
Organic Chemistry,5th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry,and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Definitions Conjugated double bonds are separated by one single bond.Example:1,3-pentadiene. Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds.1,4-pentadiene. Cumulated double bonds are on adjacent carbons.Example:1,2-pentadiene. 二> Chaper 15 2
Chaper 15 2 Definitions • Conjugated double bonds are separated by one single bond. Example: 1,3-pentadiene. • Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds. 1,4-pentadiene. • Cumulated double bonds are on adjacent carbons. Example: 1,2-pentadiene. =>
Resonance Energy Heat of hydrogenation for trans-1,3- pentadiene is less than expected. ·△Hfor1-pentene is30.0kcal/mol and for trans-2-pentene is 27.4 kcal/mol,so expect 57.4 kcal for trans-1,3-pentadiene. ·Actual△His53.7kcal,so the conjugated diene is more stable. Difference,(57.4-53.7)3.7 kcal/mol,is the resonance energy. => Chaper 15 3
Chaper 15 3 Resonance Energy • Heat of hydrogenation for trans-1,3- pentadiene is less than expected. • H for 1-pentene is 30.0 kcal/mol and for trans-2-pentene is 27.4 kcal/mol, so expect 57.4 kcal for trans-1,3-pentadiene. • Actual H is 53.7 kcal, so the conjugated diene is more stable. • Difference, (57.4 – 53.7) 3.7 kcal/mol, is the resonance energy. =>
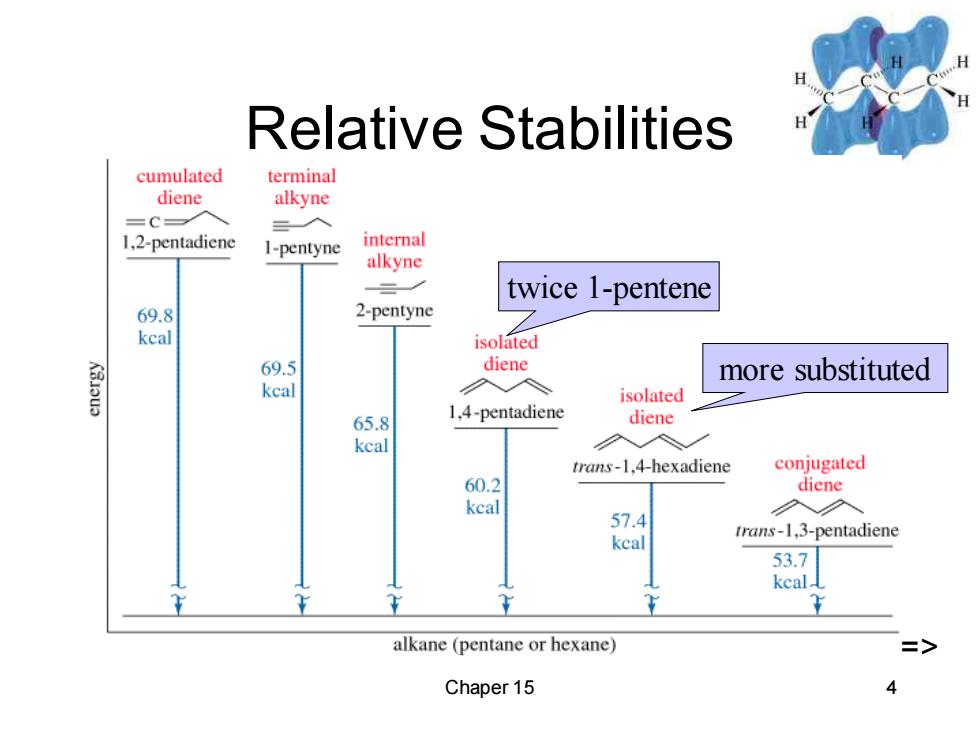
Relative Stabilities cumulated terminal diene alkyne =C- 入 1,2-pentadiene 1I-pentyne internal alkyne twice 1-pentene 69.8 2-pentyne kcal isolated 69.5 diene more substituted kcal isolated 65.8 1,4-pentadiene diene kcal trans-1,4-hexadiene conjugated 60.2 diene keal 57.4 trans-1,3-pentadiene kcal 53.7 kcal alkane (pentane or hexane) Chaper 15 4
Chaper 15 4 Relative Stabilities twice 1-pentene more substituted =>
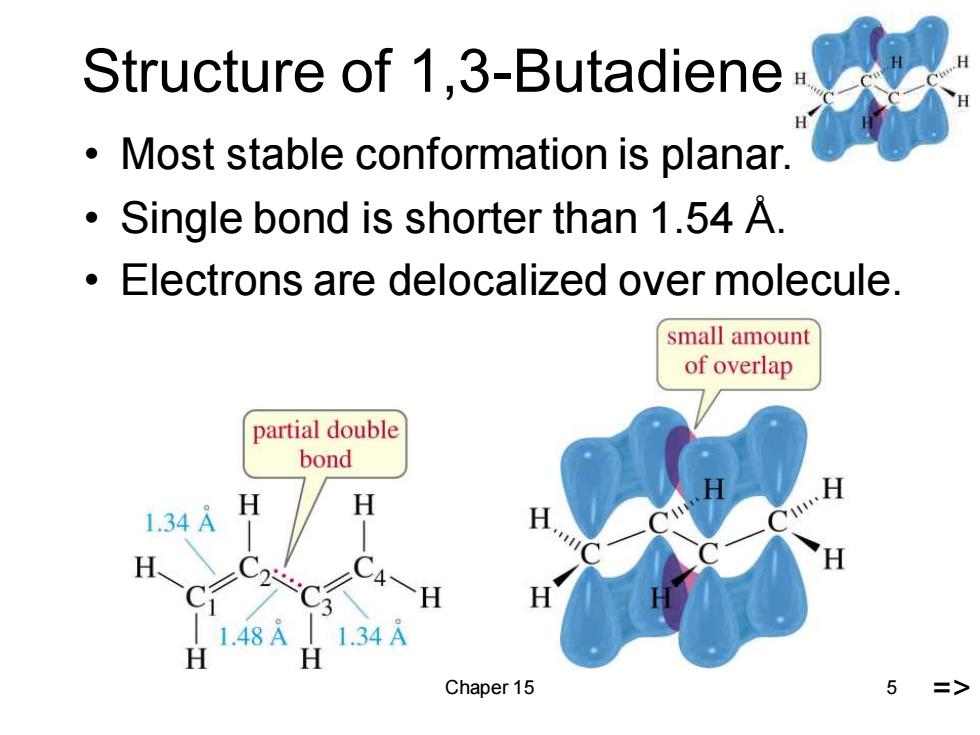
Structure of 1,3-Butadiene Most stable conformation is planar. Single bond is shorter than 1.54 A. Electrons are delocalized over molecule. small amount of overlap partial double bond 1.34A H H 1.48A 11.34A H Chaper 15 5
Chaper 15 5 Structure of 1,3-Butadiene • Most stable conformation is planar. • Single bond is shorter than 1.54 Å. • Electrons are delocalized over molecule. =>
Constructing Molecular Orbitals Pi molecular orbitals are the sideways overlap of p orbitals. p orbitals have 2 lobes.Plus (+)and minus (-)indicate the opposite phases of the wave function,not electrical charge. When lobes overlap constructively,(and +or-and-)a bonding MO is formed. When and-lobes overlap,waves cancel out and a node forms;antibonding MO.= Chaper 15 6
Chaper 15 6 Constructing Molecular Orbitals • Pi molecular orbitals are the sideways overlap of p orbitals. • p orbitals have 2 lobes. Plus (+) and minus (-) indicate the opposite phases of the wave function, not electrical charge. • When lobes overlap constructively, (+ and +, or - and -) a bonding MO is formed. • When + and - lobes overlap, waves cancel out and a node forms; antibonding MO. =>
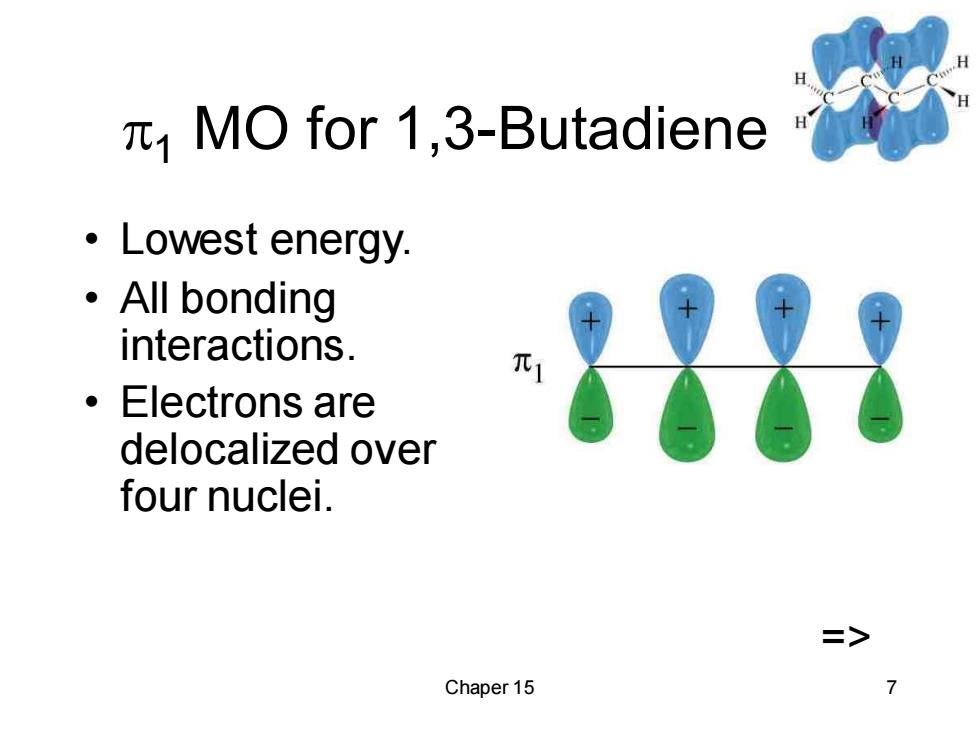
MO for 1,3-Butadiene ·Lowest energy. ·All bonding interactions. ·Electrons are delocalized over four nuclei. > Chaper 15
Chaper 15 7 1 MO for 1,3-Butadiene • Lowest energy. • All bonding interactions. • Electrons are delocalized over four nuclei. =>

2 MO for 1,3-Butadiene 。2 bonding interactions 。1 antibonding interaction ·A bonding MO => Chaper 15 8
Chaper 15 8 2 MO for 1,3-Butadiene • 2 bonding interactions • 1 antibonding interaction • A bonding MO =>
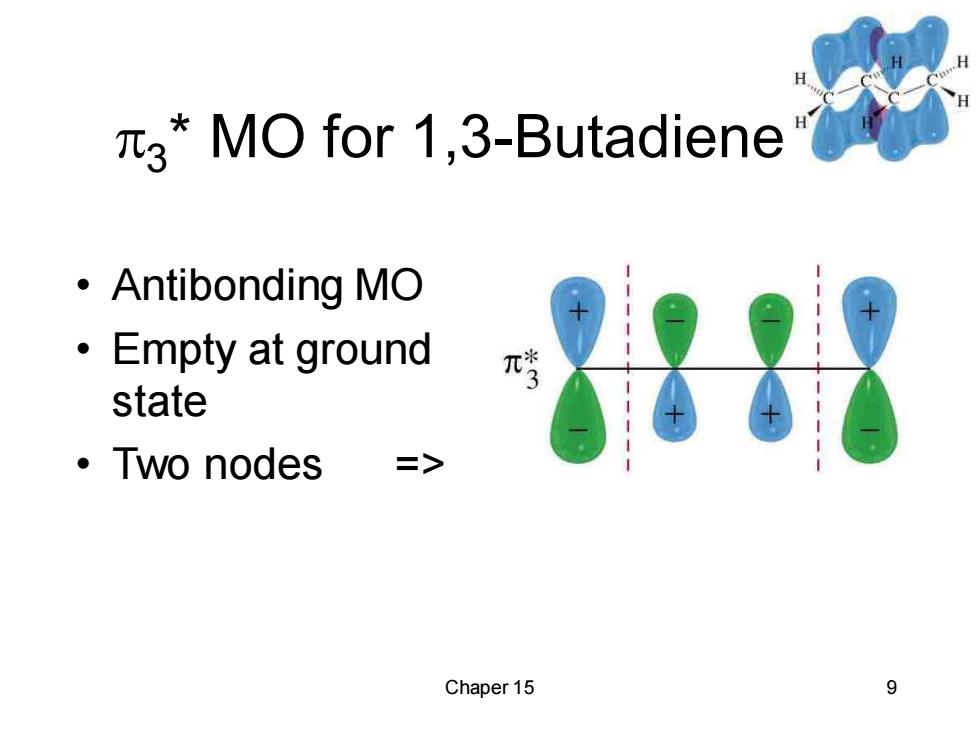
3*MO for 1,3-Butadiene ·Antibonding MO ·Empty at ground π state ·Two nodes => Chaper 15 9
Chaper 15 9 3 * MO for 1,3-Butadiene • Antibonding MO • Empty at ground state • Two nodes =>
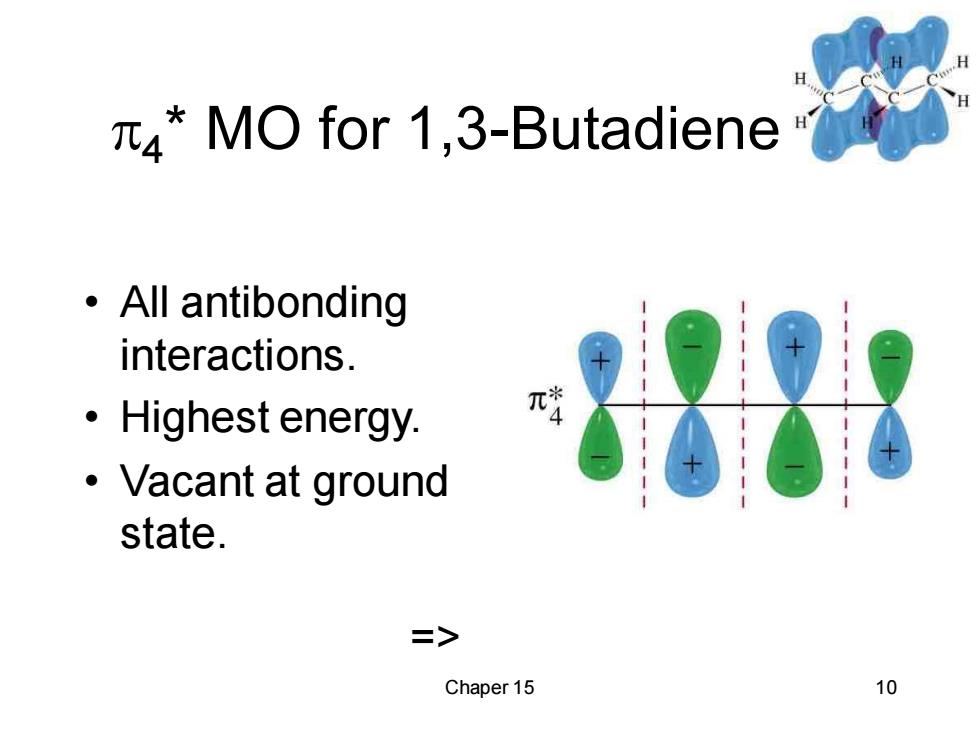
4*MO for 1,3-Butadiene ·All antibonding interactions. 刘 ·Highest energy. ·Vacant at ground state. 二> Chaper 15 10
Chaper 15 10 4 * MO for 1,3-Butadiene • All antibonding interactions. • Highest energy. • Vacant at ground state. =>