
Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc

Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to be CH6.He named it benzin. Other related compounds with low C:H ratios had a pleasant smell,so they were classified as aromatic. Chapter 16 2
Chapter 16 2 Discovery of Benzene • Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. • Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to be C6H6 . He named it benzin. • Other related compounds with low C:H ratios had a pleasant smell, so they were classified as aromatic
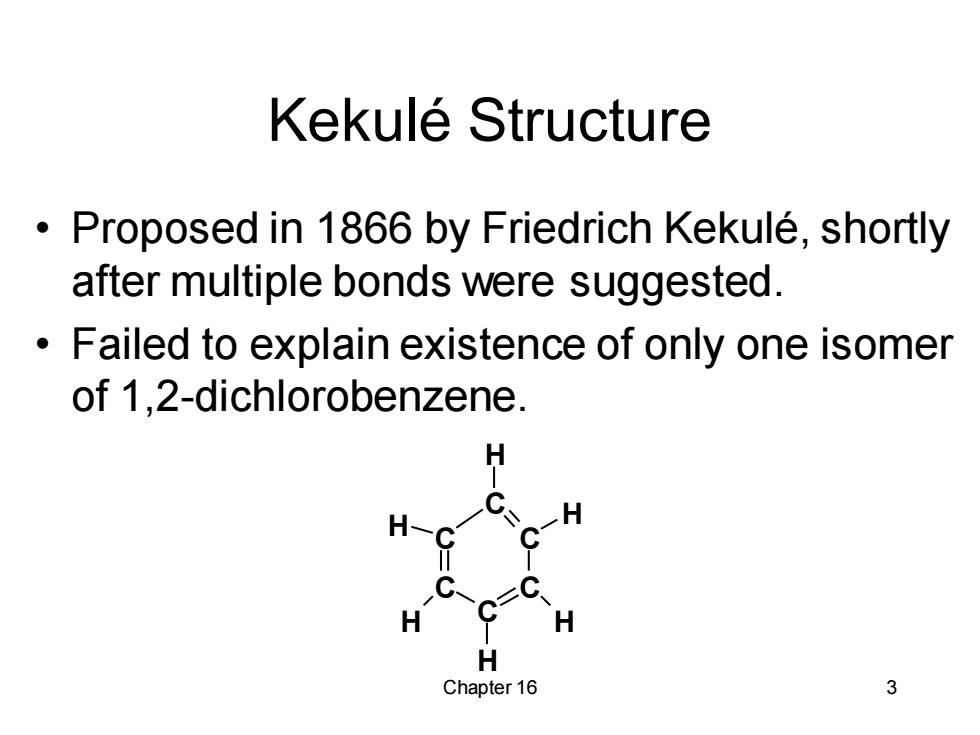
Kekule Structure Proposed in 1866 by Friedrich Kekule,shortly after multiple bonds were suggested. Failed to explain existence of only one isomer of 1,2-dichlorobenzene. H H-C H H H H Chapter 16 3
Chapter 16 3 Kekulé Structure • Proposed in 1866 by Friedrich Kekulé, shortly after multiple bonds were suggested. • Failed to explain existence of only one isomer of 1,2-dichlorobenzene. C C C C C C H H H H H H
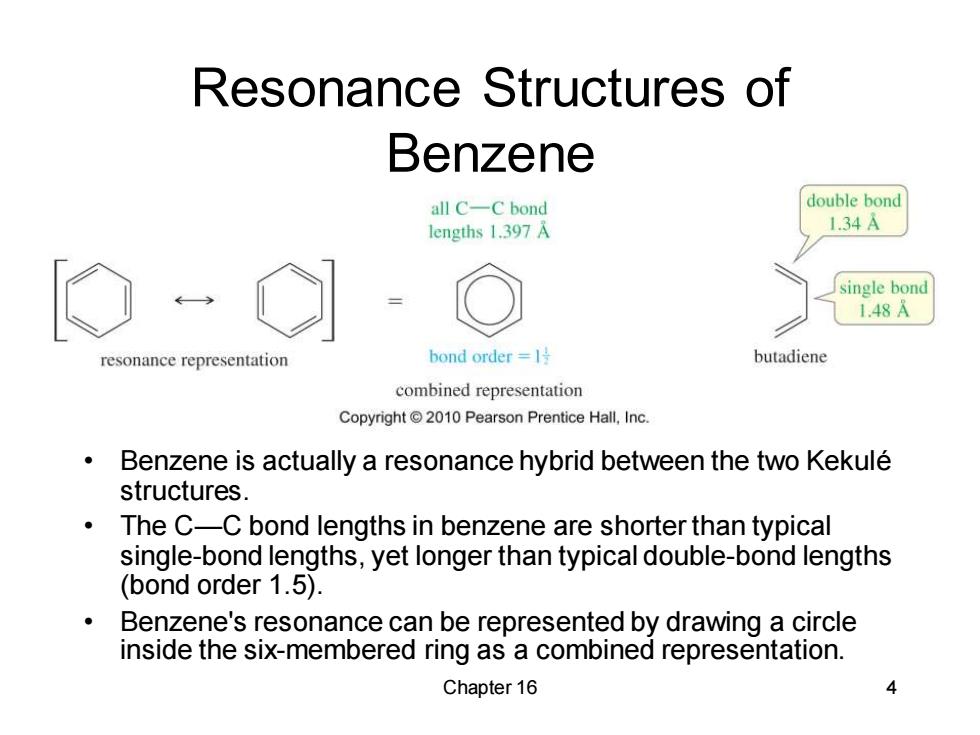
Resonance Structures of Benzene all C-C bond double bond lengths 1.397 A 1.34A single bond 1.48A resonance representation bond order=l号 butadiene combined representation Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Benzene is actually a resonance hybrid between the two Kekule structures. The C-C bond lengths in benzene are shorter than typical single-bond lengths,yet longer than typical double-bond lengths (bond order 1.5). Benzene's resonance can be represented by drawing a circle inside the six-membered ring as a combined representation. Chapter 16
Chapter 16 4 Resonance Structures of Benzene • Benzene is actually a resonance hybrid between the two Kekulé structures. • The C—C bond lengths in benzene are shorter than typical single-bond lengths, yet longer than typical double-bond lengths (bond order 1.5). • Benzene's resonance can be represented by drawing a circle inside the six-membered ring as a combined representation
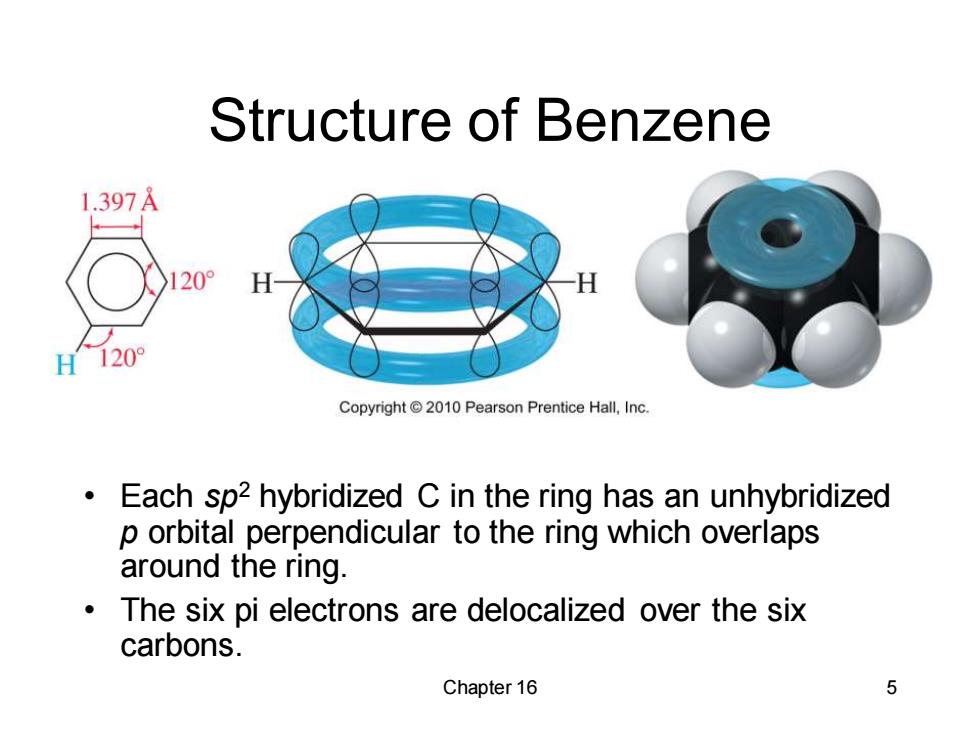
Structure of Benzene 1.397A 20° H 120° Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Each sp2 hybridized C in the ring has an unhybridized p orbital perpendicular to the ring which overlaps around the ring. The six pi electrons are delocalized over the six carbons. Chapter 16 5
Chapter 16 5 Structure of Benzene • Each sp2 hybridized C in the ring has an unhybridized p orbital perpendicular to the ring which overlaps around the ring. • The six pi electrons are delocalized over the six carbons
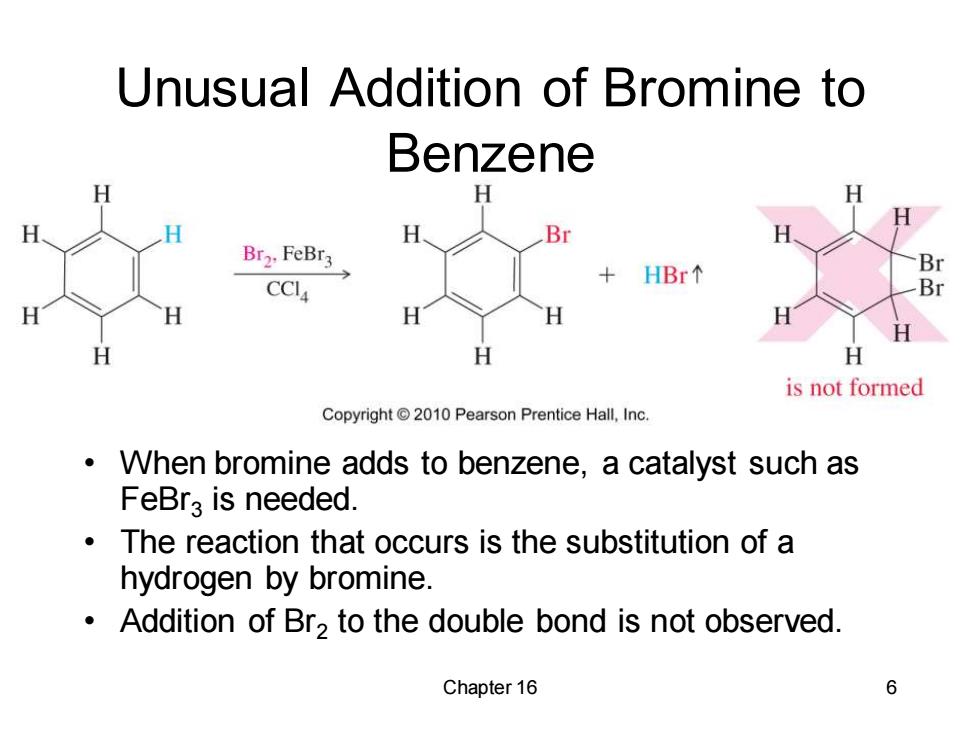
Unusual Addition of Bromine to Benzene H H H Br Br2.FeBr3 HBr Br CCI Br H H H H H is not formed Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. When bromine adds to benzene,a catalyst such as FeBra is needed. The reaction that occurs is the substitution of a hydrogen by bromine. Addition of Br2 to the double bond is not observed. Chapter 16 6
Chapter 16 6 Unusual Addition of Bromine to Benzene • When bromine adds to benzene, a catalyst such as FeBr3 is needed. • The reaction that occurs is the substitution of a hydrogen by bromine. • Addition of Br2 to the double bond is not observed

Resonance Energy Benzene does not have the predicted heat of hydrogenation of-359 kJ/mol. The observed heat of hydrogenation is -208 kJ/mol,a difference of 151 kJ. This difference between the predicted and the observed value is called the resonance energy. Chapter 16 7
Chapter 16 7 Resonance Energy • Benzene does not have the predicted heat of hydrogenation of -359 kJ/mol. • The observed heat of hydrogenation is -208 kJ/mol, a difference of 151 kJ. • This difference between the predicted and the observed value is called the resonance energy
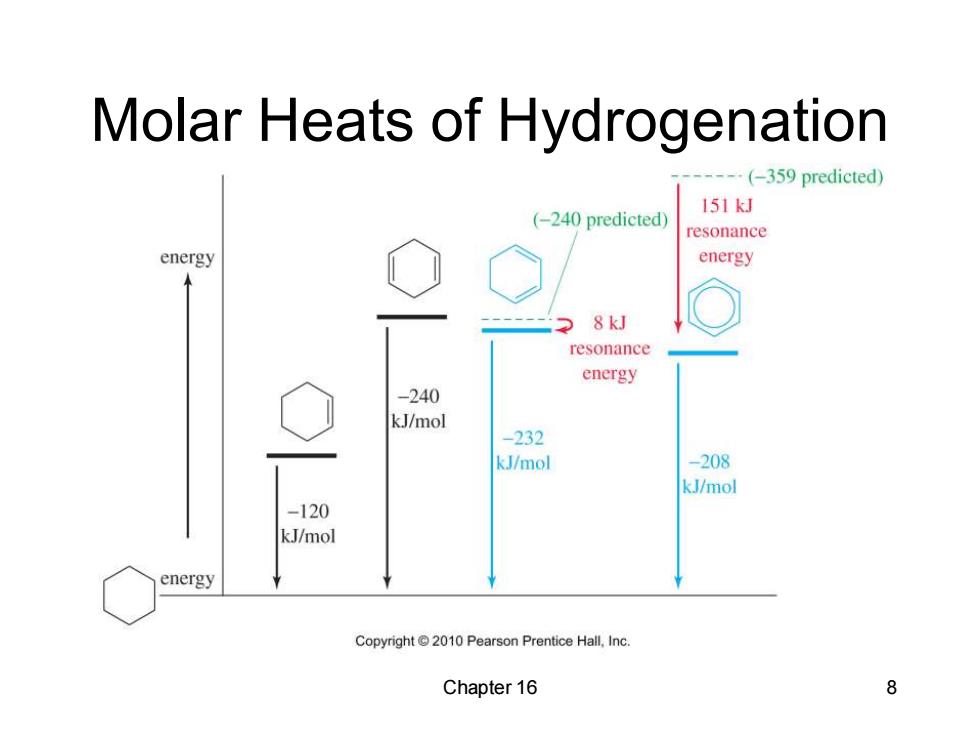
Molar Heats of Hydrogenation ---(-359 predicted) (-240 predicted) 151kJ resonance energy energy 2 8kJ resonance energy -240 kJ/mol -232 kJ/mol -208 kJ/mol -120 kJ/mol energy Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 16 8
Chapter 16 8 Molar Heats of Hydrogenation

Annulenes cyclobutadiene benzene cyclooctatetraene cyclodecapentaene [4]annulene [6]annulene [8]annulene [10]annulene Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Annulenes are hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds. Benzene is a six-membered annulene,so it can be named [6]-annulene.Cylobutadiene is [4]-annulene, cyclooctatetraene is [8]-annulene. Chapter 16 9
Chapter 16 9 Annulenes • Annulenes are hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds. • Benzene is a six-membered annulene, so it can be named [6]-annulene. Cylobutadiene is [4]-annulene, cyclooctatetraene is [8]-annulene
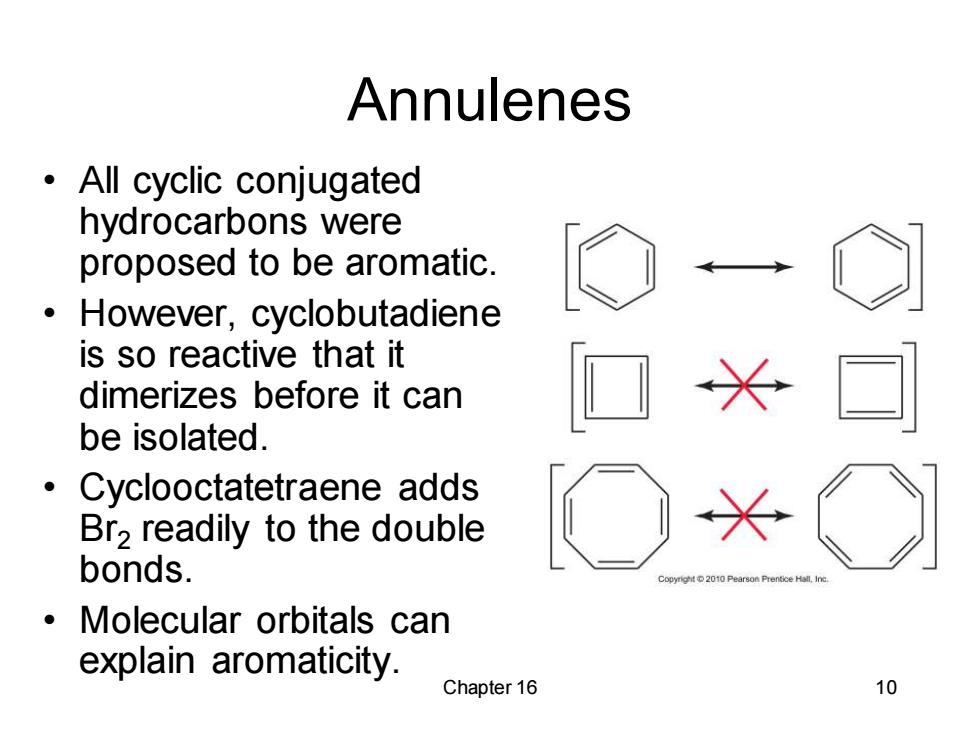
Annulenes All cyclic conjugated hydrocarbons were proposed to be aromatic. However,cyclobutadiene is so reactive that it dimerizes before it can be isolated. Cyclooctatetraene adds Br2 readily to the double bonds. Molecular orbitals can explain aromaticity. Chapter 16 10
Chapter 16 10 Annulenes • All cyclic conjugated hydrocarbons were proposed to be aromatic. • However, cyclobutadiene is so reactive that it dimerizes before it can be isolated. • Cyclooctatetraene adds Br2 readily to the double bonds. • Molecular orbitals can explain aromaticity