
POCH-c CH Organic Chemistry,7th Edition COOH L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 21 Part 1:Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 21 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Part 1: Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives

Acid Derivatives R-C-X R& 0-R R-C-NH R-CN acid halide anhydride ester amide nitrile Condensed structure:RCOX (RCO)O RCO,R' RCONH, RCN Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. All the derivatives can be converted to the carboxylic acid by acidic or basic hydrolysis Esters and amides are commonly found in nature. Chapter 21 2
Chapter 21 2 Acid Derivatives ▪ All the derivatives can be converted to the carboxylic acid by acidic or basic hydrolysis. ▪ Esters and amides are commonly found in nature

Esters from Carboxylic Acids R一COH+ R'-OH R-C-O-R'+H,O acid alcohol ester Esters can be made from the carboxylic acid through the Fischer esterification. Excess alcohol is used to drive the equilibrium toward the ester. Chapter 21 3
Chapter 21 3 Esters from Carboxylic Acids ▪ Esters can be made from the carboxylic acid through the Fischer esterification. ▪ Excess alcohol is used to drive the equilibrium toward the ester
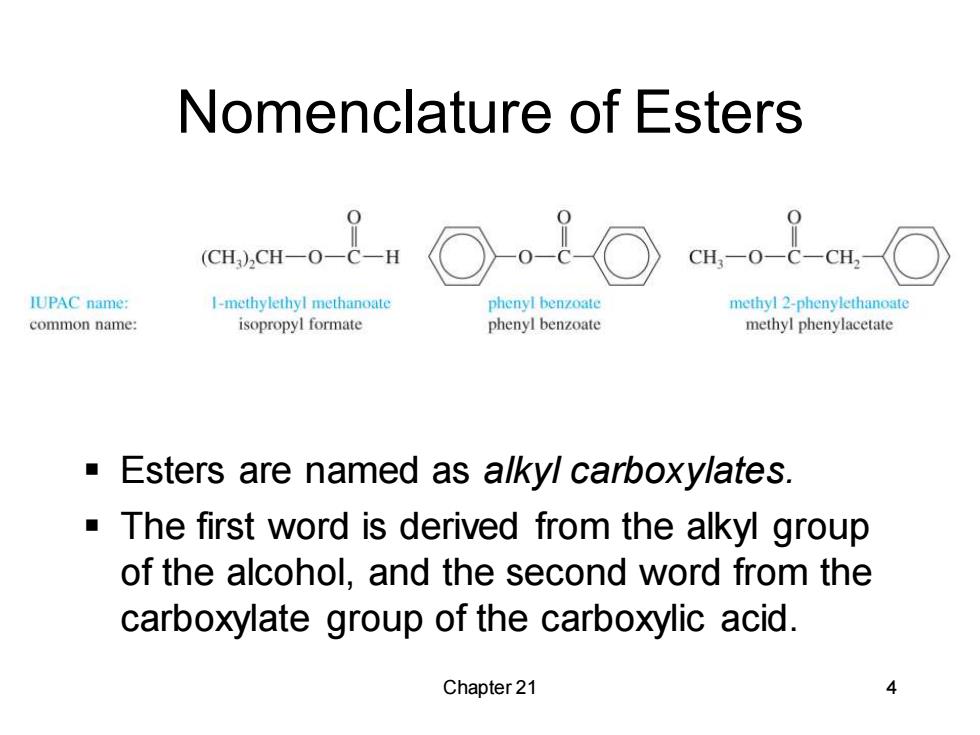
Nomenclature of Esters (CH)2CH一O CH,-0-C-CH,- IUPAC name: 1-methylethyl methanoate phenyl benzoate methyl 2-phenylethanoate common name: isopropyl formate phenyl benzoate methyl phenylacetate ▣ Esters are named as alkyl carboxylates. The first word is derived from the alkyl group of the alcohol,and the second word from the carboxylate group of the carboxylic acid. Chapter 21
Chapter 21 4 Nomenclature of Esters ▪ Esters are named as alkyl carboxylates. ▪ The first word is derived from the alkyl group of the alcohol, and the second word from the carboxylate group of the carboxylic acid
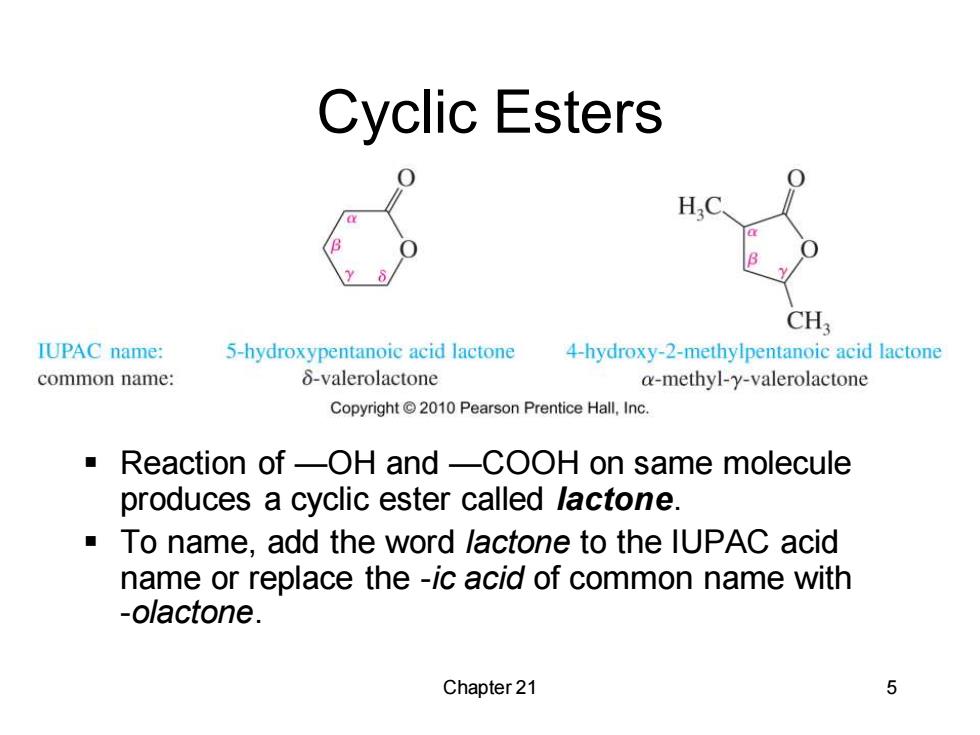
Cyclic Esters H,C CH3 IUPAC name: 5-hydroxypentanoic acid lactone 4-hydroxy-2-methylpentanoic acid lactone common name: 8-valerolactone a-methyl-y-valerolactone Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Reaction of-OH and-COOH on same molecule produces a cyclic ester called lactone. To name,add the word lactone to the IUPAC acid name or replace the -ic acid of common name with -olactone. Chapter 21 5
Chapter 21 5 Cyclic Esters ▪ Reaction of —OH and —COOH on same molecule produces a cyclic ester called lactone. ▪ To name, add the word lactone to the IUPAC acid name or replace the -ic acid of common name with -olactone
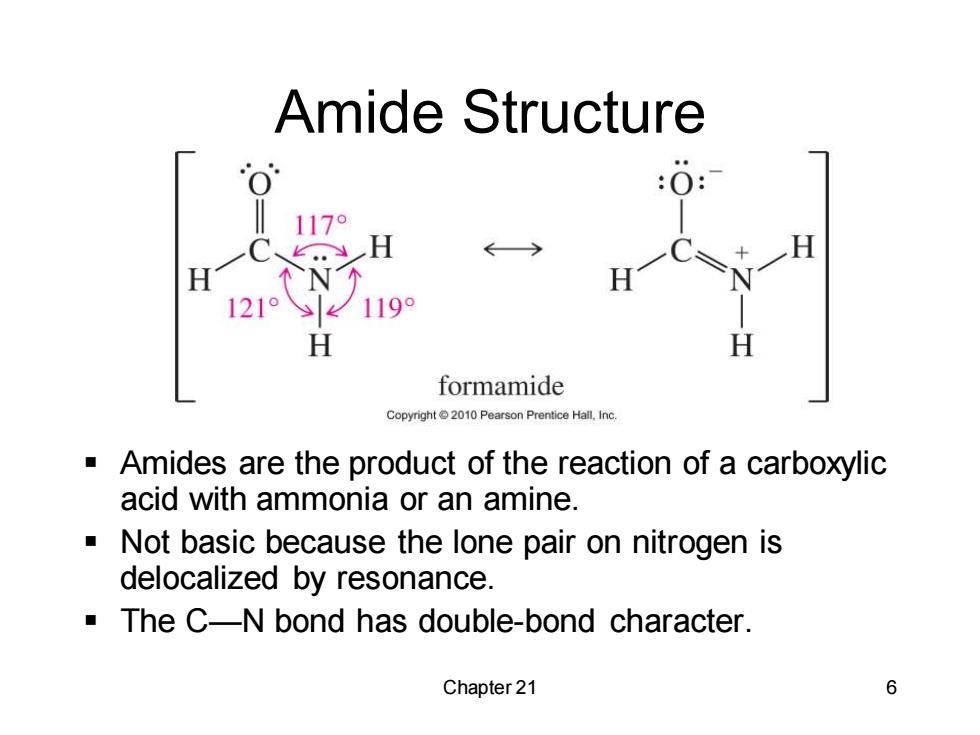
Amide Structure :O: 1179 、,H ←> H N H 121° 119 H H formamide Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc Amides are the product of the reaction of a carboxylic acid with ammonia or an amine. Not basic because the lone pair on nitrogen is delocalized by resonance. The C-N bond has double-bond character. Chapter 21 6
Chapter 21 6 Amide Structure ▪ Amides are the product of the reaction of a carboxylic acid with ammonia or an amine. ▪ Not basic because the lone pair on nitrogen is delocalized by resonance. ▪ The C—N bond has double-bond character
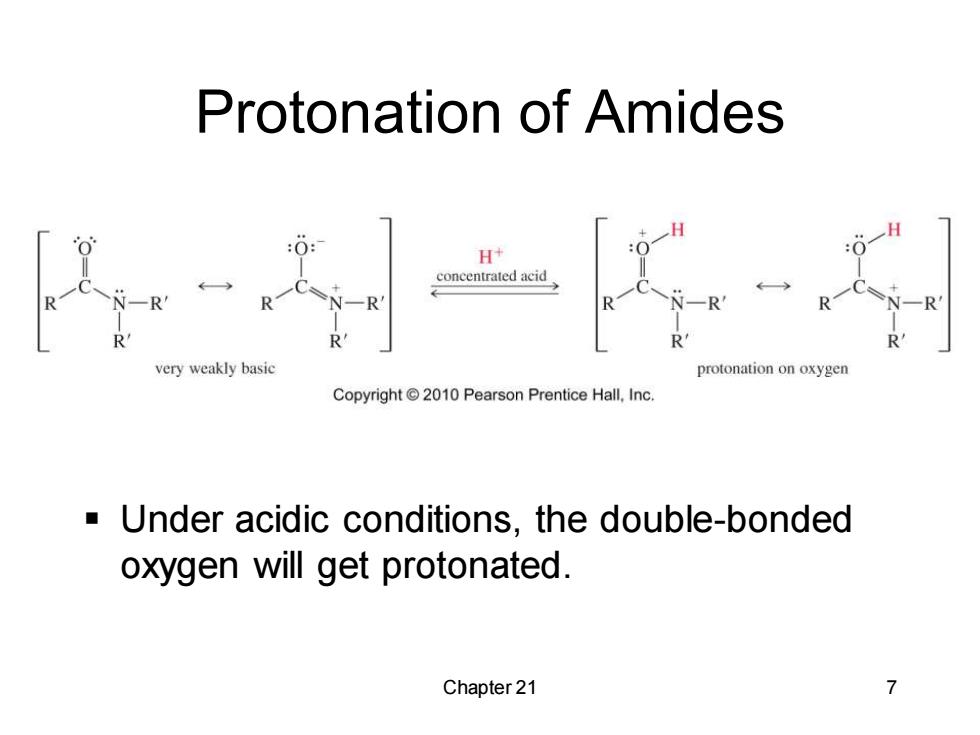
Protonation of Amides H+ concentrated acid N一R very weakly basic protonation on oxygen Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc -Under acidic conditions,the double-bonded oxygen will get protonated. Chapter 21 7
Chapter 21 7 Protonation of Amides ▪ Under acidic conditions, the double-bonded oxygen will get protonated
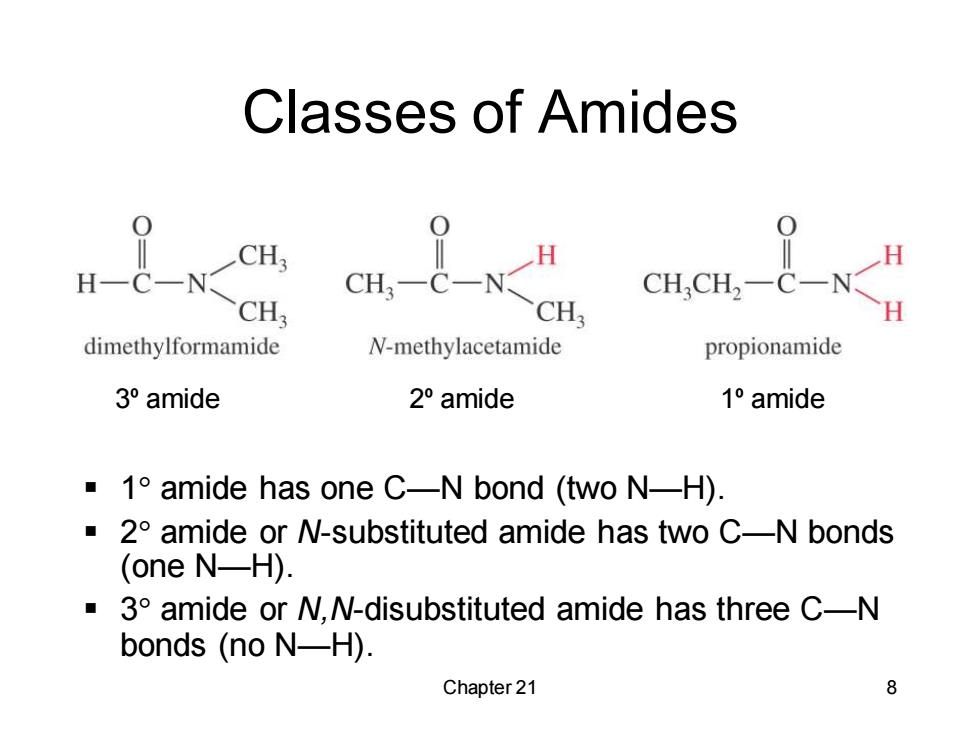
Classes of Amides 0 CH3 H H-C-N CH3-C-N CHCH2-C-N CH: CH dimethylformamide N-methylacetamide propionamide 3°amide 2°amide 1°amide 1 amide has one C-N bond (two N-H). 2 amide or N-substituted amide has two C-N bonds (one N-H). 3 amide or N,N-disubstituted amide has three C-N bonds (no N-H). Chapter 21 8
Chapter 21 8 Classes of Amides ▪ 1 amide has one C—N bond (two N—H). ▪ 2 amide or N-substituted amide has two C—N bonds (one N—H). ▪ 3 amide or N,N-disubstituted amide has three C—N bonds (no N—H). 3º amide 2º amide 1º amide
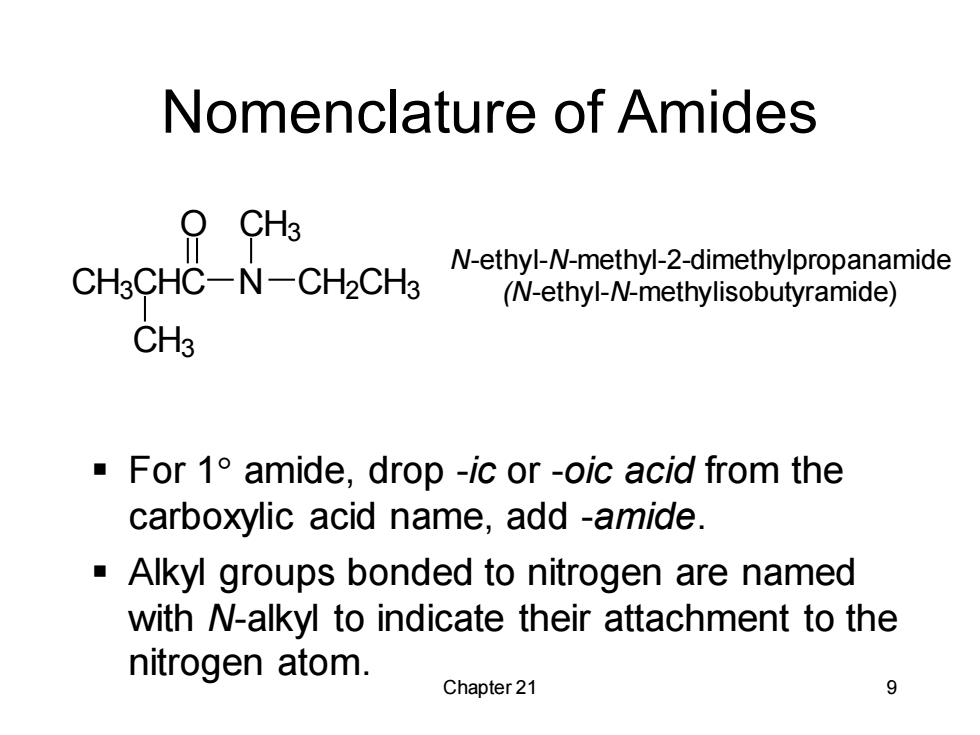
Nomenclature of Amides CH3 N-ethyl-N-methyl-2-dimethylpropanamide CH3CHC-N-CH2CH3 (N-ethyl-N-methylisobutyramide) CH3 For 1 amide,drop -ic or -oic acid from the carboxylic acid name,add -amide. Alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen are named with N-alkyl to indicate their attachment to the nitrogen atom. Chapter 21 9
Chapter 21 9 Nomenclature of Amides ▪ For 1 amide, drop -ic or -oic acid from the carboxylic acid name, add -amide. ▪ Alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen are named with N-alkyl to indicate their attachment to the nitrogen atom. N-ethyl-N-methyl-2-dimethylpropanamide CH3CHC N (N-ethyl-N-methylisobutyramide) O CH2CH3 CH3 CH3
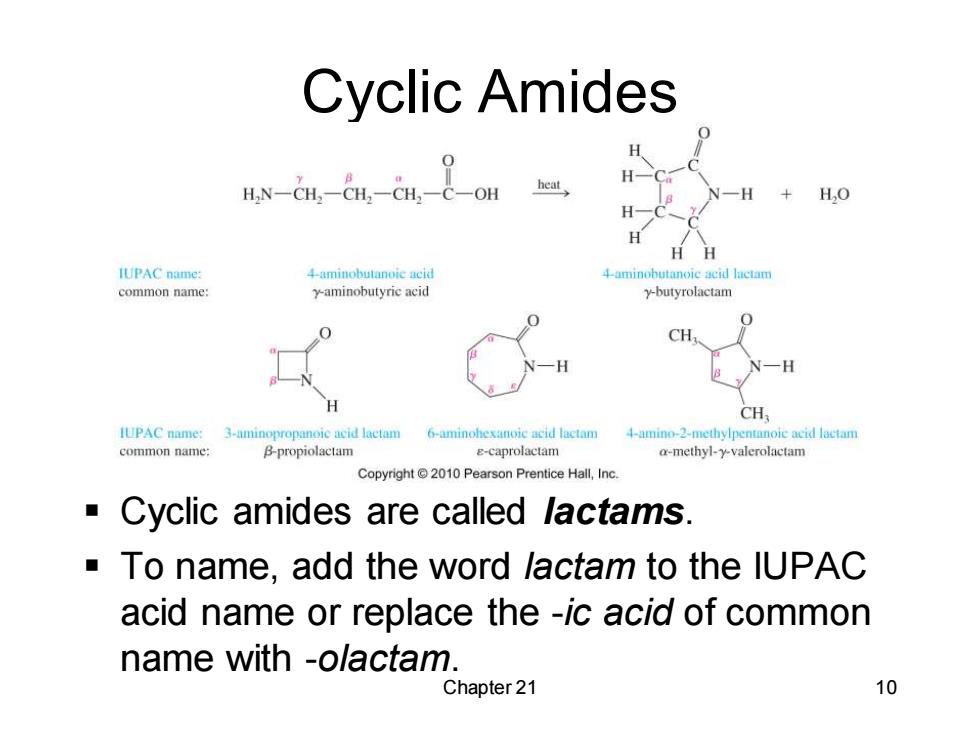
Cyclic Amides H.N-CH,CH,-CH,-c-OH H heat H,0 HH IUPAC name: 4-aminobutanoie acid 4-aminobutanoic acid lactam common name: y-aminobutyric acid y-butyrolactam CH CH IUPAC name: 3-aminopropanoic acid lactam 6-aminohexanoic acid lactam 4-amino-2-methylpentanoie acid lactam common name: B-propiolactam e-caprolactam a-methyl-y-valerolactam Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Cyclic amides are called lactams. To name,add the word lactam to the lUPAC acid name or replace the -ic acid of common name with -olactam. Chapter 21 10
Chapter 21 10 Cyclic Amides ▪ Cyclic amides are called lactams. ▪ To name, add the word lactam to the IUPAC acid name or replace the -ic acid of common name with -olactam