正在加载图片...
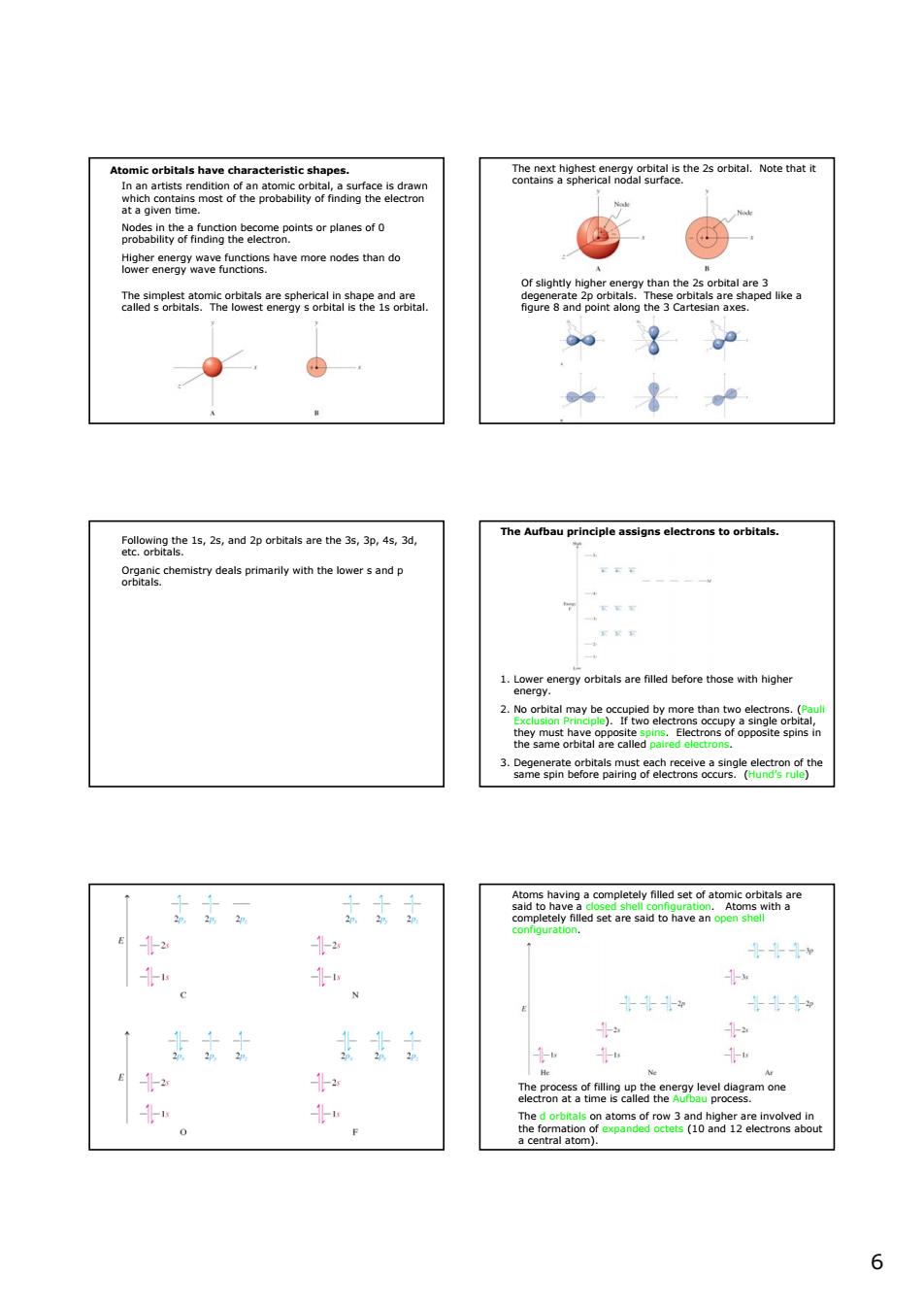
nt5 m品 esohngranrgameeemeponsorplanesot0 ave moreoetho atea0o6aomeo8eangwg2oaanta2 aily with the wersand p -2 女黄 m one 0 66 Atomic orbitals have characteristic shapes. In an artists rendition of an atomic orbital, a surface is drawn which contains most of the probability of finding the electron at a given time. Nodes in the a function become points or planes of 0 probability of finding the electron. Higher energy wave functions have more nodes than do lower energy wave functions. The simplest atomic orbitals are spherical in shape and are called s orbitals. The lowest energy s orbital is the 1s orbital. The next highest energy orbital is the 2s orbital. Note that it contains a spherical nodal surface. Of slightly higher energy than the 2s orbital are 3 degenerate 2p orbitals. These orbitals are shaped like a figure 8 and point along the 3 Cartesian axes. Following the 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals are the 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, etc. orbitals. Organic chemistry deals primarily with the lower s and p orbitals. The Aufbau principle assigns electrons to orbitals. 1. Lower energy orbitals are filled before those with higher energy. 2. No orbital may be occupied by more than two electrons. (Pauli Exclusion Principle). If two electrons occupy a single orbital, they must have opposite spins. Electrons of opposite spins in the same orbital are called paired electrons. 3. Degenerate orbitals must each receive a single electron of the same spin before pairing of electrons occurs. (Hund’s rule) Atoms having a completely filled set of atomic orbitals are said to have a closed shell configuration. Atoms with a completely filled set are said to have an open shell configuration. The process of filling up the energy level diagram one electron at a time is called the Aufbau process. The d orbitals on atoms of row 3 and higher are involved in the formation of expanded octets (10 and 12 electrons about a central atom)