正在加载图片...
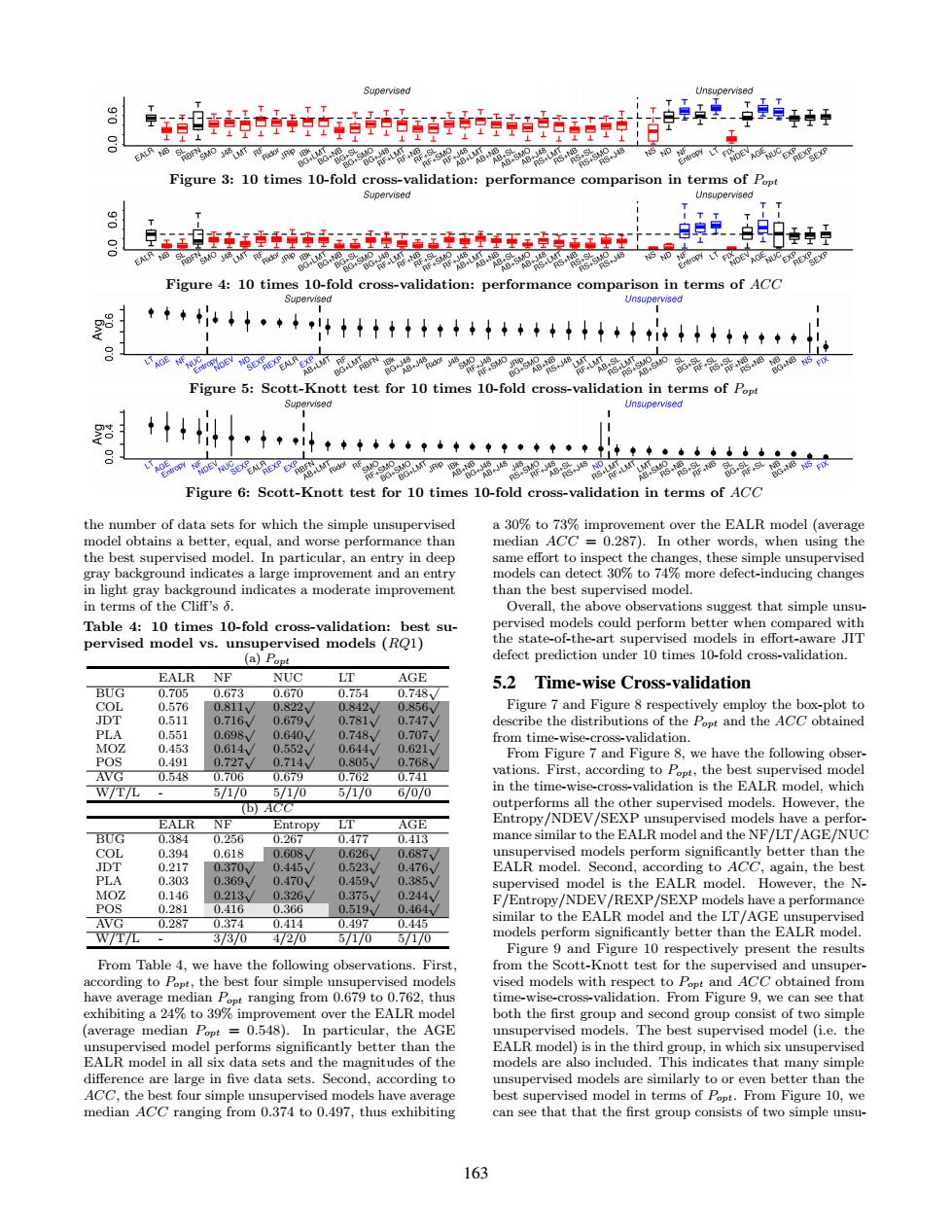
Supervised Unsupervised 8卓自站时中话古的活孕单: T tT T ⊥上上 人山4 1日 雨o0w89喝9a8是 Figure 3:10 times 10-fold cross-validation:performance comparison in terms of Popt Supervised Unsupervised TT I TT T 可oo Figure 4:10 times 10-fold cross-validation:performance comparison in terms of ACC Supervised Unsupervised +◆4·4?+*++i04++**州 0 bel ofetcoon ofs8”器如帝蒂 Figure 5:Scott-Knott test for 10 times 10-fold cross-validation in terms of Popt Supervised Unsupervised + 、↑·外↑++++·?·↑·↑↑·◆↑·◆中年年·小g小女 家吗o如8”%品-88装%离g转6— Figure 6:Scott-Knott test for 10 times 10-fold cross-validation in terms of ACC the number of data sets for which the simple unsupervised a 30%to 73%improvement over the EALR model (average model obtains a better,equal,and worse performance than median ACC=0.287).In other words,when using the the best supervised model.In particular,an entry in deep same effort to inspect the changes,these simple unsupervised gray background indicates a large improvement and an entry models can detect 30%to 74%more defect-inducing changes in light gray background indicates a moderate improvement than the best supervised model. in terms of the Cliff's 5. Overall,the above observations suggest that simple unsu- Table 4:10 times 10-fold cross-validation:best su- pervised models could perform better when compared with pervised model vs.unsupervised models (RQ1) the state-of-the-art supervised models in effort-aware JIT ((a)Popt defect prediction under 10 times 10-fold cross-validation. EAlr Ne NUC LT AGE BUG 0.705 0.748V/ 5.2 Time-wise Cross-validation 0.673 0.670 0.754 COL 0.576 0.811/ 0.822V 0.842V 0.856√/ Figure 7 and Figure 8 respectively employ the box-plot to JDT 0.511 0.716 0.679Y 0.781y 0.747V describe the distributions of the Popt and the ACC obtained PLA 0.551 0.698 0.640 0.748 0.707V from time-wise-cross-validation. MOZ 0.453 0.614 0.552y 0.644 0.621√ POS From Figure 7 and Figure 8,we have the following obser- 0.491 0.727 0.714y 0.805 0.768 AVG 0.548 0.706 0.679 0.762 0.741 vations.First,according to Ppt,the best supervised model W/TL 5/1/0 5/1/0 5/1/0 6/0/0 in the time-wise-cross-validation is the EALR model.which (b)ACC outperforms all the other supervised models.However,the EALR NF Entropy LT AGE Entropy/NDEV/SEXP unsupervised models have a perfor- BUG 0.384 0.256 0.267 0.477 0.413 mance similar to the EALR model and the NF/LT/AGE/NUC COL 0.394 0.618 0.08. 0.626/ 0.687V unsupervised models perform significantly better than the 0.217 0.370 0.445 0.523 0.476/ EALR model.Second,according to ACC,again,the best PLA 0.303 0.369 0.470/ 0.459y 0.385V supervised model is the EALR model.However,the N- MOZ 0.146 0.213 0.326v 0.375 0.244V POS 0.281 0.416 0.366 0.519 0.464V F/Entropy/NDEV/REXP/SEXP models have a performance AVG 0.287 0.374 0.414 0.497 0.445 similar to the EALR model and the LT/AGE unsupervised WTL 31370 4720 57170 5/170 models perform significantly better than the EALR model. Figure 9 and Figure 10 respectively present the results From Table 4,we have the following observations.First. from the Scott-Knott test for the supervised and unsuper- according to Popt,the best four simple unsupervised models vised models with respect to Popt and ACC obtained from have average median Popt ranging from 0.679 to 0.762,thus time-wise-cross-validation.From Figure 9,we can see that exhibiting a 24%to 39%improvement over the EALR model both the first group and second group consist of two simple (average median Popt 0.548).In particular,the AGE unsupervised models.The best supervised model(i.e.the unsupervised model performs significantly better than the EALR model)is in the third group,in which six unsupervised EALR model in all six data sets and the magnitudes of the models are also included.This indicates that many simple difference are large in five data sets.Second,according to unsupervised models are similarly to or even better than the ACC,the best four simple unsupervised models have average best supervised model in terms of Popt.From Figure 10,we median ACC ranging from 0.374 to 0.497,thus exhibiting can see thatthat the first group consists of two simple unsu- 163Figure 3: 10 times 10-fold cross-validation: performance comparison in terms of Popt Figure 4: 10 times 10-fold cross-validation: performance comparison in terms of ACC Figure 5: Scott-Knott test for 10 times 10-fold cross-validation in terms of Popt Figure 6: Scott-Knott test for 10 times 10-fold cross-validation in terms of ACC the number of data sets for which the simple unsupervised model obtains a better, equal, and worse performance than the best supervised model. In particular, an entry in deep gray background indicates a large improvement and an entry in light gray background indicates a moderate improvement in terms of the Cliff’s δ. Table 4: 10 times 10-fold cross-validation: best supervised model vs. unsupervised models (RQ1) (a) Popt EALR NF NUC LT AGE BUG 0.705 0.673 0.670 0.754 0.748√ COL 0.576 0.811√ 0.822√ 0.842√ 0.856√ JDT 0.511 0.716√ 0.679√ 0.781√ 0.747√ PLA 0.551 0.698√ 0.640√ 0.748√ 0.707√ MOZ 0.453 0.614√ 0.552√ 0.644√ 0.621√ POS 0.491 0.727√ 0.714√ 0.805√ 0.768√ AVG 0.548 0.706 0.679 0.762 0.741 W/T/L - 5/1/0 5/1/0 5/1/0 6/0/0 (b) ACC EALR NF Entropy LT AGE BUG 0.384 0.256 0.267 0.477 0.413 COL 0.394 0.618 0.608√ 0.626√ 0.687√ JDT 0.217 0.370√ 0.445√ 0.523√ 0.476√ PLA 0.303 0.369√ 0.470√ 0.459√ 0.385√ MOZ 0.146 0.213√ 0.326√ 0.375√ 0.244√ POS 0.281 0.416 0.366 0.519√ 0.464√ AVG 0.287 0.374 0.414 0.497 0.445 W/T/L - 3/3/0 4/2/0 5/1/0 5/1/0 From Table 4, we have the following observations. First, according to Popt, the best four simple unsupervised models have average median Popt ranging from 0.679 to 0.762, thus exhibiting a 24% to 39% improvement over the EALR model (average median Popt = 0.548). In particular, the AGE unsupervised model performs significantly better than the EALR model in all six data sets and the magnitudes of the difference are large in five data sets. Second, according to ACC, the best four simple unsupervised models have average median ACC ranging from 0.374 to 0.497, thus exhibiting a 30% to 73% improvement over the EALR model (average median ACC = 0.287). In other words, when using the same effort to inspect the changes, these simple unsupervised models can detect 30% to 74% more defect-inducing changes than the best supervised model. Overall, the above observations suggest that simple unsupervised models could perform better when compared with the state-of-the-art supervised models in effort-aware JIT defect prediction under 10 times 10-fold cross-validation. 5.2 Time-wise Cross-validation Figure 7 and Figure 8 respectively employ the box-plot to describe the distributions of the Popt and the ACC obtained from time-wise-cross-validation. From Figure 7 and Figure 8, we have the following observations. First, according to Popt, the best supervised model in the time-wise-cross-validation is the EALR model, which outperforms all the other supervised models. However, the Entropy/NDEV/SEXP unsupervised models have a performance similar to the EALR model and the NF/LT/AGE/NUC unsupervised models perform significantly better than the EALR model. Second, according to ACC, again, the best supervised model is the EALR model. However, the NF/Entropy/NDEV/REXP/SEXP models have a performance similar to the EALR model and the LT/AGE unsupervised models perform significantly better than the EALR model. Figure 9 and Figure 10 respectively present the results from the Scott-Knott test for the supervised and unsupervised models with respect to Popt and ACC obtained from time-wise-cross-validation. From Figure 9, we can see that both the first group and second group consist of two simple unsupervised models. The best supervised model (i.e. the EALR model) is in the third group, in which six unsupervised models are also included. This indicates that many simple unsupervised models are similarly to or even better than the best supervised model in terms of Popt. From Figure 10, we can see that that the first group consists of two simple unsu- 163