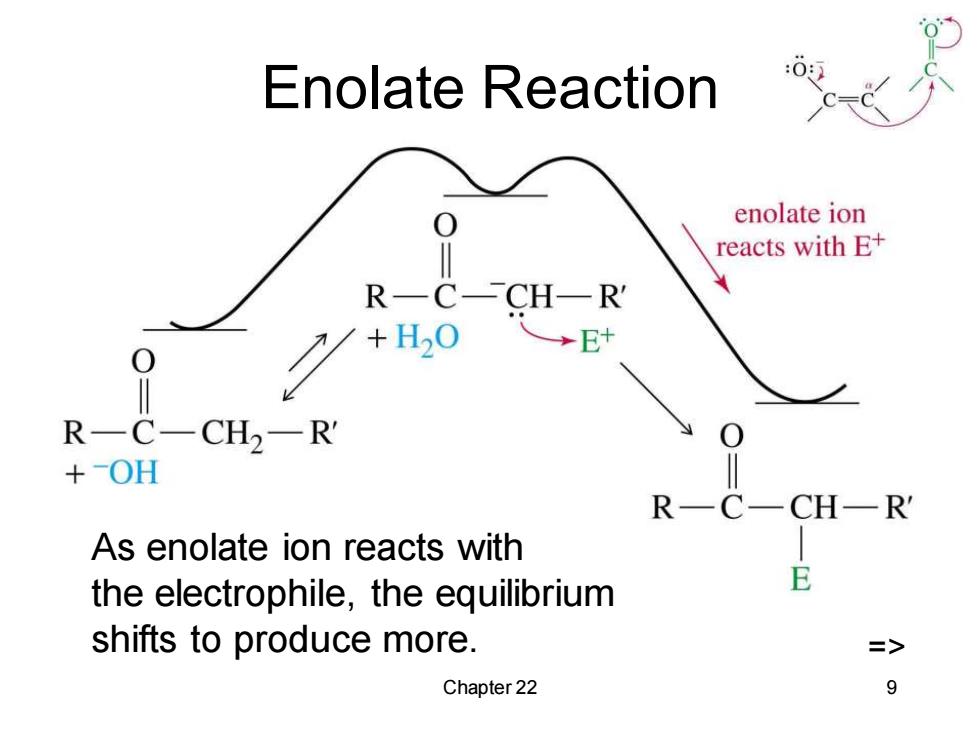
Enolate Reaction enolate ion reacts with E+ RC—CH—R +H20 人→E R-C-CH2-R' +OH R-C CHR As enolate ion reacts with the electrophile,the equilibrium E shifts to produce more. => Chapter 22 9
Chapter 22 9 Enolate Reaction => As enolate ion reacts with the electrophile, the equilibrium shifts to produce more
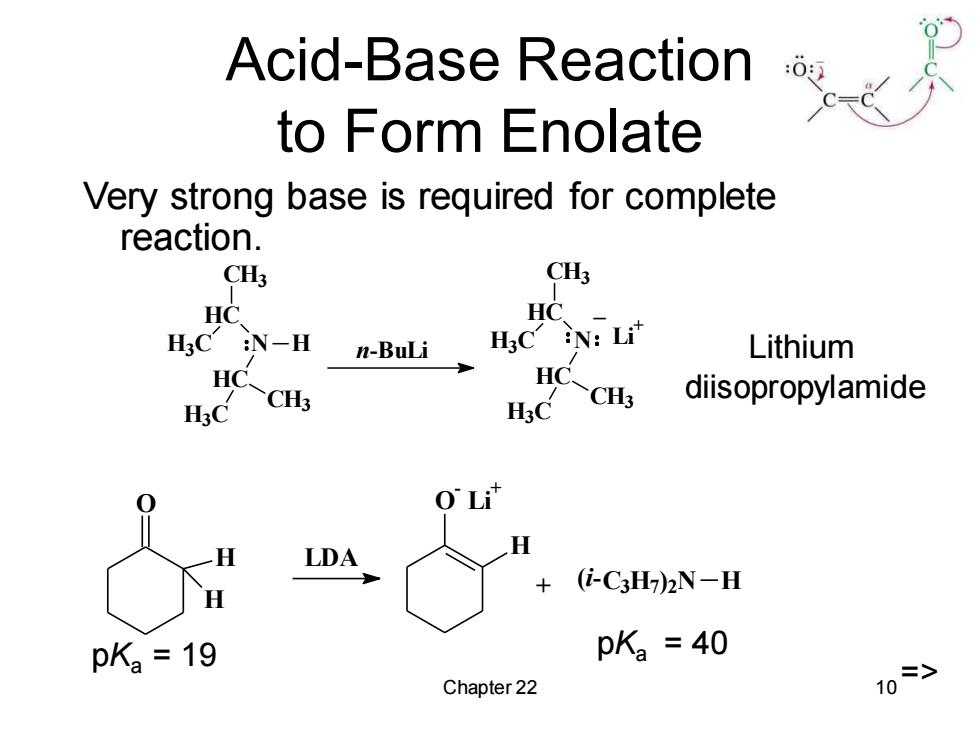
Acid-Base Reaction to Form Enolate Very strong base is required for complete reaction. CH3 CH3 HC HC H3CN-H n-BuLi Lithium HC-CH3 HC ~CH3 diisopropylamide O Li" LDA (-C3H)2N-H pK=19 pK2=40 Chapter 22
Chapter 22 10 Acid-Base Reaction to Form Enolate Very strong base is required for complete reaction. Lithium diisopropylamide N H HC CH3 H3C HC CH3 H3C n-BuLi N HC CH3 H3C HC CH3 H3C Li + _ O H H O - Li + H LDA + C3H7 ) (i- 2N H pKa = 19 pKa = 40 =>