正在加载图片...
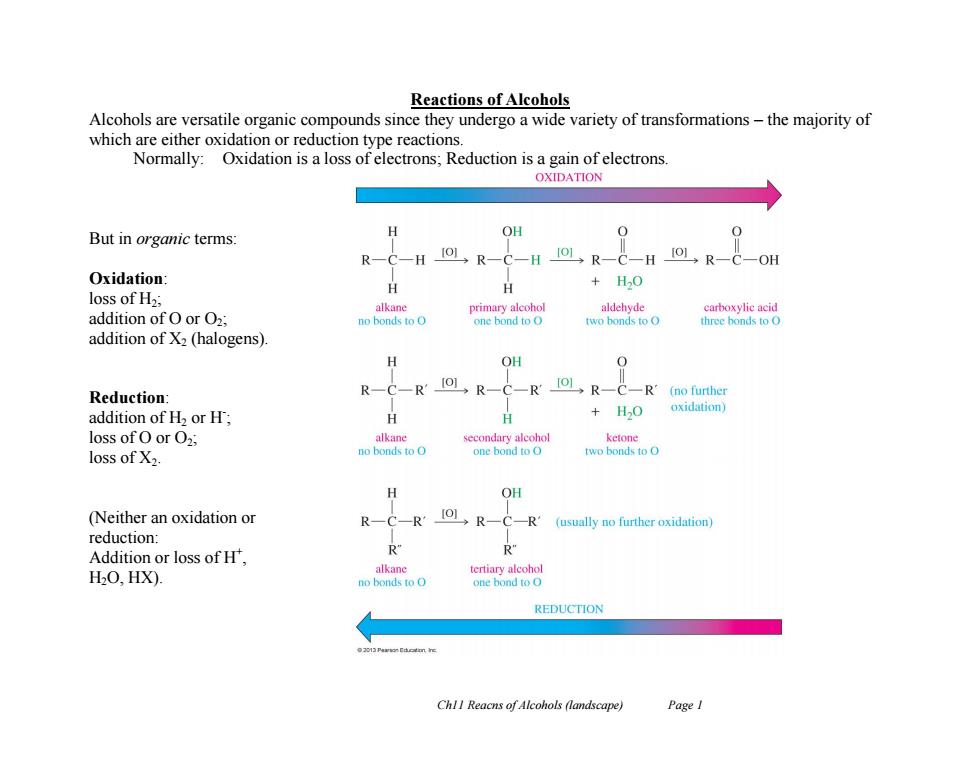
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations-the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally:Oxidation is a loss of electrons;Reduction is a gain of electrons. OXIDATION But in organic terms: OH Io] H →R CH[OL,R- Oxidation H H +H0 loss of H2; alkane primary alcohol aldehyde carboxylie acid addition of O or O2; no bonds to O one bond to O two bonds to O three honds to O addition of X2 (halogens). H OH Reduction: R'10L,R-C-R1OL,R-C-R'(no further oxidation) addition of H2 or H; H +B0 loss of O or O2 alkane secondary alcohol ketone loss of X2. no bonds to o one bond to O two bonds to 0 OH (Neither an oxidation or 101,R-C- -R'(usually no further oxidation) reduction: Addition or loss of H, R" H2O.,HX). alkane tertiary alcohol no bonds to one bond to O REDUCTION ChlI Reacns of Alcohols (landscape) Page ICh11 Reacns of Alcohols (landscape) Page 1 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations – the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation is a loss of electrons; Reduction is a gain of electrons. But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H2; addition of O or O2; addition of X2 (halogens). Reduction: addition of H2 or H- ; loss of O or O2; loss of X2. (Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H+ , H2O, HX)