正在加载图片...
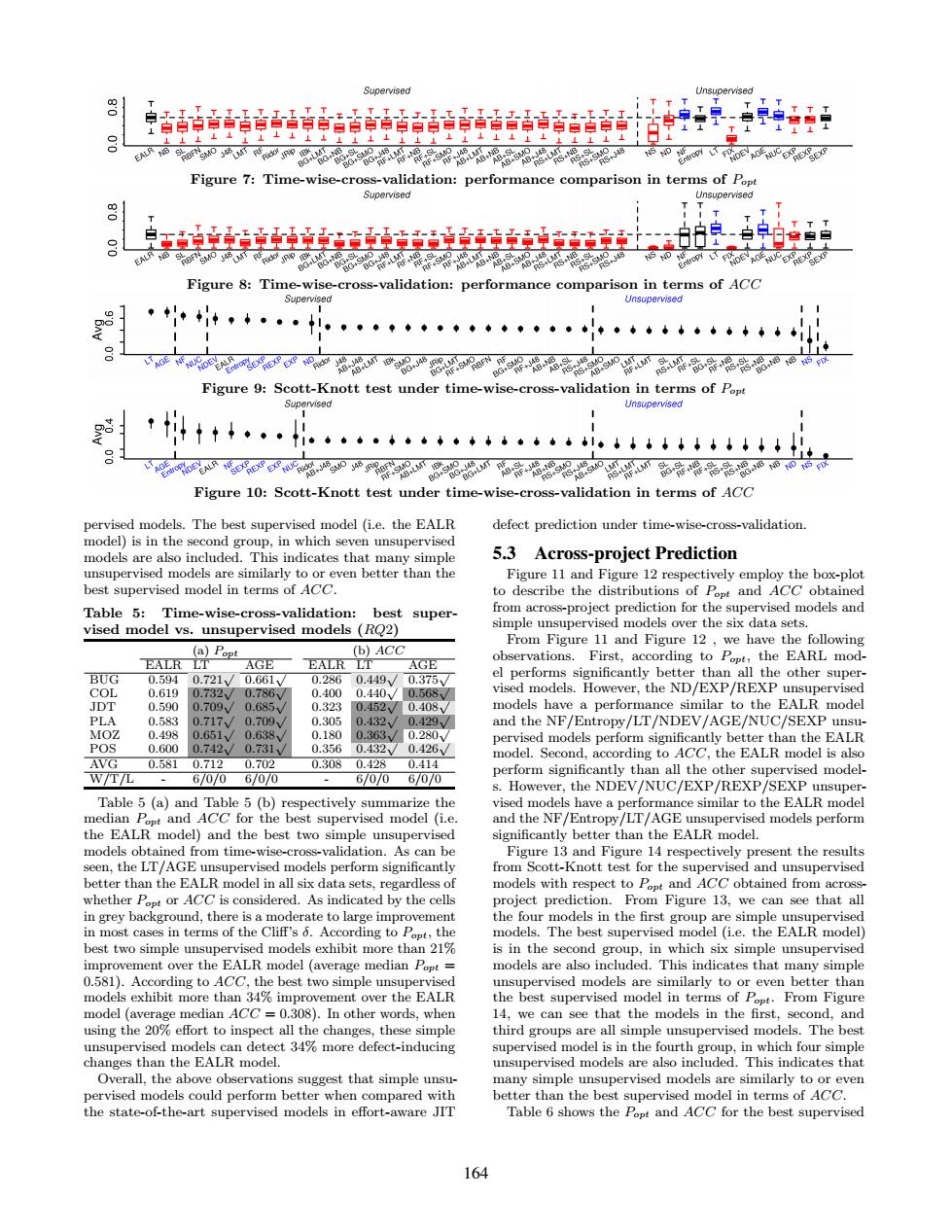
Supervised Unsupervised T IT TT TT 转酯音黄音销音封醋音销音酷请 T 申工 TTT T⊥ 上上1上1144上上上上4 西oP州a”品喂架-89帽卷%是89oowe Figure 7:Time-wise-cross-validation:performance comparison in terms of Popt Supervised Unsupervised T TT TTT 白-白卓白合白白 Figure 8:Time-wise-cross-validation:performance comparison in terms of ACC Supervised Unsupervised 8 T Figure 9:Scott-Knott test under time-wise-cross-validation in terms of Popt Supervised Unsupervised 8 十中◆·…i。·心·4··◆◆◆+·。···川↓↓+↓↓ ooog8oaP张 Figure 10:Scott-Knott test under time-wise-cross-validation in terms of ACC pervised models.The best supervised model (i.e.the EALR defect prediction under time-wise-cross-validation model)is in the second group,in which seven unsupervised models are also included.This indicates that many simple 5.3 Across-project Prediction unsupervised models are similarly to or even better than the Figure 11 and Figure 12 respectively employ the box-plot best supervised model in terms of ACC to describe the distributions of Popt and ACC obtained Table 5:Time-wise-cross-validation: best super- from across-project prediction for the supervised models and vised model vs.unsupervised models (RO2) simple unsupervised models over the six data sets From Figure 11 and Figure 12,we have the following (a)Popt (b)ACC EALR LT AGE EALR LT AGE observations.First,according to Popt,the EARL mod- BUG 0.594 .721V0.661W 0.2860.449、/ el performs significantly better than all the other super- 0.375V/ ●●】 0.619 0732、 0.400 0.440、/ 0.568/ vised models.However.the ND/EXP/REXP unsupervised .. JDT 0.590 0.709 0.685、 0.323 0.452/ 0.4087 models have a performance similar to the EALR model PLA 0.583 0.717 0.709 0.305 0.432 0.429/ and the NF/Entropy/LT/NDEV/AGE/NUC/SEXP unsu- MOZ 0.498 0.65、 0.6.38 0.180 0.363、/ 0.2807 pervised models perform significantly better than the EALR POS 0.600 0.742 0.731y 0.356 0.432/ 0.426/ model.Second,according to ACC,the EALR model is also AVG 0.5810.7120.702 0.3080.428 0.414 perform significantly than all the other supervised model- W/T/L 6/0/06/0/0 6/0/06/0/0 s.However,the NDEV/NUC/EXP/REXP/SEXP unsuper- Table 5 (a)and Table 5(b)respectively summarize the vised models have a performance similar to the EALR model median Popt and ACC for the best supervised model (i.e and the NF/Entropy/LT/AGE unsupervised models perform the EALR model)and the best two simple unsupervised significantly better than the EALR model. models obtained from time-wise-cross-validation.As can be Figure 13 and Figure 14 respectively present the results seen,the LT/AGE unsupervised models perform significantly from Scott-Knott test for the supervised and unsupervised better than the EALR model in all six data sets,regardless of models with respect to Popt and ACC obtained from across- whether Popt or ACC is considered.As indicated by the cells project prediction.From Figure 13,we can see that all in grey background,there is a moderate to large improvement the four models in the first group are simple unsupervised in most cases in terms of the Cliff's 6.According to Popt,the models.The best supervised model(i.e.the EALR model) best two simple unsupervised models exhibit more than 21% is in the second group,in which six simple unsupervised improvement over the EALR model(average median Popt = models are also included.This indicates that many simple 0.581).According to ACC,the best two simple unsupervised unsupervised models are similarly to or even better than models exhibit more than 34%improvement over the EALR the best supervised model in terms of Popt.From Figure model (average median ACC =0.308).In other words,when 14,we can see that the models in the first,second,and using the 20%effort to inspect all the changes,these simple third groups are all simple unsupervised models.The best unsupervised models can detect 34%more defect-inducing supervised model is in the fourth group,in which four simple changes than the EALR model. unsupervised models are also included.This indicates that Overall,the above observations suggest that simple unsu- many simple unsupervised models are similarly to or even pervised models could perform better when compared with better than the best supervised model in terms of ACC. the state-of-the-art supervised models in effort-aware JIT Table 6 shows the Popt and ACC for the best supervised 164Figure 7: Time-wise-cross-validation: performance comparison in terms of Popt Figure 8: Time-wise-cross-validation: performance comparison in terms of ACC Figure 9: Scott-Knott test under time-wise-cross-validation in terms of Popt Figure 10: Scott-Knott test under time-wise-cross-validation in terms of ACC pervised models. The best supervised model (i.e. the EALR model) is in the second group, in which seven unsupervised models are also included. This indicates that many simple unsupervised models are similarly to or even better than the best supervised model in terms of ACC. Table 5: Time-wise-cross-validation: best supervised model vs. unsupervised models (RQ2) (a) Popt (b) ACC EALR LT AGE EALR LT AGE BUG 0.594 0.721√ 0.661√ 0.286 0.449√ 0.375√ COL 0.619 0.732√ 0.786√ 0.400 0.440√ 0.568√ JDT 0.590 0.709√ 0.685√ 0.323 0.452√ 0.408√ PLA 0.583 0.717√ 0.709√ 0.305 0.432√ 0.429√ MOZ 0.498 0.651√ 0.638√ 0.180 0.363√ 0.280√ POS 0.600 0.742√ 0.731√ 0.356 0.432√ 0.426√ AVG 0.581 0.712 0.702 0.308 0.428 0.414 W/T/L - 6/0/0 6/0/0 - 6/0/0 6/0/0 Table 5 (a) and Table 5 (b) respectively summarize the median Popt and ACC for the best supervised model (i.e. the EALR model) and the best two simple unsupervised models obtained from time-wise-cross-validation. As can be seen, the LT/AGE unsupervised models perform significantly better than the EALR model in all six data sets, regardless of whether Popt or ACC is considered. As indicated by the cells in grey background, there is a moderate to large improvement in most cases in terms of the Cliff’s δ. According to Popt, the best two simple unsupervised models exhibit more than 21% improvement over the EALR model (average median Popt = 0.581). According to ACC, the best two simple unsupervised models exhibit more than 34% improvement over the EALR model (average median ACC = 0.308). In other words, when using the 20% effort to inspect all the changes, these simple unsupervised models can detect 34% more defect-inducing changes than the EALR model. Overall, the above observations suggest that simple unsupervised models could perform better when compared with the state-of-the-art supervised models in effort-aware JIT defect prediction under time-wise-cross-validation. 5.3 Across-project Prediction Figure 11 and Figure 12 respectively employ the box-plot to describe the distributions of Popt and ACC obtained from across-project prediction for the supervised models and simple unsupervised models over the six data sets. From Figure 11 and Figure 12 , we have the following observations. First, according to Popt, the EARL model performs significantly better than all the other supervised models. However, the ND/EXP/REXP unsupervised models have a performance similar to the EALR model and the NF/Entropy/LT/NDEV/AGE/NUC/SEXP unsupervised models perform significantly better than the EALR model. Second, according to ACC, the EALR model is also perform significantly than all the other supervised models. However, the NDEV/NUC/EXP/REXP/SEXP unsupervised models have a performance similar to the EALR model and the NF/Entropy/LT/AGE unsupervised models perform significantly better than the EALR model. Figure 13 and Figure 14 respectively present the results from Scott-Knott test for the supervised and unsupervised models with respect to Popt and ACC obtained from acrossproject prediction. From Figure 13, we can see that all the four models in the first group are simple unsupervised models. The best supervised model (i.e. the EALR model) is in the second group, in which six simple unsupervised models are also included. This indicates that many simple unsupervised models are similarly to or even better than the best supervised model in terms of Popt. From Figure 14, we can see that the models in the first, second, and third groups are all simple unsupervised models. The best supervised model is in the fourth group, in which four simple unsupervised models are also included. This indicates that many simple unsupervised models are similarly to or even better than the best supervised model in terms of ACC. Table 6 shows the Popt and ACC for the best supervised 164