正在加载图片...
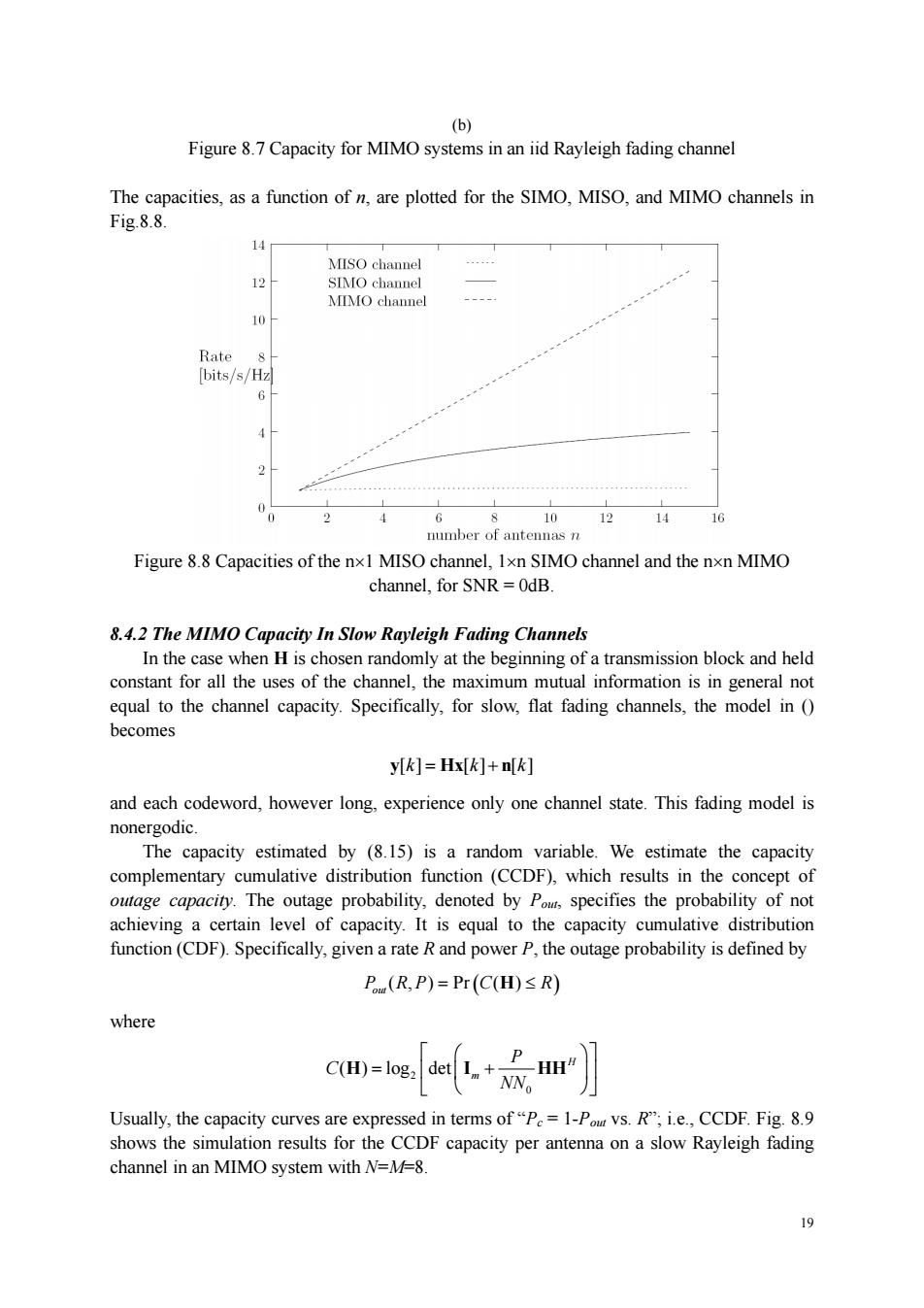
(b) Figure 8.7 Capacity for MIMO systems in an iid Rayleigh fading channel The capacities,as a function of n,are plotted for the SIMO,MISO,and MIMO channels in Fig.8.8. 14 T chann 12 MIMO channel 10 ts/ 2 12 number of antennas n 8.4.2 The MIMO Capacity In Slow Rayleigh Fading Channels In the case when H is chosen randomly at the beginning of a transmission block and held constant for all the uses of the channel.the r xim utual info 18 neral not equal to the channel capacity.Specifically,for slow,flat fading channels,the model in( becomes y[k]=Hx[]+n[k] and each codeword,however long,experience only one channel state.This fading model is sya时(S 15)sarm wibe w complementary cumulative distribution function (CCDF),which results in the concept of outage capacity.The outage probability,denoted by Pom specifies the probability of not achieving a certain level of capacity.It is equal to the capacity cumulative distribution function(CDF).Specifically,given a rate R and power P,the outage probability is defined by P (R,P)=Pr(C(H)S R) where C(H)=log: -HH" Usually,the capacity curves are expressed in terms of"P=1-Pom vs.R";i.e.,CCDF.Fig.8.9 shows the simulation results for the CCDF capacity per antenna on a slow Rayleigh fading channel in an MIMO system with N=M=8. 19 19 (b) Figure 8.7 Capacity for MIMO systems in an iid Rayleigh fading channel The capacities, as a function of n, are plotted for the SIMO, MISO, and MIMO channels in Fig.8.8. Figure 8.8 Capacities of the n1 MISO channel, 1n SIMO channel and the nn MIMO channel, for SNR = 0dB. 8.4.2 The MIMO Capacity In Slow Rayleigh Fading Channels In the case when H is chosen randomly at the beginning of a transmission block and held constant for all the uses of the channel, the maximum mutual information is in general not equal to the channel capacity. Specifically, for slow, flat fading channels, the model in () becomes y[] [] [] k kk Hx n and each codeword, however long, experience only one channel state. This fading model is nonergodic. The capacity estimated by (8.15) is a random variable. We estimate the capacity complementary cumulative distribution function (CCDF), which results in the concept of outage capacity. The outage probability, denoted by Pout, specifies the probability of not achieving a certain level of capacity. It is equal to the capacity cumulative distribution function (CDF). Specifically, given a rate R and power P, the outage probability is defined by ( , ) Pr ( ) P RP C R out H where 2 0 ( ) log det H m P C NN H I HH Usually, the capacity curves are expressed in terms of “Pc = 1-Pout vs. R”; i.e., CCDF. Fig. 8.9 shows the simulation results for the CCDF capacity per antenna on a slow Rayleigh fading channel in an MIMO system with N=M=8