
Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 3 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc. Chapter 3 1
Chapter 3 1 Chapter 3 Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes

Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen ONLY. TABLE 3-1 Hydrocarbon Classifications Compound Type Functional Group Example alkanes none (no double or triple bonds) CH3-CH2-CH3,propane alkenes C=C double bond CH2=CH-CH3.propene alkynes -C=C-triple bond H-C=C-CH3.propyne CHCH, aromatics benzene ring ethylbenzene Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 3 2
Chapter 3 2 Hydrocarbons are molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen ONLY. Hydrocarbons

Alkanes General formula:CH2n+2 Found in everything from natural gas to petroleum. The smaller alkanes have very low boiling points (b.p.)therefore they are gases. CH4 C2H6 C3Hg b.p.-160C -89C -42C Chapter 3 3
Chapter 3 3 Alkanes • General formula: CnH2n+2 • Found in everything from natural gas to petroleum. • The smaller alkanes have very low boiling points (b.p.) therefore they are gases. CH4 C2H6 C3H8 b.p. -160oC -89oC -42oC

Alkane Examples H H HHH HHHH CH3 H-C-C-C-C-H CH3-CH-CH3 HH HHH HHHH methane,CHa ethane,C2H propane.C3Hs butane.CHio isobutane,CHo CH3 CH3 CH3-CH2一CH2-CH2-CH3 CH3一CH-CH2-CH CH3-C-CH3 or H-(CH2)s-H CH3 pentane.CsH2 isopentane,CsH2 neopentane,CsH2 Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 3 4
Chapter 3 4 Alkane Examples

Small Alkanes(CnH2n+2) ·Methane CH4 Ethane CH3-CH3 。Propane CH3-CH2-CH3 Chapter 3 5
Chapter 3 5 Small Alkanes (CnH2n+2) • Methane • Ethane • Propane CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 CH3 CH4
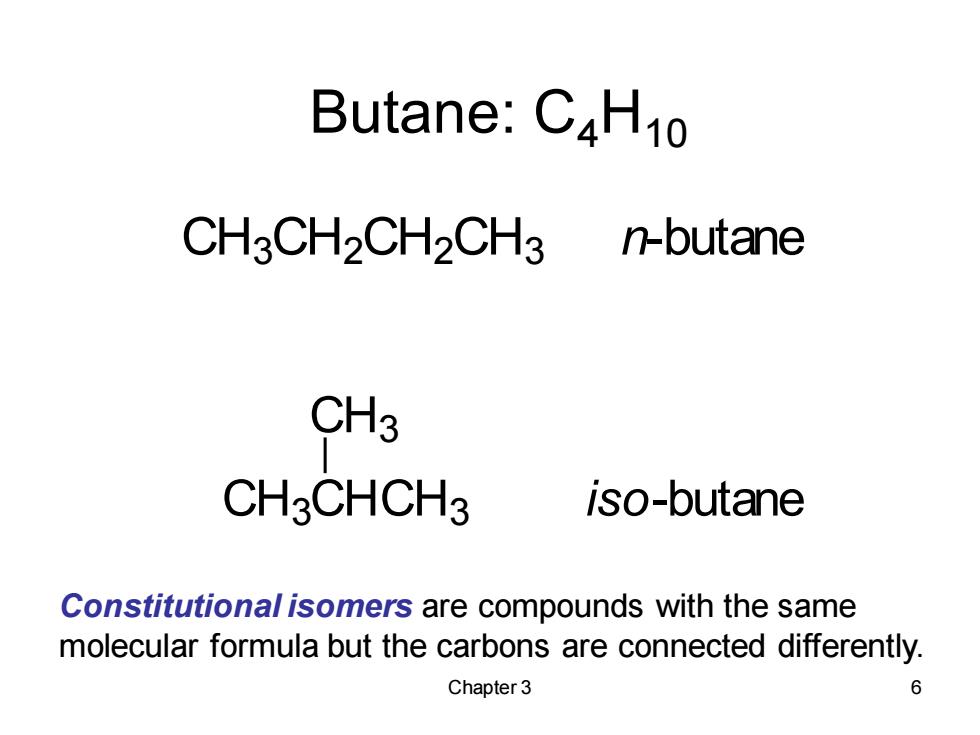
Butane:C4H10 CH3CH2CH2CH3 n-butane CH3 CH3CHCH3 iso-butane Constitutional isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but the carbons are connected differently. Chapter 3 6
Chapter 3 6 Butane: C4H10 Constitutional isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but the carbons are connected differently. CH3CH2CH2CH3 n-butane CH3CHCH3 iso-butane CH3
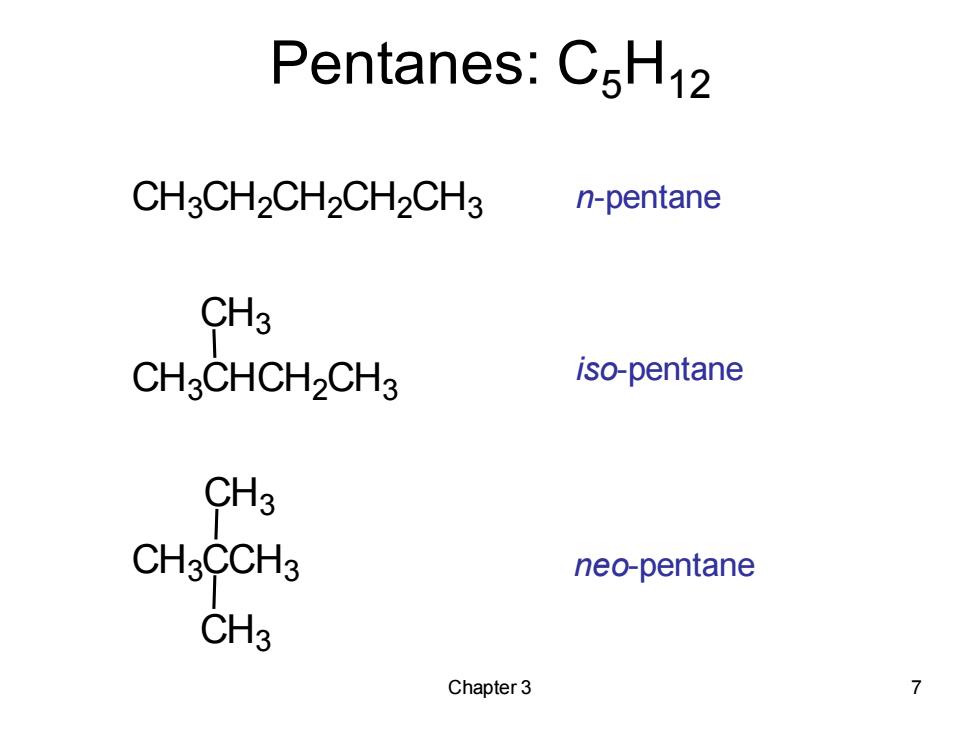
Pentanes:C5H12 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 n-pentane CH3 CHCHCH2CH3 iso-pentane CH3 CH3CCH3 neo-pentane CH3 Chapter 3 7
Chapter 3 7 Pentanes: C5H12 n-pentane iso-pentane neo-pentane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CHCH2CH3 CH3CCH3 CH3 CH3 CH3

IUPAC International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Common names kept:methane,ethane, propane,butane. ·Alkanes:suffix“-ane”will be used after the number of carbons. -Example:An alkane with5 carbons is“penta” for five and the suffix "-ane": pentane Chapter 3 8
Chapter 3 8 IUPAC • International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry • Common names kept: methane, ethane, propane, butane. • Alkanes: suffix “-ane” will be used after the number of carbons. – Example: An alkane with 5 carbons is “penta” for five and the suffix “-ane”: pentane

IUPAC Rules Rule 1:Find the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms,and use the name of this chain as the base name of the compound. ● Rule 2:Number the longest chain,beginning with the end of the chain nearest a substituent. 。 Rule 3:Name the groups attached to the longest chain as alkyl groups.Give the location of each alkyl group by the number of the main chain carbon atom to which it is attached. 。 Write the alkyl groups in alphabetical order regardless of their position on the chain. Chapter 3 9
Chapter 3 9 IUPAC Rules • Rule 1: Find the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms, and use the name of this chain as the base name of the compound. • Rule 2: Number the longest chain, beginning with the end of the chain nearest a substituent. • Rule 3: Name the groups attached to the longest chain as alkyl groups. Give the location of each alkyl group by the number of the main chain carbon atom to which it is attached. • Write the alkyl groups in alphabetical order regardless of their position on the chain
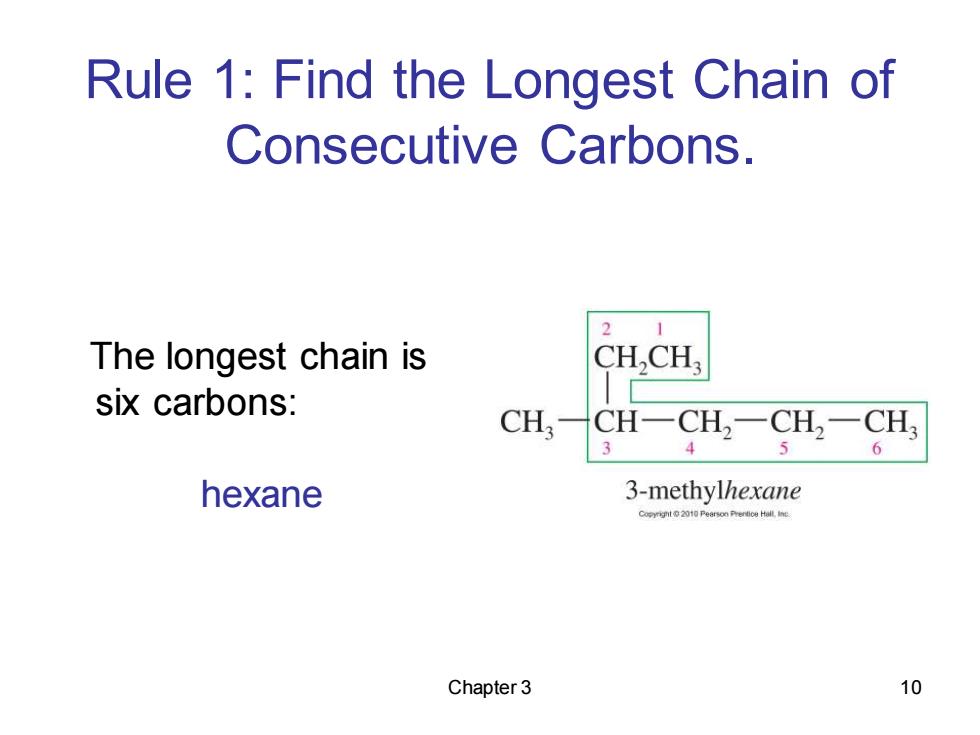
Rule 1:Find the Longest Chain of Consecutive Carbons. 2 The longest chain is CH,CH, six carbons: CHCH-CH,一CH,-CH 3 4 6 hexane 3-methylhexane o01 PearsonPrertice Hllne Chapter 3 10
Chapter 3 10 Rule 1: Find the Longest Chain of Consecutive Carbons. The longest chain is six carbons: hexane