正在加载图片...
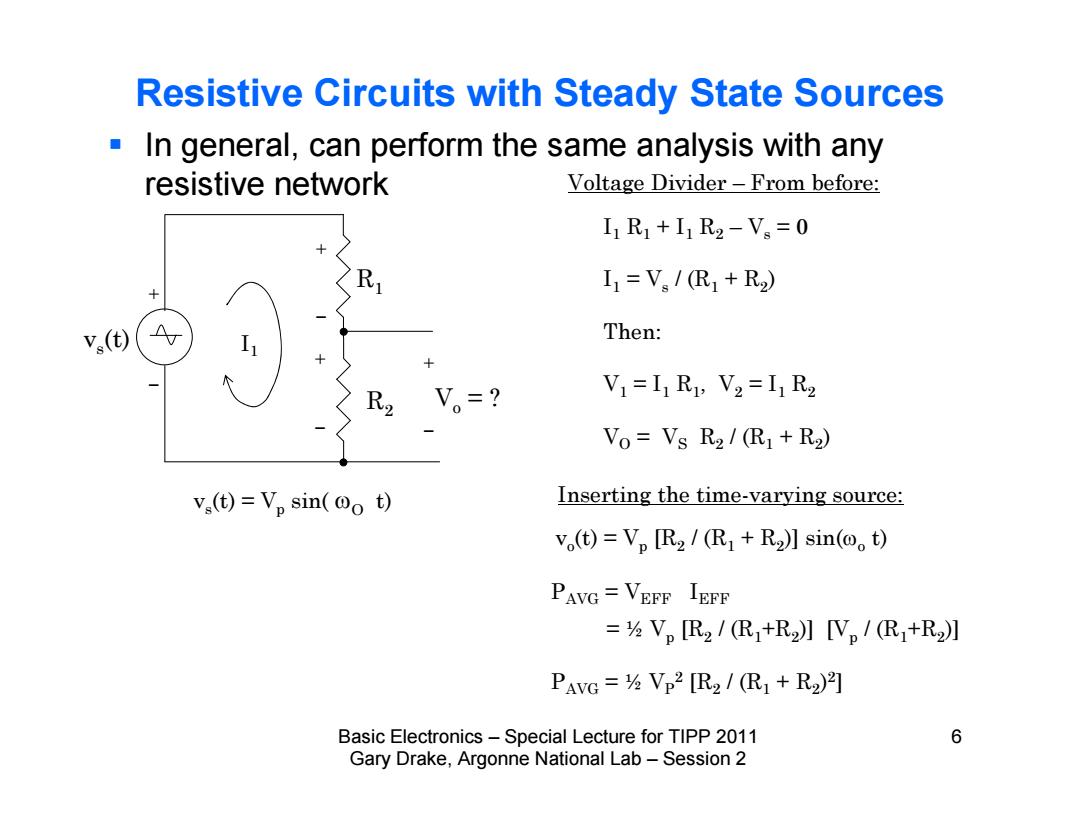
Resistive Circuits with Steady State Sources In general,can perform the same analysis with any resistive network Voltage Divider-From before: I1R1+I1R2-V。=0 I1=V/R1+R2) v(t) Then: V1=I1R1,V2=I1R2 Vo=Vs R2/(R1+R2) vs(t)=Vp sin(@o t) Inserting the time-varying source: v。(t)=VpR2/(R1+R2】sin(o。t) PAVG VEFF IEFF =⅓V,R2/R1+R2】V。/(R+R2] PAVG =Vp2 [R2 /(R1+R2)2] Basic Electronics-Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 6 Gary Drake,Argonne National Lab-Session 2Basic Electronics – Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 6 Gary Drake, Argonne National Lab – Session 2 Resistive Circuits with Steady State Sources In general, can perform the same analysis with any resistive network vs(t) = Vp sin( t) Voltage Divider – From before: R1 R2 Vo = ? I1 vs(t) I1 R1 + I1 R2 – Vs = 0 I1 = Vs / (R1 + R2) Then: V1 = I1 R1, V2 = I1 R2 VO = VS R2 / (R1 + R2) Inserting the time-varying source: vo(t) = Vp [R2 / (R1 + R2)] sin(o t) PAVG = VEFF IEFF = ½ Vp [R2 / (R1+R2)] [Vp / (R1+R2)] PAVG = ½ VP2 [R2 / (R1 + R2)2]