正在加载图片...
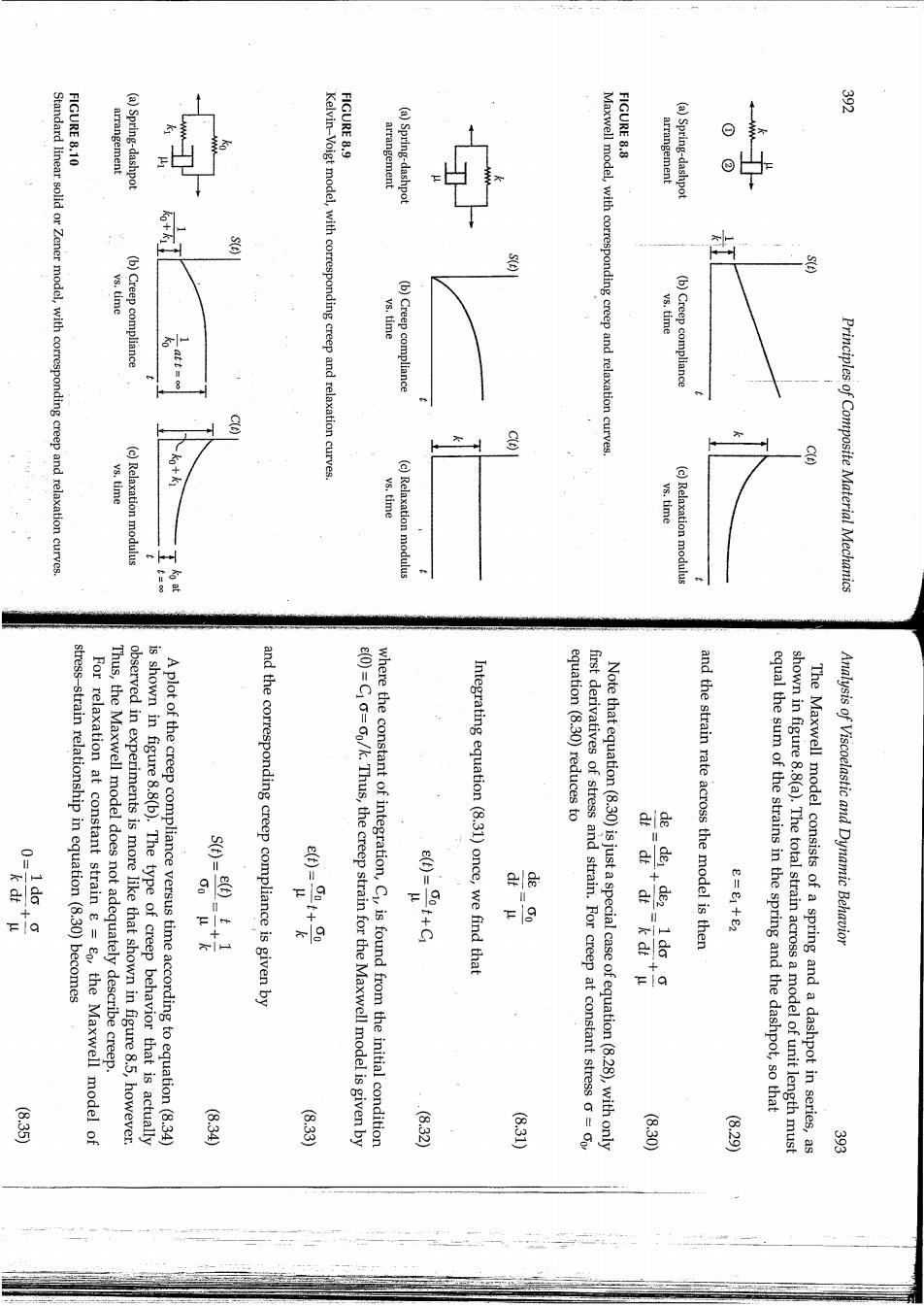
FIGURE 8.10 常 arrangement (a)Spring-dashpot FIGURE 8.9 Kelvin-Voigt model,with corresponding creep and relaxation curves arrangement (a)Spring-dashpot FIGURE 8.8 Standard linear solid or Zener model,with corresponding creep and relaxation curves. vs.time (b)Creep compliance ys.time (b)Creep compliance Maxwell model,with corresponding creep and relaxation curves. arrangement (a)Spring-dashpot vs.time (b)Creep compliance ys.time (c)Relaxation modulus + 8 ys,time (c)Relaxation modulus vs.time (c)Relaxation modulus Principles of Composite Material Mechanics 入 stress-strain relationship in equation(8.30)becomes For relaxation at constant strain g =8o,the Maxwell model of Thus,the Maxwell model does not adequately describe creep. observed in experiments is more like that shown in figure 8.5,however. is shown in figure 8.8(b).The type of creep behavior that is actually A plot of the creep compliance versus time according to equation(8.34) and the corresponding creep compliance is given by e(0)=Cio=0o/k.Thus,the creep strain for the Maxwell model is given by where the constant of integration,C1,is found from the initial condition O-8+O Integrating equation(8.31)once,we find that first derivatives of stress and strain.For creep at constant stress o=oo equation(8.30)reduces to Note that equation(8.30)is just a special case of equation(8.28),with only and the strain rate across the model is then 8-e+e2 Analysis of Viscoelastic and Dynamic Behavior 18 equal the sum of the strains in the spring and the dashpot,so that shown in figure 8.8(a).The total strain across a model of unit length must The Maxwell model consists of a spring and a dashpot in series,as 835 9.33 (8.32 (8.30 (639 常