
Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 25 Lipids Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 25 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Lipids

Introduction Lipids are compounds that can be extracted from cells by nonpolar organic solvents. Complex lipids are easily hydrolyzed. Long-chain esters called fatty acids. -Simple lipids are not easily hydrolyzed in acid or base. ·Steroids ·Prostaglandins ■Terpenes Chapter 25 2
Chapter 25 2 Introduction ▪ Lipids are compounds that can be extracted from cells by nonpolar organic solvents. ▪ Complex lipids are easily hydrolyzed. ▪ Long-chain esters called fatty acids. ▪ Simple lipids are not easily hydrolyzed in acid or base. ▪ Steroids ▪ Prostaglandins ▪ Terpenes
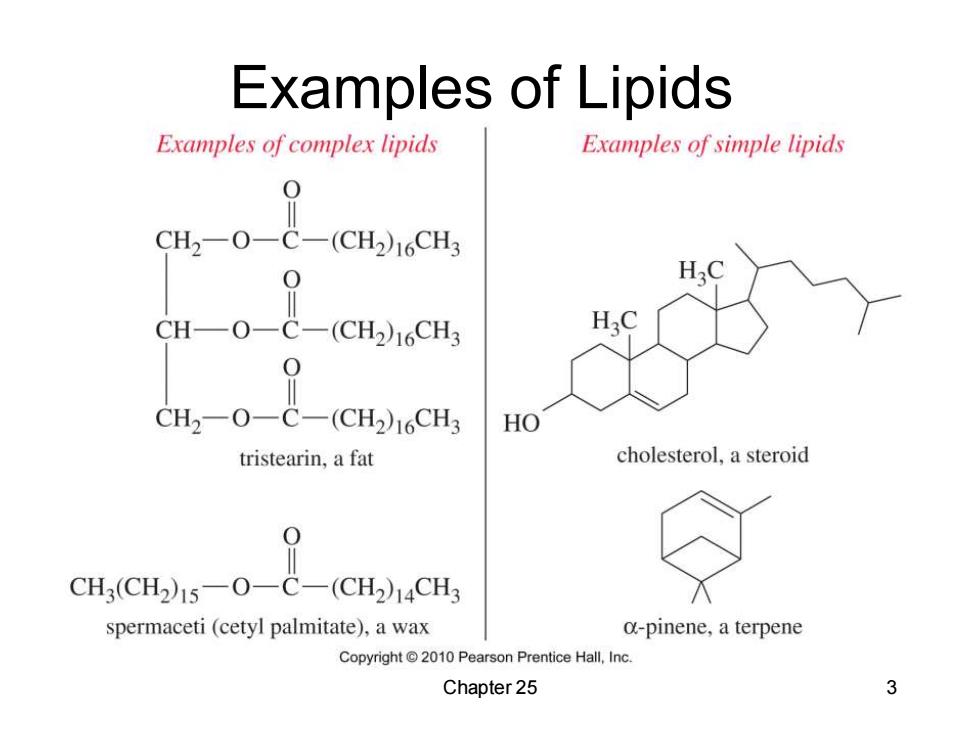
Examples of Lipids Examples of complex lipids Examples of simple lipids CH2-O-C-(CH2)16CH3 0 CH—O-C- (CH2)16CH3 CH2-O-C-(CH2)16CH3 HO tristearin,a fat cholesterol,a steroid CH3(CH2)15-O-C-(CH2)14CH3 spermaceti(cetyl palmitate),a wax a-pinene,a terpene Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 25 3
Chapter 25 3 Examples of Lipids

Waxes Esters of long-chain fatty acids with long-chain alcohols. Commonly found in nature. Spermaceti is found in the head of the sperm whale. Beeswax is a mixture of waxes,hydrocarbons,and alcohols that bees used to make their honeycomb. Carnauba wax is a mixture of waxes of high molecular weights 0 CHa(CH)O- (CH2)24CH3 CH3(CH2)23O- (CH2)26CH3 a component of beeswax a component of carnauba wax Chapter 25
Chapter 25 4 Waxes ▪ Esters of long-chain fatty acids with long-chain alcohols. ▪ Commonly found in nature. ▪ Spermaceti is found in the head of the sperm whale. ▪ Beeswax is a mixture of waxes, hydrocarbons, and alcohols that bees used to make their honeycomb. ▪ Carnauba wax is a mixture of waxes of high molecular weights. CH3(CH2)29O C O (CH2)24CH3 CH3(CH2)23O C O (CH2)26CH3 a component of beeswax a component of carnauba wax

Fatty Acids Unbranched carboxylic acids with 12-20 carbons. Most contain an even number of carbons because they are built from acetic acid units. Melting points increase with increasing molecular weights. Unsaturation greatly lowers the melting point. Chapter 25 5
Chapter 25 5 Fatty Acids ▪ Unbranched carboxylic acids with 12–20 carbons. ▪ Most contain an even number of carbons because they are built from acetic acid units. ▪ Melting points increase with increasing molecular weights. ▪ Unsaturation greatly lowers the melting point

Glycerides Fatty acid esters of the triol glycerol Tryglycerides are the most common glycerides and they are used for long-term energy storage in plants and animals. Fats Solid at room temperature. Most are derived from mammals. ·Oils Liquid at room temperature. Most are derived from plants or cold-blooded animals. Chapter 25 6
Chapter 25 6 Glycerides ▪ Fatty acid esters of the triol glycerol. ▪ Tryglycerides are the most common glycerides and they are used for long-term energy storage in plants and animals. ▪ Fats ▪ Solid at room temperature. ▪ Most are derived from mammals. ▪ Oils ▪ Liquid at room temperature. ▪ Most are derived from plants or cold-blooded animals
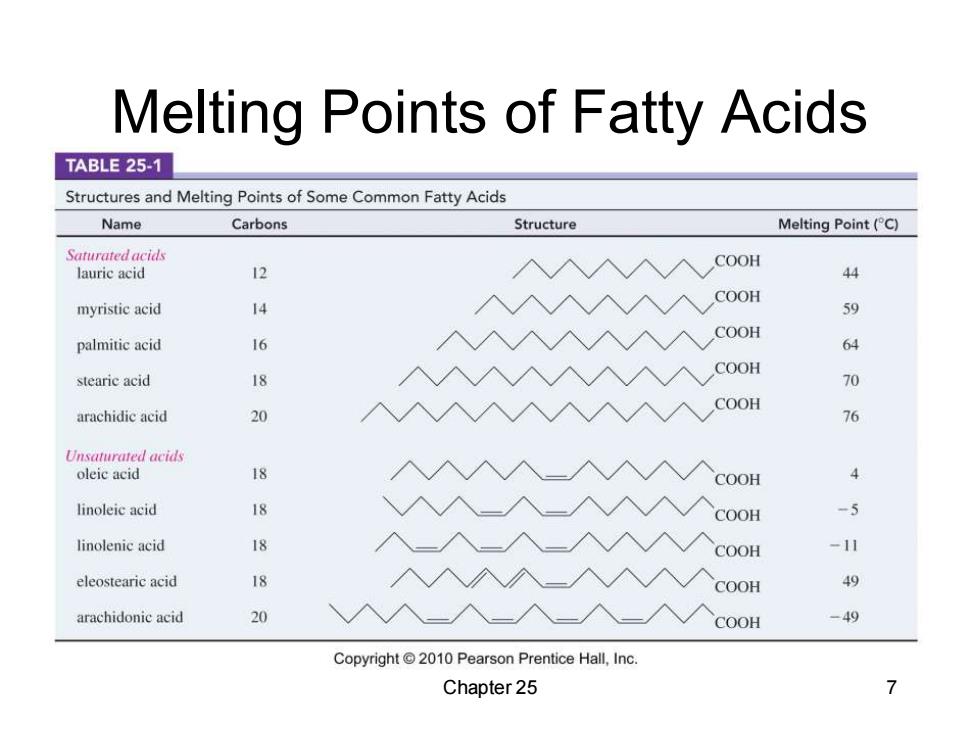
Melting Points of Fatty Acids TABLE 25-1 Structures and Melting Points of Some Common Fatty Acids Name Carbons Structure Melting Point(C) Saturated acids COOH lauric acid 12 44 COOH myristic acid 4 59 COOH palmitic acid 16 64 COOH stearie acid 18 70 arachidic acid 20 COOH 76 Unsaturated acids oleic acid 18 COOH 4 linoleic acid 18 COOH -5 linolenic acid 18 COOH -11 eleostearic acid 18 COOH 49 arachidonic acid 20 COOH -49 Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 25 7
Melting Points of Fatty Acids Chapter 25 7

Melting Points COOH COOH stearic acid,mp 70C oleic acid,mp 4C Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The cis double bond in oleic acid lowers the melting point by66°C. A cis double bond bends the molecule,so it cannot pack efficiently. -A trans double bond has less effect. Chapter 25 8
Chapter 25 8 Melting Points ▪ The cis double bond in oleic acid lowers the melting point by 66°C. ▪ A cis double bond bends the molecule, so it cannot pack efficiently. ▪ A trans double bond has less effect

Fats and Oils CH-0 CH一O CH2-0 tristearin,mp 72C 0 CH,一OC CH-0 CH,一O一C triolein.mp-4 C Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Unsaturated triglycerides have lower melting points because their unsaturated fatty acids do not pack as well in a solid lattice. Chapter 25 9
Chapter 25 9 Fats and Oils ▪ Unsaturated triglycerides have lower melting points because their unsaturated fatty acids do not pack as well in a solid lattice
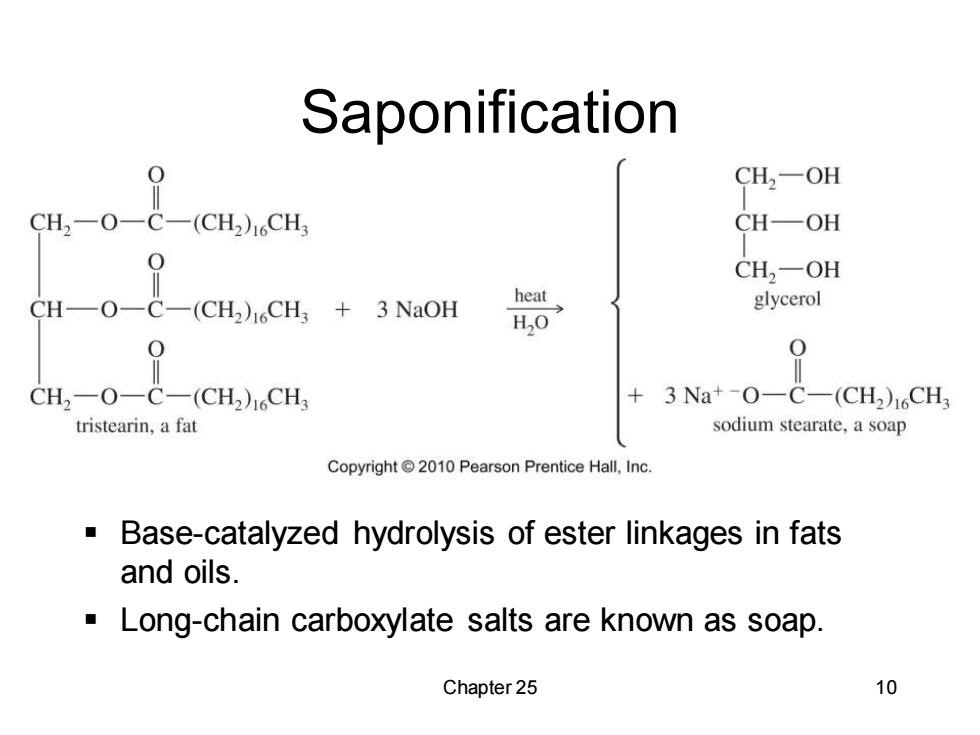
Saponification H-0二69 CH2一OH (CH2)1CH CH—OH CH2-OH CH-O-C-(CH2)16CH3 +3 NaOH heat glycerol HO 0 0 CH2-O-C-(CH2)1CHs 3Na+-O一C-(CH2)16CH3 tristearin,a fat sodium stearate,a soap Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Base-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester linkages in fats and oils. Long-chain carboxylate salts are known as soap. Chapter 25 10
Chapter 25 10 Saponification ▪ Base-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester linkages in fats and oils. ▪ Long-chain carboxylate salts are known as soap