
Organic Chemistry,5th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 9 Alkynes Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 9 Alkynes Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

H Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is CnH2n-2 Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. Some reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions are specific to alkynes. 三> Chapter9 2
Chapter 9 2 Introduction • Alkynes contain a triple bond. • General formula is CnH2n-2 • Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. • Some reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. • Some reactions are specific to alkynes. =>
Nomenclature:IUPAC Find the longest chain containing the triple bond. Change -ane ending to -yne. Number the chain,starting at the end closest to the triple bond. Give branches or other substituents a number to locate their position. => Chapter 9 3
Chapter 9 3 Nomenclature: IUPAC • Find the longest chain containing the triple bond. • Change -ane ending to -yne. • Number the chain, starting at the end closest to the triple bond. • Give branches or other substituents a number to locate their position. =>
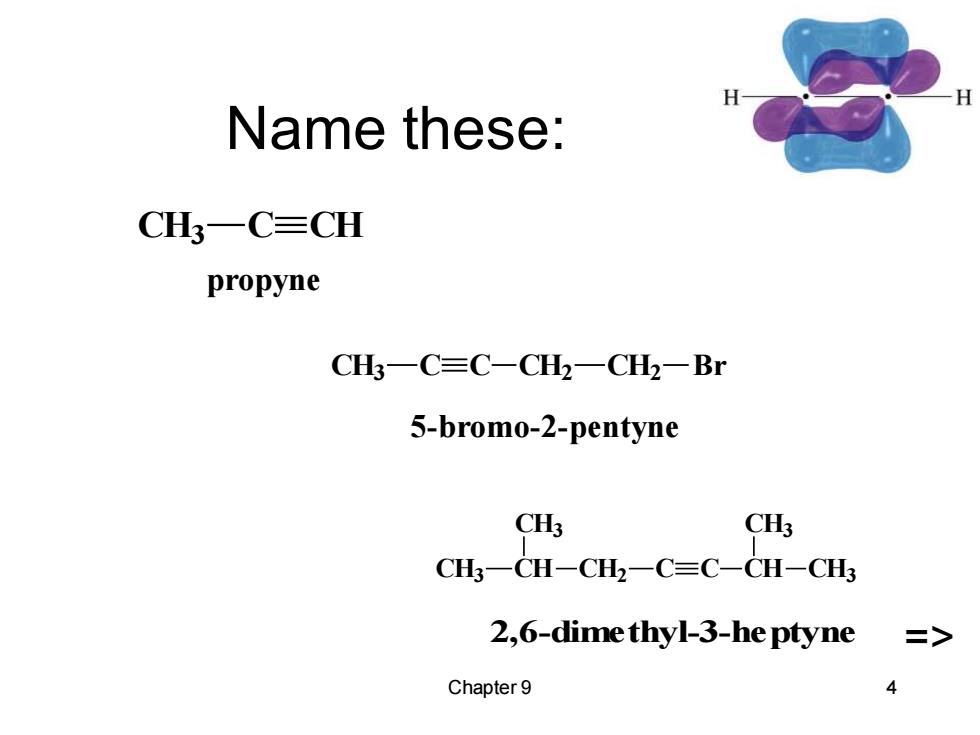
H Name these: CH3一C≡CH propyne CH一C=C-CH一CH一Br 5-bromo-2-pentyne CH3 CH3 CH3一CH一CH一C=C-CH-CH 2,6-dime thyl-3-he ptyne > Chapter 9 4
Chapter 9 4 Name these: CH3 CH CH3 CH2 C C CH CH3 CH3 CH3 C C CH2 CH2 Br CH3 C CH propyne 5-bromo-2-pentyne 2,6-dimethyl-3-heptyne =>

Additional Functional H Groups All other functional groups,except ethers and halides have a higher priority than alkynes. For a complete list of naming priorities, look inside the back cover of your text. => Chapter 9 5
Chapter 9 5 Additional Functional Groups • All other functional groups, except ethers and halides have a higher priority than alkynes. • For a complete list of naming priorities, look inside the back cover of your text. =>
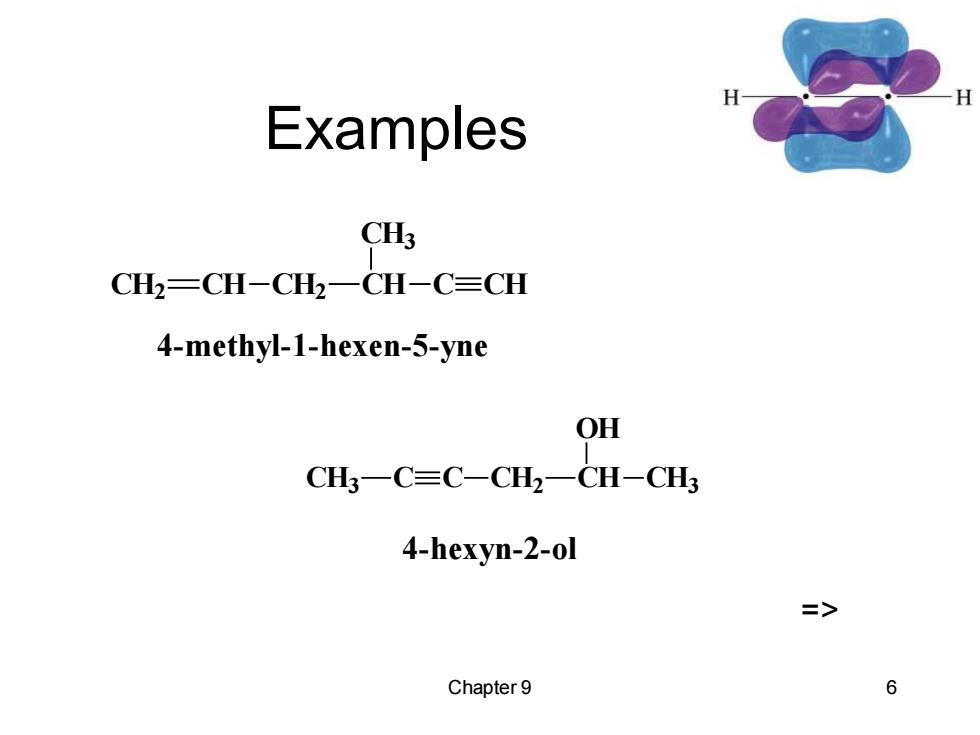
Examples C CH2-CH-CH2-CH-C=CH 4-methyl-1-hexen-5-yne OH CH3一C=C-CH2一CH-CH3 4-hexyn-2-ol 3> Chapter 9 6
Chapter 9 6 Examples CH2 CH CH2 CH CH3 C CH 4-methyl-1-hexen-5-yne CH3 C C CH2 CH OH CH3 4-hexyn-2-ol =>
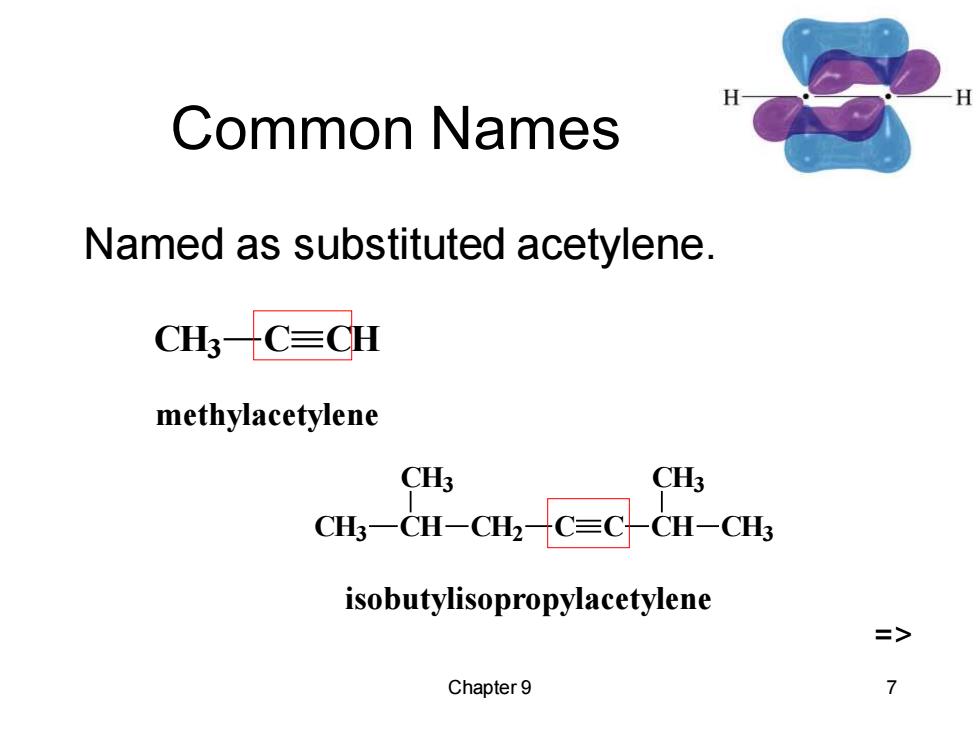
Common Names Named as substituted acetylene. CH3-C=CH methylacetylene CH3 CH3 CH;-CH-CH2-C=CCH-CH3 isobutylisopropylacetylene Chapter 9
Chapter 9 7 Common Names Named as substituted acetylene. CH3 C CH methylacetylene CH3 CH CH3 CH2 C C CH CH3 CH3 isobutylisopropylacetylene =>

Physical Properties Nonpolar,insoluble in water. Soluble in most organic solvents. Boiling points similar to alkane of same size. Less dense than water. Up to 4 carbons,gas at room temperature. 二> Chapter9 8
Chapter 9 8 Physical Properties • Nonpolar, insoluble in water. • Soluble in most organic solvents. • Boiling points similar to alkane of same size. • Less dense than water. • Up to 4 carbons, gas at room temperature. =>

Acetylene Acetylene is used in welding torches. In pure oxygen,temperature of flame reaches 2800C. It would violently decompose to its elements,but the cylinder on the torch contains crushed firebrick wet with acetone to moderate it. > Chapter 9 9
Chapter 9 9 Acetylene • Acetylene is used in welding torches. • In pure oxygen, temperature of flame reaches 2800C. • It would violently decompose to its elements, but the cylinder on the torch contains crushed firebrick wet with acetone to moderate it. =>
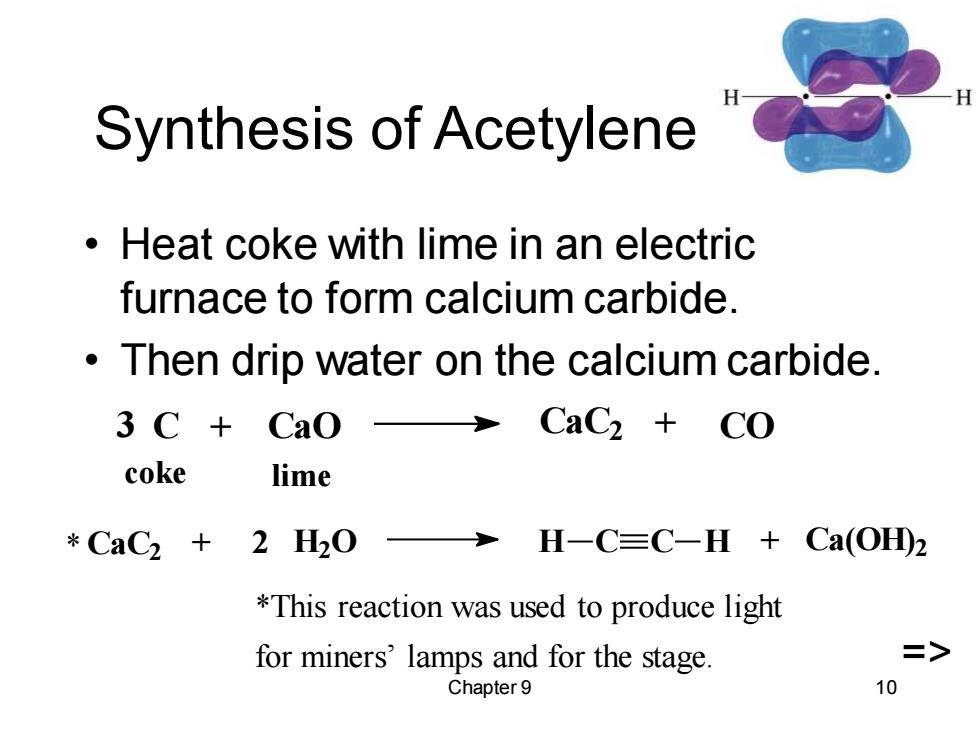
Synthesis of Acetylene Heat coke with lime in an electric furnace to form calcium carbide. Then drip water on the calcium carbide. 3 C+CaO CaC2+CO coke lime *CaC2+2H20> H-C≡C-H+Ca(OHD2 *This reaction was used to produce light for miners'lamps and for the stage => Chapter 9 10
Chapter 9 10 Synthesis of Acetylene • Heat coke with lime in an electric furnace to form calcium carbide. • Then drip water on the calcium carbide. CaC2 + 2 H2O H C C H + Ca(OH) 2 3 C + CaO CaC2 + CO coke lime *This reaction was used to produce light for miners’ lamps and for the stage. => *