
Organic Chemistry,5th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Chirality ·“Handedness"”:right glove doesn't fit the left hand. Mirror-image object is different from the original object. =>
Chapter 5 2 Chirality • “Handedness”: right glove doesn’t fit the left hand. • Mirror-image object is different from the original object. =>
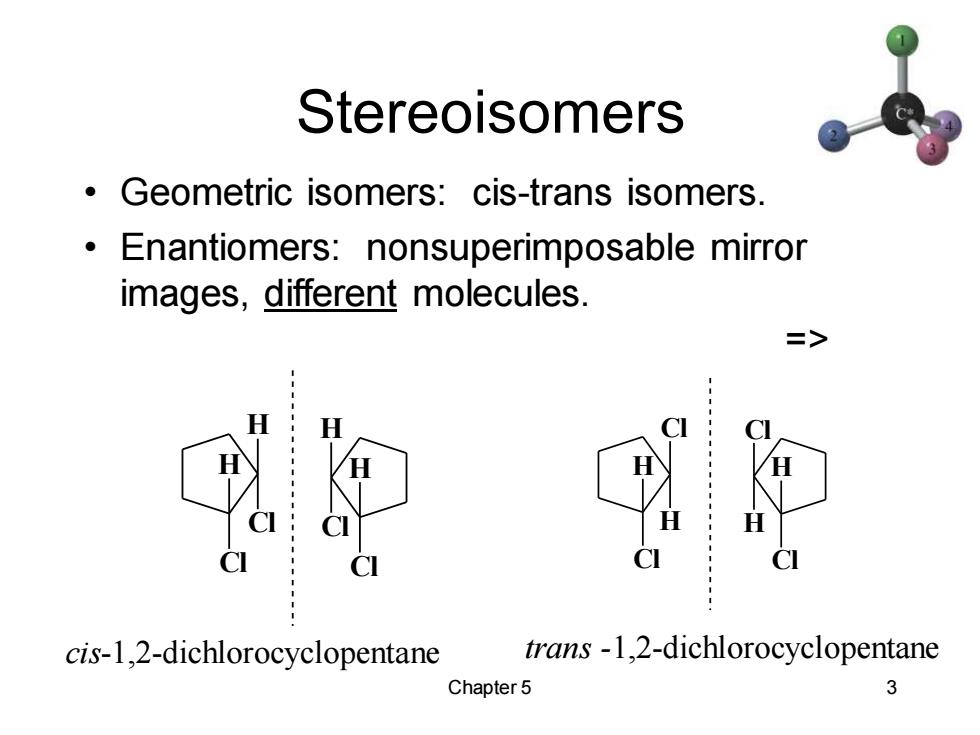
Stereoisomers Geometric isomers:cis-trans isomers. Enantiomers:nonsuperimposable mirror images,different molecules. => cis-1,2-dichlorocyclopentane trans-1,2-dichlorocyclopentane Chapter 5 3
Chapter 5 3 Stereoisomers • Geometric isomers: cis-trans isomers. • Enantiomers: nonsuperimposable mirror images, different molecules. => cis-1,2-dichlorocyclopentane trans -1,2-dichlorocyclopentane H Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl Cl H H Cl Cl H
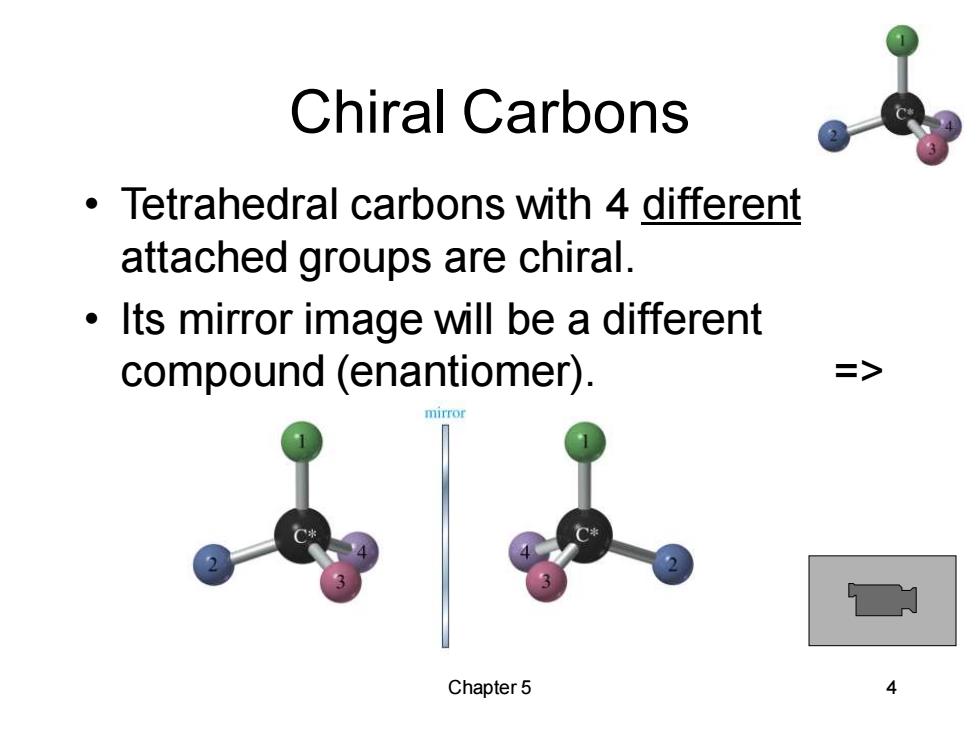
Chiral Carbons Tetrahedral carbons with 4 different attached groups are chiral. Its mirror image will be a different compound (enantiomer). > Chapter5
Chapter 5 4 Chiral Carbons • Tetrahedral carbons with 4 different attached groups are chiral. • Its mirror image will be a different compound (enantiomer). =>
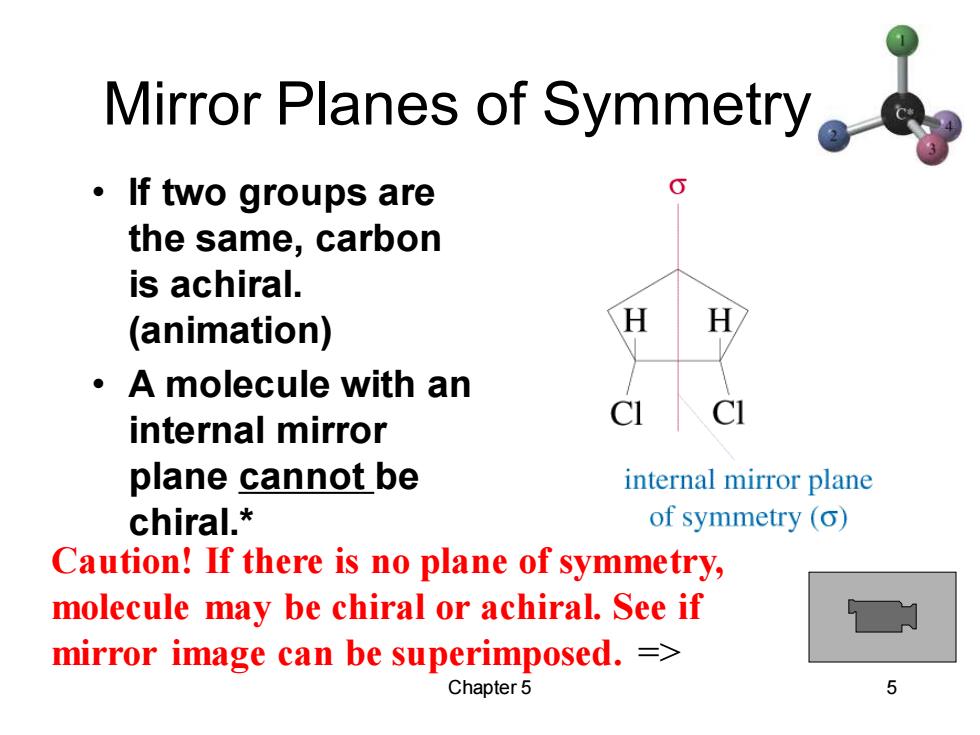
Mirror Planes of Symmetry ·If two groups are the same,carbon is achiral. (animation) 。A molecule with an C 1 internal mirror plane cannot be internal mirror plane chiral.* of symmetry (o) Caution!If there is no plane of symmetry, molecule may be chiral or achiral.See if mirror image can be superimposed.= Chapter 5 5
Chapter 5 5 Mirror Planes of Symmetry • If two groups are the same, carbon is achiral. (animation) • A molecule with an internal mirror plane cannot be chiral.* Caution! If there is no plane of symmetry, molecule may be chiral or achiral. See if mirror image can be superimposed. =>
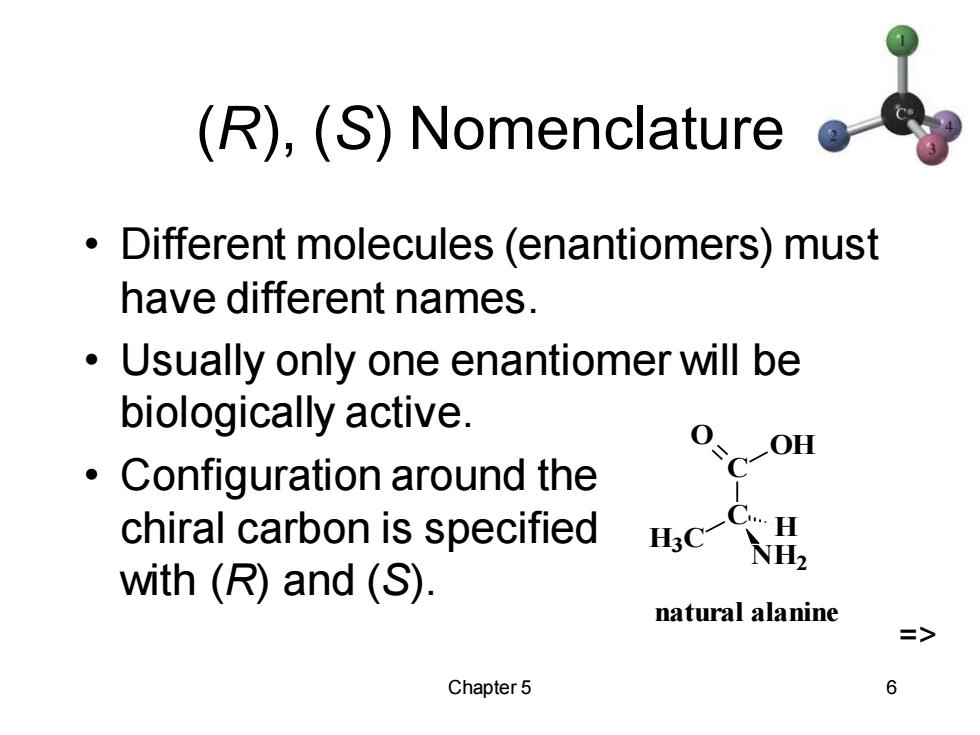
(R),(S)Nomenclature Different molecules (enantiomers)must have different names. Usually only one enantiomer will be biologically active. Configuration around the C-OH chiral carbon is specified C…H NH2 with (R)and (S). natural alanine > Chapter 5 6
Chapter 5 6 (R), (S) Nomenclature • Different molecules (enantiomers) must have different names. • Usually only one enantiomer will be biologically active. • Configuration around the chiral carbon is specified with (R) and (S). C C O OH H3C NH2 H natural alanine =>

Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules Assign a priority number to each group attached to the chiral carbon. Atom with highest atomic number assigned the highest priority #1. In case of ties,look at the next atoms along the chain. Double and triple bonds are treated like bonds to duplicate atoms. => Chapter 5
Chapter 5 7 Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules • Assign a priority number to each group attached to the chiral carbon. • Atom with highest atomic number assigned the highest priority #1. • In case of ties, look at the next atoms along the chain. • Double and triple bonds are treated like bonds to duplicate atoms. =>
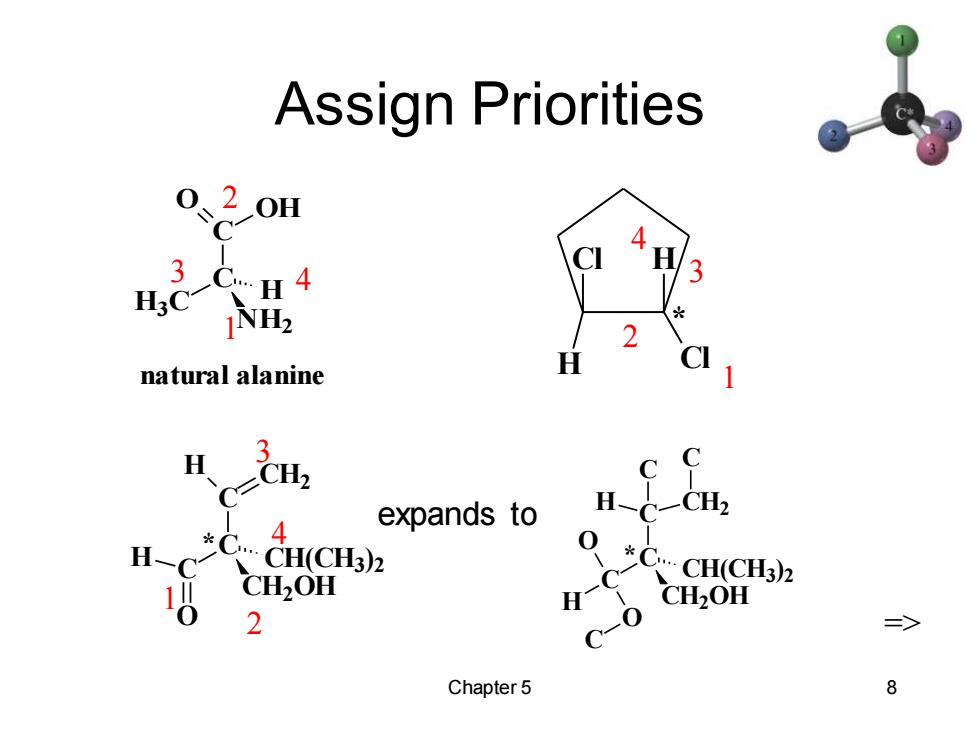
Assign Priorities 0、20H C 3C..H4 H3C NH2 natural alanine H expands to H 4 H *C CH(CH3)2 CH(CH3)2 CH2OH H CH2OH 2 c-0 Chapter 5 8
Chapter 5 8 Assign Priorities C C O OH H3C NH2 H natural alanine 1 2 3 4 Cl Cl H H * 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 => C C O H C H CH2 CH2OH CH(CH3) 2 * C C C CH2OH CH(CH3 ) 2 H O O C C H CH2 C * expands to
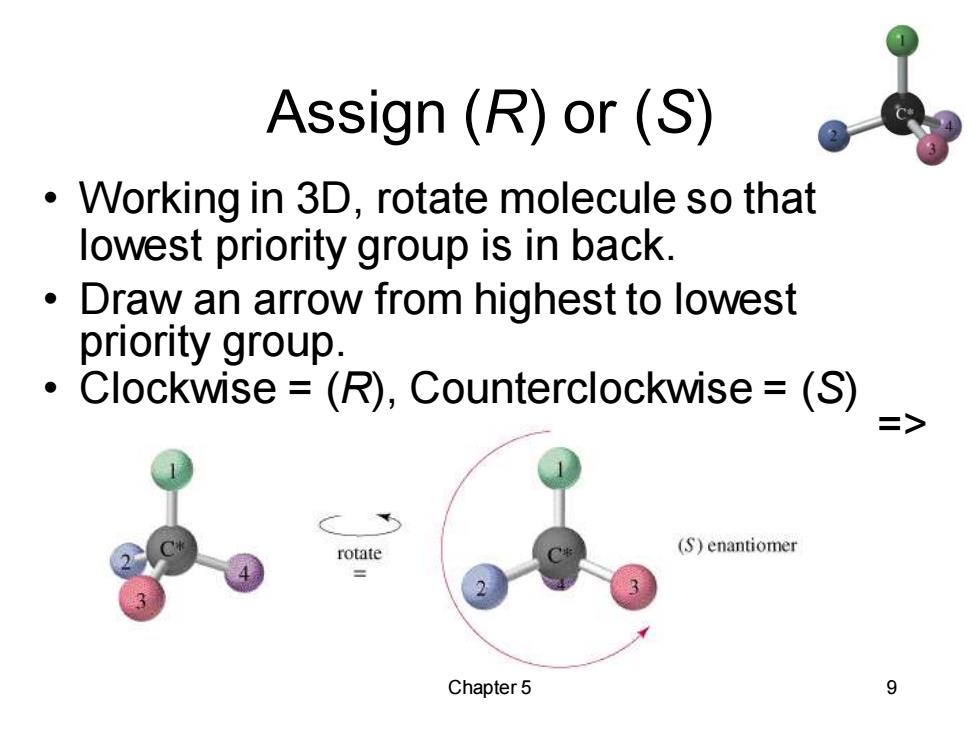
Assign(R)or(S) Working in 3D,rotate molecule so that 。 lowest priority group is in back. Draw an arrow from highest to lowest priority group. Clockwise =(R),Counterclockwise =(S) rotate (S)enantiomer Chapter 5 9
Chapter 5 9 Assign (R) or (S) • Working in 3D, rotate molecule so that lowest priority group is in back. • Draw an arrow from highest to lowest priority group. • Clockwise = (R), Counterclockwise = (S) =>

Properties of Enantiomers Same boiling point,melting point,density Same refractive index Different direction of rotation in polarimeter Different interaction with other chiral molecules Enzymes Taste buds,scent => Chapter 5 10
Chapter 5 10 Properties of Enantiomers • Same boiling point, melting point, density • Same refractive index • Different direction of rotation in polarimeter • Different interaction with other chiral molecules – Enzymes – Taste buds, scent =>