正在加载图片...
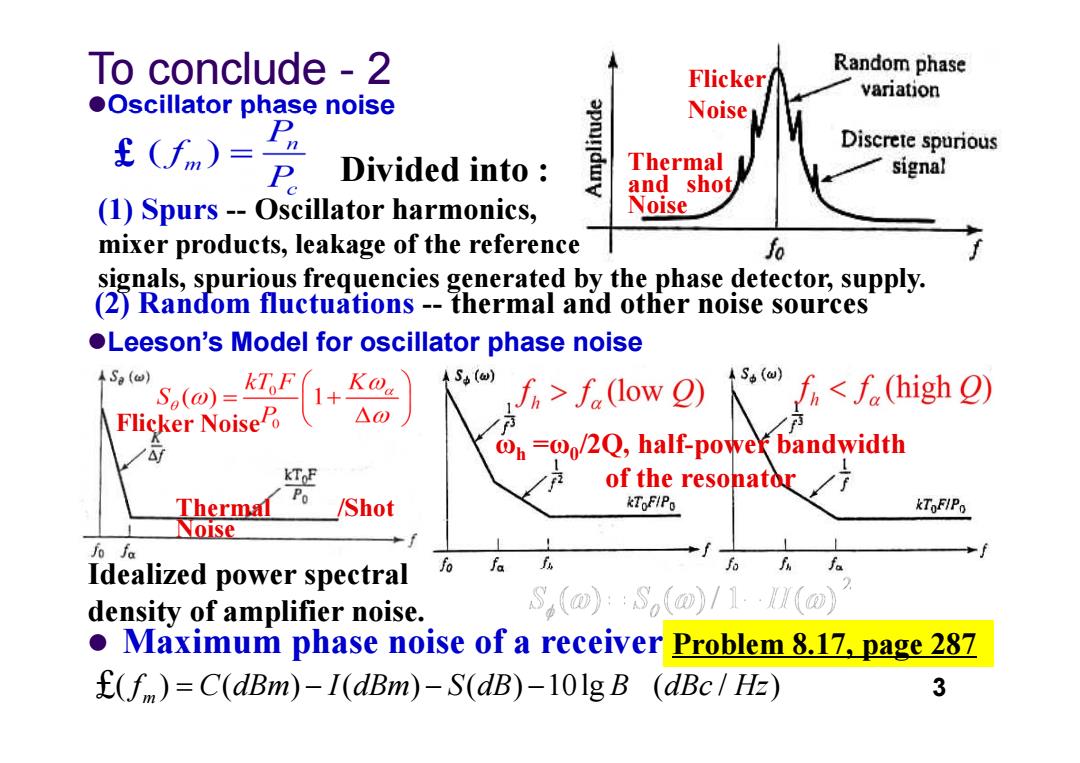
To conclude-2 Flicker Random phase variation Oscillator phase noise Noise £(fm)= Discrete spurious P Divided into Thermal signal and shot (1)Spurs--Oscillator harmonics, Noise mixer products,leakage of the reference fo signals,spurious frequencies generated by the phase detector,supply. (2)Random fluctuations--thermal and other noise sources Leeson's Model for oscillator phase noise ASp(w) So(@)=kZiF 1+ S(w) S.(w) fi<f (high O) Flicker NoiseP f>f(low e) /f @n=00/2Q,half-power bandwidth KToF of the resonator Po Thermal /Shot kToFIPo kToFIPo Noise 6 Idealized power spectral fo fa fa density of amplifier noise. S(0):S,m)/1·以(@ Maximum phase noise of a receiver Problem 8.17,page 287 (f )=C(dBm)-I(dBm)-S(dB)-101g B (dBc/Hz) 3Oscillator phase noise To conclude - 2 Flicker Noise Thermal and shot Noise Divided into : (1) Spurs -- Oscillator harmonics, mixer products, leakage of the reference signals, spuriousfrequencies generated by the phase detector, supply. (2) Random fluctuations -- thermal and other noise sources £ Leeson’s Model for oscillator phase noise Flicker Noise Thermal /Shot Noise Idealized power spectral density of amplifier noise. ωh =ω0/2Q, half-power bandwidth of the resonator Maximum phase noise of a receiver £( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 10lg ( / ) 3 mf C dBm I dBm S dB B dBc Hz Problem 8.17, page 287