
Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 1 Introduction and Review Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 1 1
Chapter 1 1 Chapter 1 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Introduction and Review

Organic Chemistry HHS.CHa CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CONH- S6H50 CH3 COONa H5C6 N H OH HO 2-Pentenylpenicillin CH3O H5C6 0= CH3 NCH3 Taxol HO Codeine Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. Chapter 1 2
Chapter 1 2 Organic Chemistry • Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. H5C6 N H O O C6H5 OH O O O O OH O O O CH3 O O H5C6 HO Taxol O CH3O H NCH3 HO Codeine 2-Pentenylpenicillin N S CHCH2CONH H H O CH3 CH3 COONa CH3CH2CH

Electronic Structure of the Atom ·An atom has a dense, positively charged electron density nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons distance -distance from the The electron density is nucleus highest at the nucleus nucleus and drops off exponentially with increasing distance from the nucleus in any direction. Chapter 1 3
Chapter 1 3 Electronic Structure of the Atom • An atom has a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons. • The electron density is highest at the nucleus and drops off exponentially with increasing distance from the nucleus in any direction
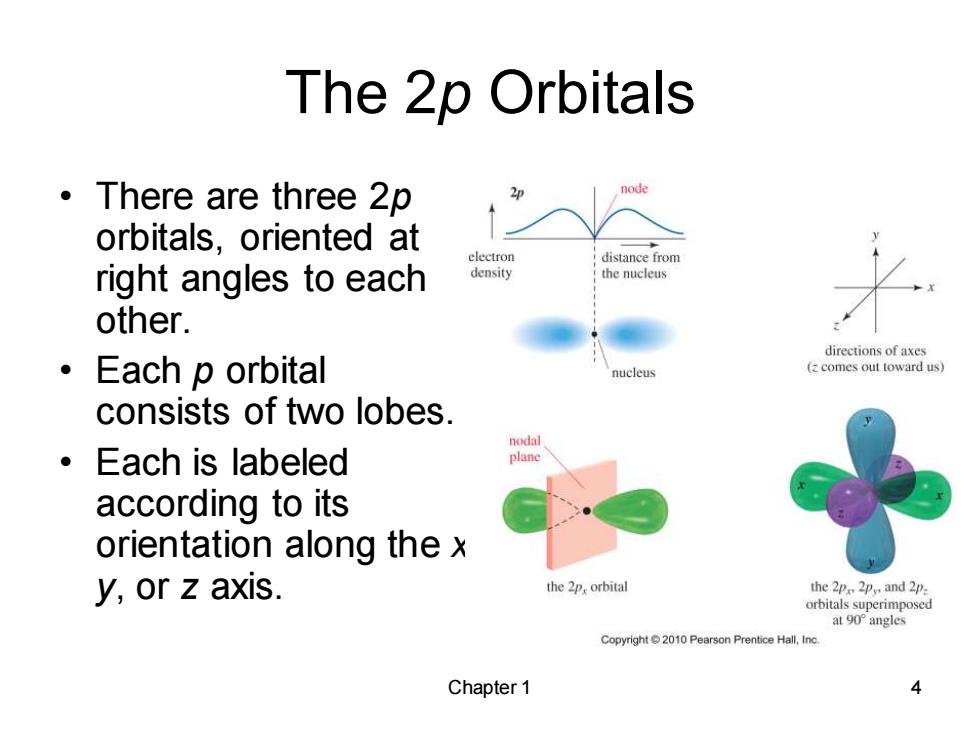
The 2p Orbitals 。There are three2p orbitals,oriented at electron distance from right angles to each density the nucleus other. directions of axes 。 Each p orbital nucleus (z comes out toward us) consists of two lobes. nodal 。Each is labeled plane according to its orientation along the x y,or z axis. the 2p,orbital the 2p 2py and 2p. orbitals superimposed at 90 angles Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 1
Chapter 1 4 The 2p Orbitals • There are three 2p orbitals, oriented at right angles to each other. • Each p orbital consists of two lobes. • Each is labeled according to its orientation along the x, y, or z axis
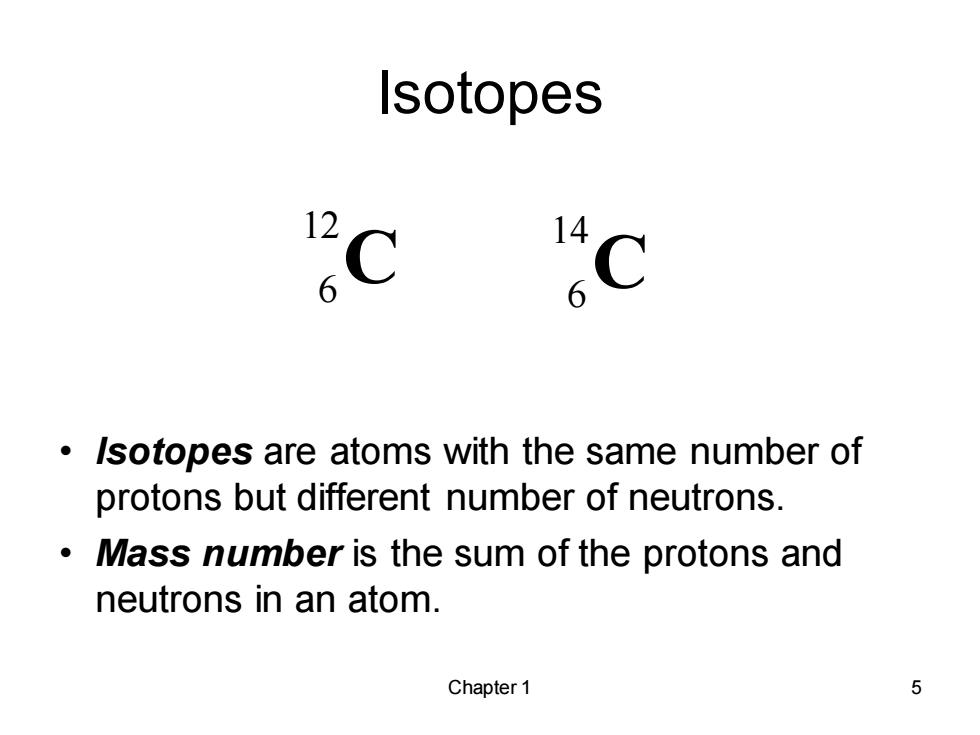
Isotopes 12 14 6 C Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. Chapter 1 5
Chapter 1 5 Isotopes • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. • Mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. C 12 6 6 C 14

Electronic Configurations of Atoms Valence electrons are electrons on the outermost shell of the atom. TABLE 1-1 Electronic Configurations of the Elements of the First and Second Rows Element Configuration Valence Electrons H l 1 He 1s2 2 Li 1s22J 1 Be 1s222 2 B 1s22s22p 3 C 1s2222p2py 4 N 1s2222p2p2p 5 0 1s22s22p22p2p 6 1s22s22p22p32p Ne 1s22s22p22p2p 8 Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 1 6
Chapter 1 6 Electronic Configurations of Atoms • Valence electrons are electrons on the outermost shell of the atom

Electronic Configurations The aufbau principle Relative orbital energies states to fill the lowest 12px 12p -2p. energy orbitals first. Hund's rule states that energy when there are two or more orbitals of the same energy 1s (degenerate),electrons will go into different orbitals Electronic configuration of carbon rather than pairing up in the same orbital. Chapter 1 7
Chapter 1 7 Electronic Configurations • The aufbau principle states to fill the lowest energy orbitals first. • Hund’s rule states that when there are two or more orbitals of the same energy (degenerate), electrons will go into different orbitals rather than pairing up in the same orbital. Electronic configuration of carbon

lonic Bonding ·To obtain a noble gas configuration (a full valence shell),atoms may transfer electrons from one atom to Na+:CI another. The atoms,now bearing opposite charges,stay ionic bond together by electrostatic attraction. Chapter 1 8
Chapter 1 8 Ionic Bonding • To obtain a noble gas configuration (a full valence shell), atoms may transfer electrons from one atom to another. • The atoms, now bearing opposite charges, stay together by electrostatic attraction
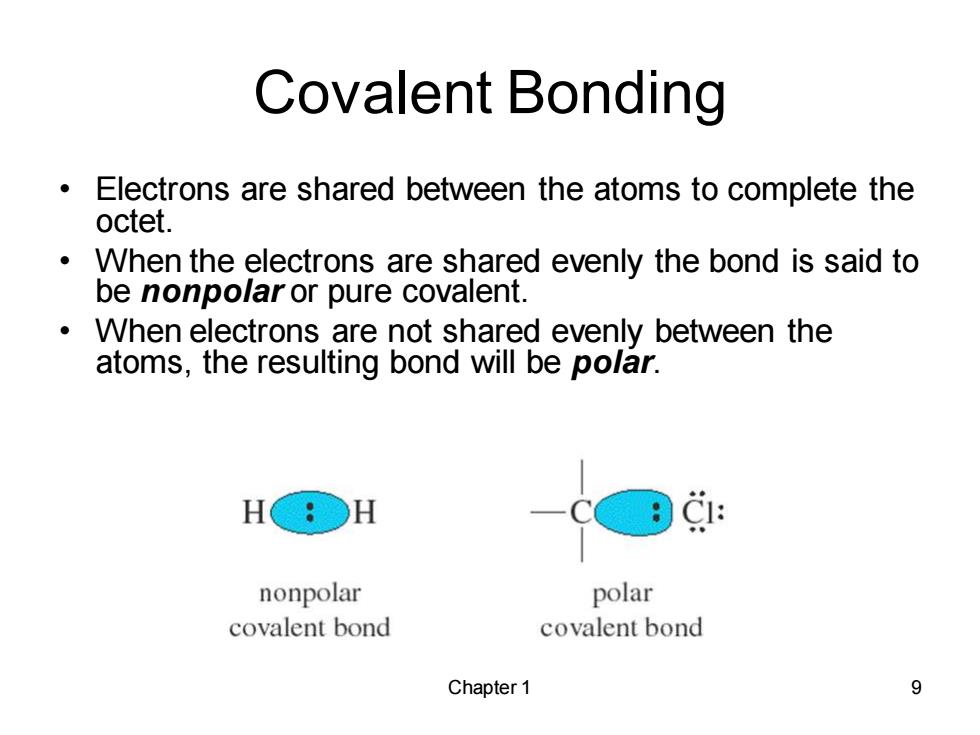
Covalent Bonding Electrons are shared between the atoms to complete the octet. When the electrons are shared evenly the bond is said to be nonpolar or pure covalent. When electrons are not shared evenly between the atoms,the resulting bond will be polar. H&○H C1: nonpolar polar covalent bond covalent bond Chapter 1 9
Chapter 1 9 Covalent Bonding • Electrons are shared between the atoms to complete the octet. • When the electrons are shared evenly the bond is said to be nonpolar or pure covalent. • When electrons are not shared evenly between the atoms, the resulting bond will be polar
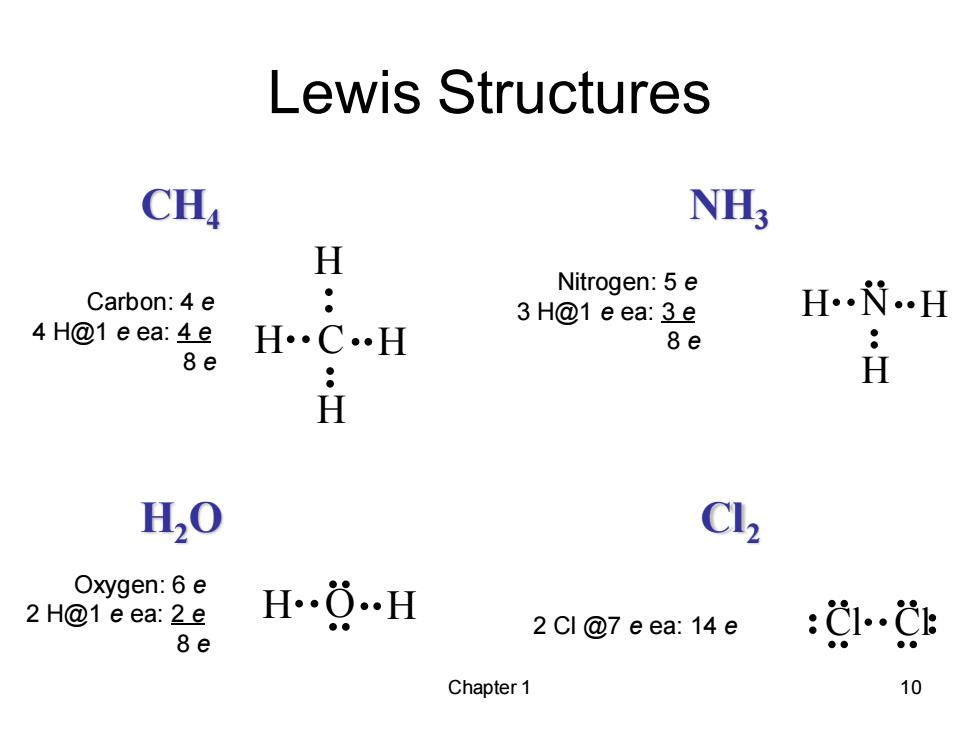
Lewis Structures CH4 NH; H Carbon:4 e ● Nitrogen:5 e 3 H@1 eea:3e H H 4H@1 eea:4e H 8e 8e H H H20 Cl2 Oxygen:6 e 2 H@1 e ea:2e HO…H 2 Cl @7 e ea:14e 8e :g…g Chapter 1 10
Chapter 1 10 CH4 NH3 H2O Cl2 Lewis Structures C H H H H N H H H H O H Cl Cl Carbon: 4 e 4 H@1 e ea: 4 e 8 e Nitrogen: 5 e 3 H@1 e ea: 3 e 8 e Oxygen: 6 e 2 H@1 e ea: 2 e 8 e 2 Cl @7 e ea: 14 e