正在加载图片...
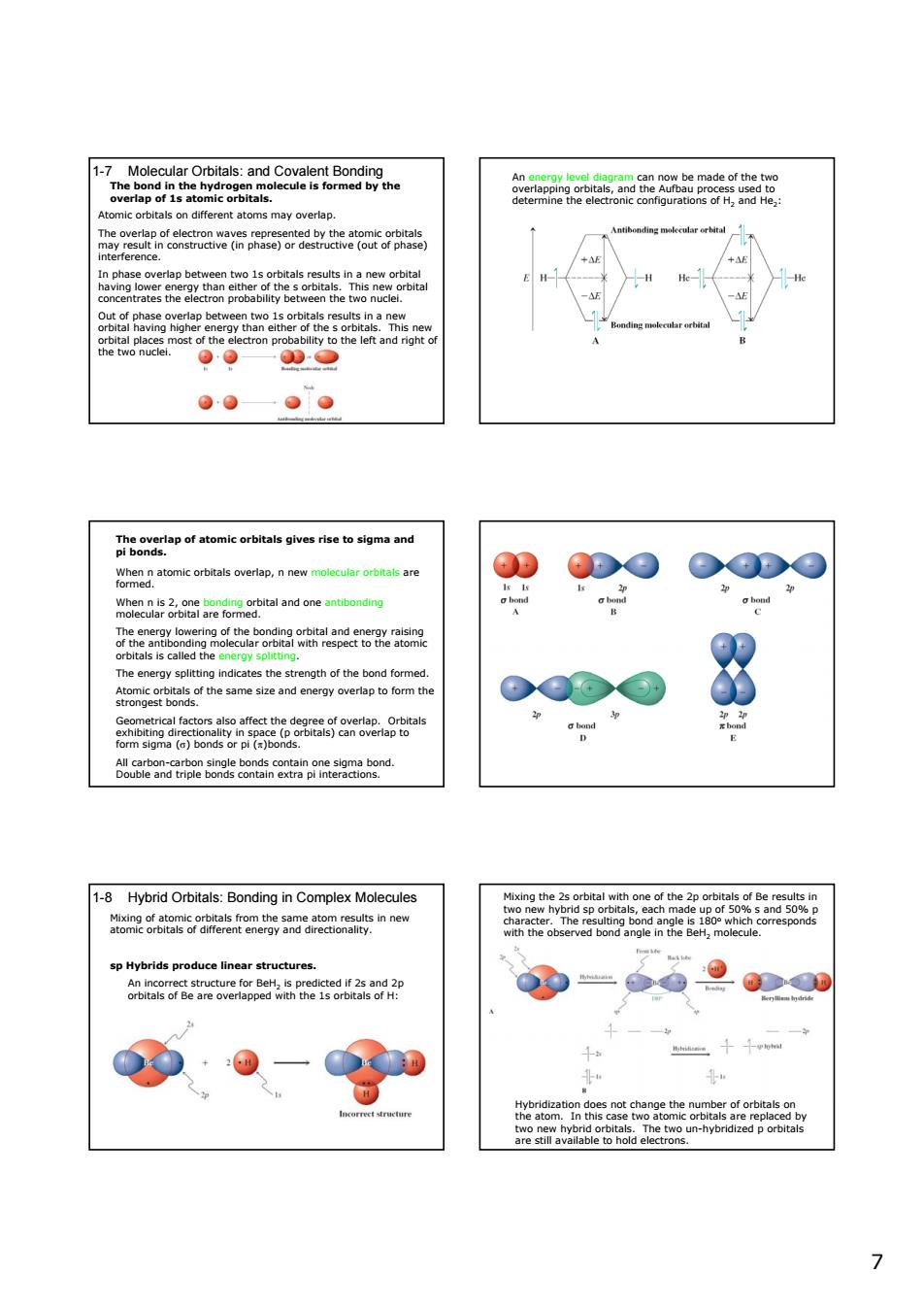
7Moeataotasaaceeaneaibn is form 90—0D5 ●●●● of tomic 00 DO ©Do ben&oasneochtalandoneantbandy 0 OQ⊙③ 68btanantoe2onmtinoaanarmgaated 1-8 Hybrid Orbitals:Bonding in Complex Molecules aom28rlas6ramentemeoeaauemoaynnG sp Hybrids produce linear structures ooseoeteaorepggetea2is0d20 -000 9·0-0 7 7 1-7 Molecular Orbitals: and Covalent Bonding The bond in the hydrogen molecule is formed by the overlap of 1s atomic orbitals. Atomic orbitals on different atoms may overlap. The overlap of electron waves represented by the atomic orbitals may result in constructive (in phase) or destructive (out of phase) interference. In phase overlap between two 1s orbitals results in a new orbital having lower energy than either of the s orbitals. This new orbital concentrates the electron probability between the two nuclei. Out of phase overlap between two 1s orbitals results in a new orbital having higher energy than either of the s orbitals. This new orbital places most of the electron probability to the left and right of the two nuclei. An energy level diagram can now be made of the two overlapping orbitals, and the Aufbau process used to determine the electronic configurations of H2 and He2: The overlap of atomic orbitals gives rise to sigma and pi bonds. When n atomic orbitals overlap, n new molecular orbitals are formed. When n is 2, one bonding orbital and one antibonding molecular orbital are formed. The energy lowering of the bonding orbital and energy raising of the antibonding molecular orbital with respect to the atomic orbitals is called the energy splitting. The energy splitting indicates the strength of the bond formed. Atomic orbitals of the same size and energy overlap to form the strongest bonds. Geometrical factors also affect the degree of overlap. Orbitals exhibiting directionality in space (p orbitals) can overlap to form sigma (σ) bonds or pi (π)bonds. All carbon-carbon single bonds contain one sigma bond. Double and triple bonds contain extra pi interactions. 1-8 Hybrid Orbitals: Bonding in Complex Molecules Mixing of atomic orbitals from the same atom results in new atomic orbitals of different energy and directionality. sp Hybrids produce linear structures. An incorrect structure for BeH2 is predicted if 2s and 2p orbitals of Be are overlapped with the 1s orbitals of H: Mixing the 2s orbital with one of the 2p orbitals of Be results in two new hybrid sp orbitals, each made up of 50% s and 50% p character. The resulting bond angle is 180o which corresponds with the observed bond angle in the BeH2 molecule. Hybridization does not change the number of orbitals on the atom. In this case two atomic orbitals are replaced by two new hybrid orbitals. The two un-hybridized p orbitals are still available to hold electrons