
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2006,Prentice Hall
Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2006, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Introduction A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units. First synthetic polymers: >Poly(vinyl chloride)in 1838 >Polystyrene in 1839 Now,250 billion pounds produced annually,worldwide. => Chapter 26
Chapter 26 2 Introduction • A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units. • First synthetic polymers: ➢Poly(vinyl chloride) in 1838 ➢Polystyrene in 1839 • Now, 250 billion pounds produced annually, worldwide. =>
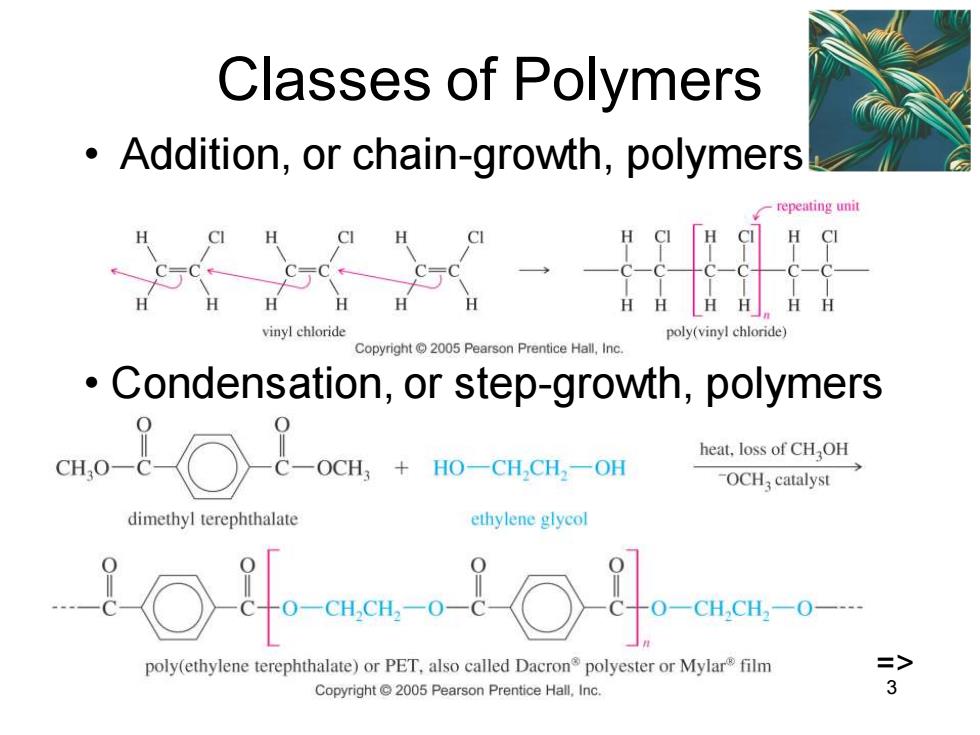
Classes of Polymers Addition,or chain-growth,polymers epeating unit H CI a.a vinyl chloride poly(vinyl chloride) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Condensation,or step-growth,polymers eHo-8-○&-+o-Gual-0m heat,loss of CHOH -OCH catalyst dimethyl terephthalate ethylene glycol 110-10 -CH,CH2O-- poly(ethylene terephthalate)or PET,also called Dacron polyester or Mylar film => Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 26 3 Classes of Polymers • Addition, or chain-growth, polymers • Condensation, or step-growth, polymers =>

Addition Polymers Three kinds of intermediates: >Free radicals >Carbocations >Carbanions ● Examples of addition polymers: >polypropylene plastics >polystyrene foam insulation >poly(acrylonitrile)Orlon fiber >poly(methyl a-methacrylate) Plexiglas. Chapter 26
Chapter 26 4 Addition Polymers • Three kinds of intermediates: ➢Free radicals ➢Carbocations ➢Carbanions • Examples of addition polymers: ➢polypropylene plastics ➢polystyrene foam insulation ➢poly(acrylonitrile) Orlon® fiber ➢poly(methyl -methacrylate) Plexiglas ® =>
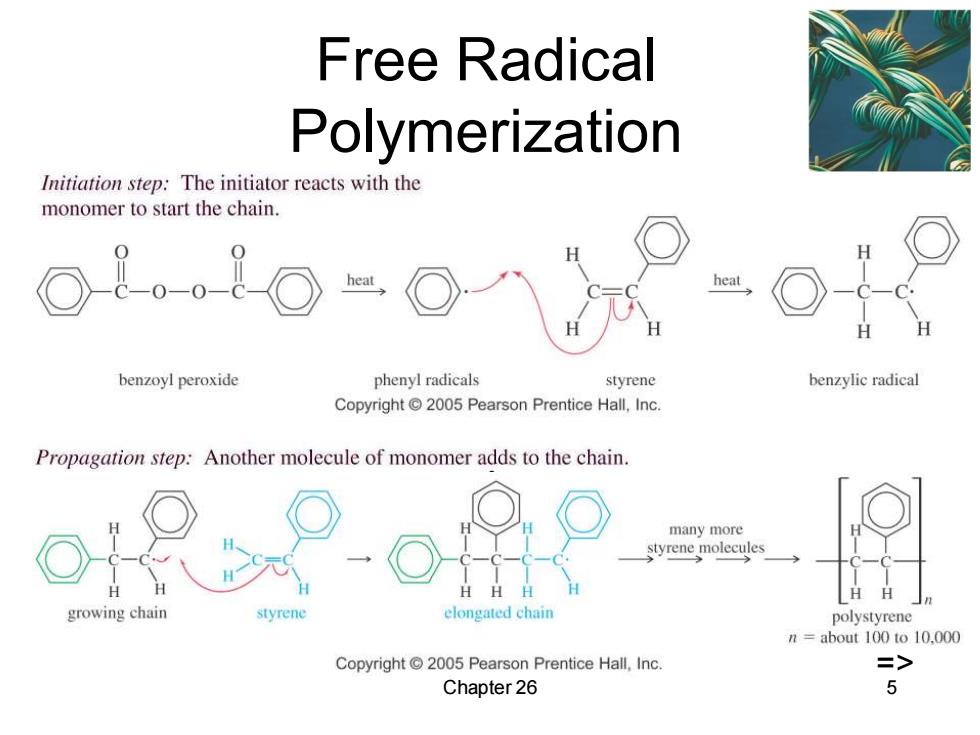
Free Radical Polymerization Initiation step:The initiator reacts with the monomer to start the chain. heat benzoyl peroxide phenyl radicals styrene benzylic radical Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. many more styrene molecules H growing chain styrene elongated chain polystyrene n=about 100 to 10.000 Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 26 5
Chapter 26 5 Free Radical Polymerization =>
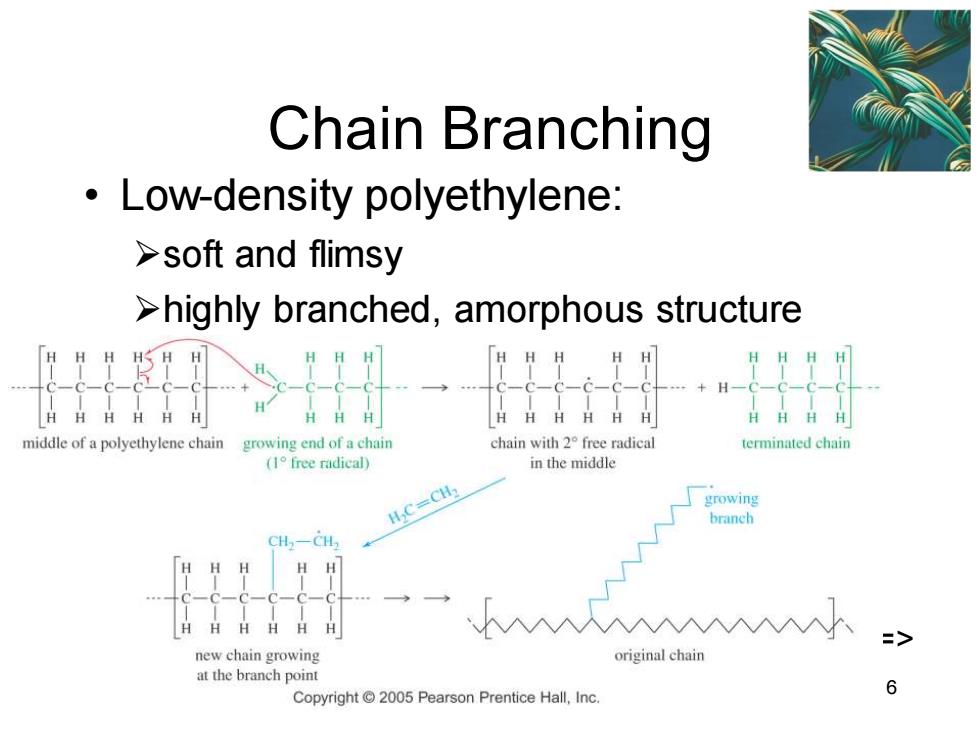
Chain Branching Low-density polyethylene: >soft and flimsy >highly branched,amorphous structure middle of a polyethylene chain growing end of a chain chain with 2 free radical terminated chain (1 free radical) in the middle H,C=CH2 growing branch CH2一CH new chain growing original chain at the branch point 6 Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 26 6 Chain Branching • Low-density polyethylene: ➢soft and flimsy ➢highly branched, amorphous structure =>
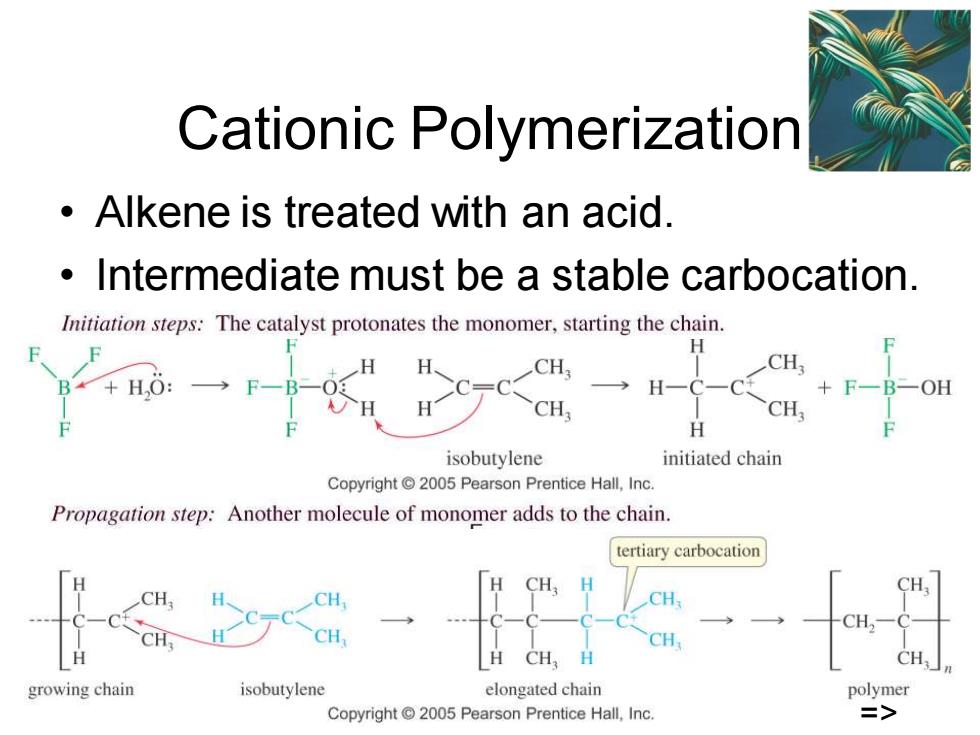
Cationic Polymerization Alkene is treated with an acid. Intermediate must be a stable carbocation. Initiation steps:The catalyst protonates the monomer,starting the chain. H CH, CH B*+HO: +F一B一OE CH. CH H isobutylene initiated chain Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. tertiary carbocation CH CH CH CH CH H CH,H CH. growing chain isobutylene elongated chain polymer Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. 三>
Chapter 26 7 Cationic Polymerization • Alkene is treated with an acid. • Intermediate must be a stable carbocation. =>
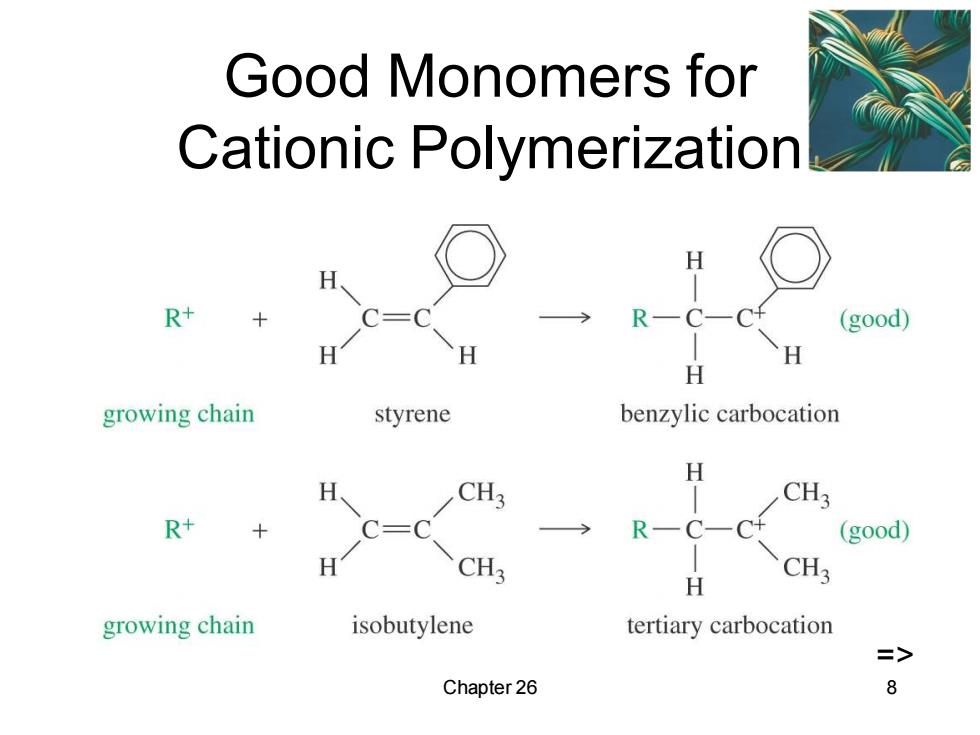
Good Monomers for Cationic Polymerization H R+ R—C-C (good) H growing chain styrene benzylic carbocation H CH3 CH3 R+ C= R一C一 (good) CH3 CH3 H growing chain isobutylene tertiary carbocation => Chapter 26 8
Chapter 26 8 Good Monomers for Cationic Polymerization =>
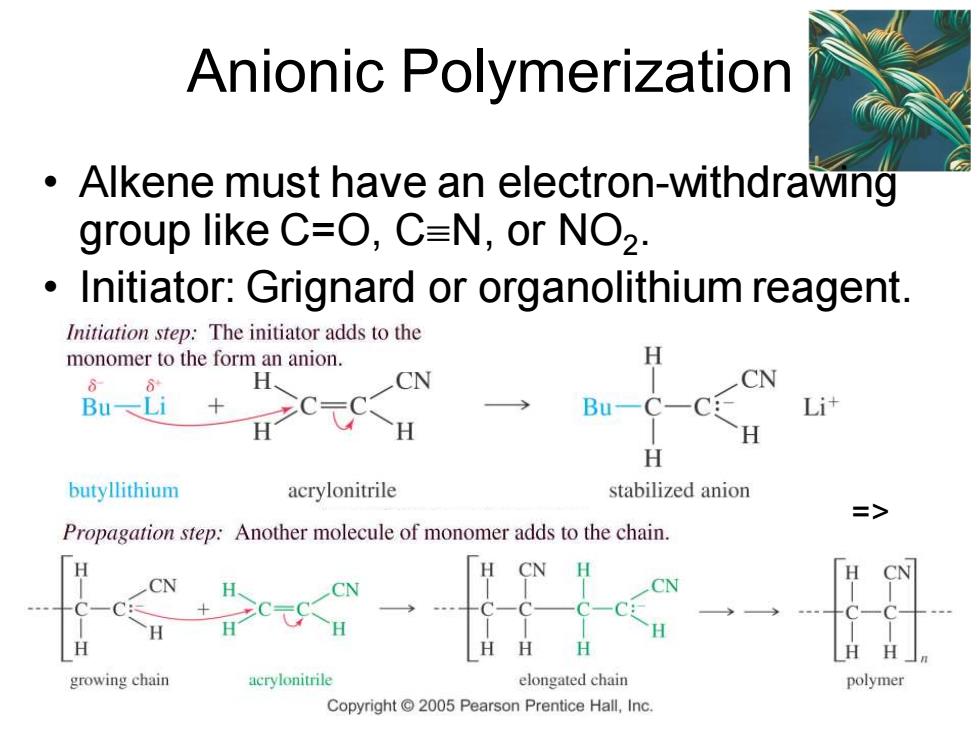
Anionic Polymerization Alkene must have an electron-withdrawing group like C=O,C=N,or NO2. Initiator:Grignard or organolithium reagent. Initiation step:The initiator adds to the monomer to the form an anion. H、 CN CN Bu-Li Bu- H H butyllithium acrylonitrile stabilized anion 三> Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. H growing chain acrylonitrile elongated chain polymer Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 26 9 Anionic Polymerization • Alkene must have an electron-withdrawing group like C=O, CN, or NO2 . • Initiator: Grignard or organolithium reagent. =>

Stereochemistry An isotactic polymer(side groups on the same side of the backbone) A syndiotactic polymer (side groups on alternating sides of the backbone) R An atactic polymer (side groups on random sides of the backbone) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 26 10
Chapter 26 10 Stereochemistry =>