
Organic Chemistry,5th Edition H L.G.Wade,Jr. CH2CH3 Chapter 19 Amines Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 19 Amines Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Introduction Organic derivatives of ammonia CH2CH3 Many are biologically active. CH2一CH一COOH OH HO CH2 H :NH2 HO CH-CH2-N CH2 CH3 HO HO dopamine epinephrine L-tryptophan a neurotransmitter an adrenal hormone an amino acid CH2OH CH2CH2NH2 HO CH2OH OH => piperazine nicotinic acid pyridoxine histamine kills intestinal worms niacin,a vitamin vitamin B6 dilates blood vessels
Chapter 19 2 Introduction • Organic derivatives of ammonia • Many are biologically active. =>

Biological Activity H CH2CH3 Neurotransmitters:dopamine Bioregulators:epinephrine ·Vitamins:niacin,Bs Alkaloids:nicotine,morphine,cocaine 。Amino acids > Chapter 19 3
Chapter 19 3 Biological Activity • Neurotransmitters: dopamine • Bioregulators: epinephrine • Vitamins: niacin, B6 • Alkaloids: nicotine, morphine, cocaine • Amino acids =>
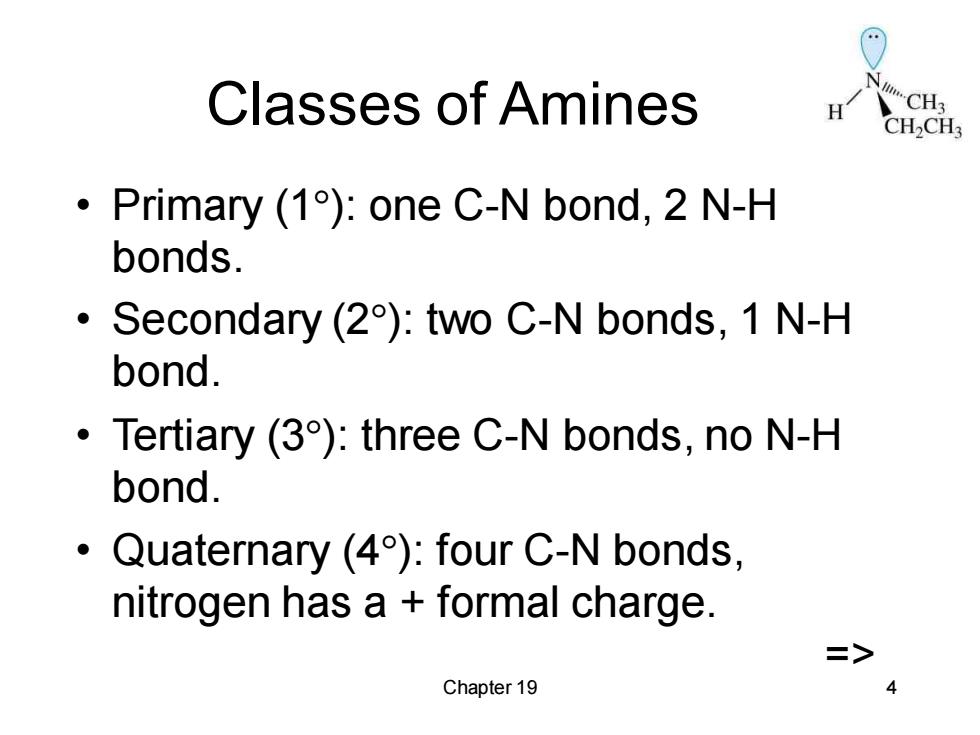
Classes of Amines CH2CH3 Primary (1):one C-N bond,2 N-H bonds. 。 Secondary (2):two C-N bonds,1 N-H bond. Tertiary (3):three C-N bonds,no N-H bond. Quaternary (4):four C-N bonds, nitrogen has a formal charge. > Chapter 19 4
Chapter 19 4 Classes of Amines • Primary (1): one C-N bond, 2 N-H bonds. • Secondary (2): two C-N bonds, 1 N-H bond. • Tertiary (3): three C-N bonds, no N-H bond. • Quaternary (4): four C-N bonds, nitrogen has a + formal charge. =>

Classify: H CH2CH3 CH3 N CH3 H CH3 Br CH3- C-NH2 CH3CH2-N-CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 三> Chapter 19 5
Chapter 19 5 Classify: N H CH3 C CH3 CH3 NH2 N CH3 CH3 CH3CH2 N CH3 CH2CH3 + Br _ =>

Common Names CH2CH3 Name the alkyl or aryl groups bonded to nitrogen,then add suffix-amine. (CH3CH2)2NCH3 diethylmethylamine NHCH3 NH. cyclopentylmethylamine Diphenylamine => Chapter 19 6
Chapter 19 6 Common Names Name the alkyl or aryl groups bonded to nitrogen, then add suffix -amine. (CH3 CH2 ) 2NCH3 NHCH3 NH diethylmethylamine cyclopentylmethylamine Diphenylamine =>
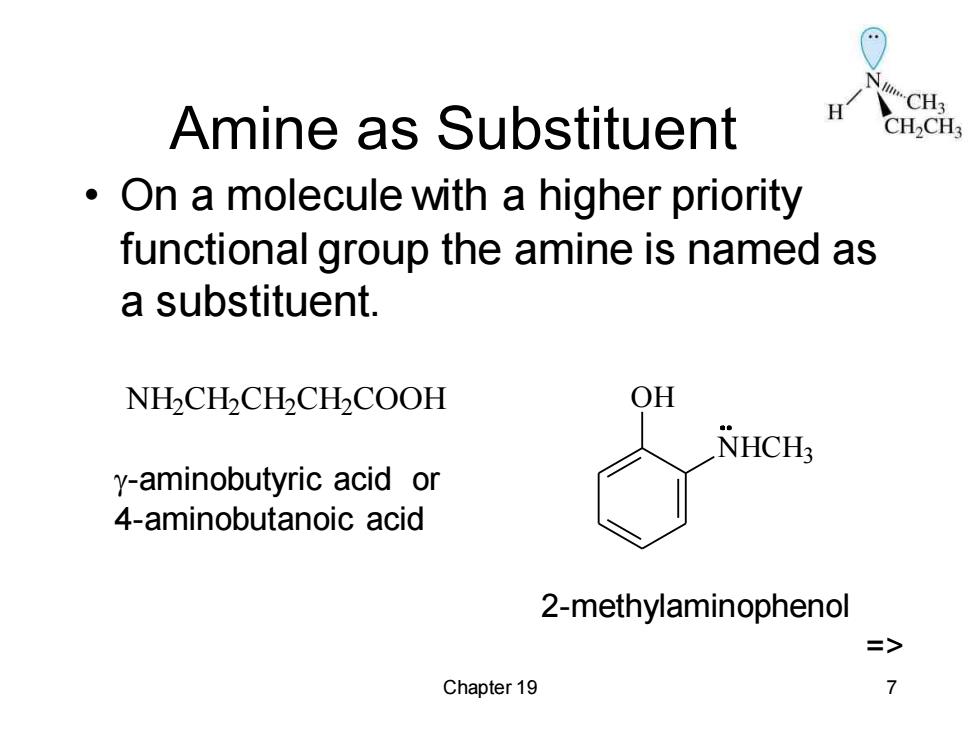
Amine as Substituent H CH2CH3 On a molecule with a higher priority functional group the amine is named as a substituent. NH2CH2CHCHCOOH OH NHCHs y-aminobutyric acid or 4-aminobutanoic acid 2-methylaminophenol Chapter 19 7
Chapter 19 7 Amine as Substituent • On a molecule with a higher priority functional group the amine is named as a substituent. NH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 COOH NHCH3 OH -aminobutyric acid or 4-aminobutanoic acid 2-methylaminophenol =>

IUPAC Names H CH2CH3 Name is based on longest carbon chain. -e of alkane is replaced with -amine. Substituents on nitrogen have N-prefix. Br N(CH3)2 NH2CHCH2CHCHCH3 CH3CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 3-bromo-1-pentanamine N,N-dimethyl-3-hexanamine => Chapter 19 8
Chapter 19 8 IUPAC Names • Name is based on longest carbon chain. • -e of alkane is replaced with -amine. • Substituents on nitrogen have N- prefix. NH2 CH2 CH2 CHCH2 CH3 Br CH3 CH2 CHCH2 CH2 CH3 N(CH3 ) 2 3-bromo-1-pentanamine N,N-dimethyl-3-hexanamine =>

Aromatic Amines H CH2CH3 Amino group is bonded to a benzene ring. Parent compound is called aniline. CH3 NH2 NH2 CH3 H:C aniline N.N-dimethylaniline 4-methylaniline or p-toluidine => Chapter 19 9
Chapter 19 9 Aromatic Amines Amino group is bonded to a benzene ring. Parent compound is called aniline. NH2 aniline N CH3 CH3 N,N-dimethylaniline =>NH2 H3C 4-methylaniline or p-toluidine

Heterocyclic Amines CH CH2CH3 The nitrogen is assigned the number 1. CH3 H H aziridine Pyridine Pyrrolidine Pyrrole 2-methylpyridine > Chapter 19 10
Chapter 19 10 Heterocyclic Amines The nitrogen is assigned the number 1. => N H N H N H N N CH3 aziridine Pyrrole Pyrrolidine Pyridine 2-methylpyridine