正在加载图片...
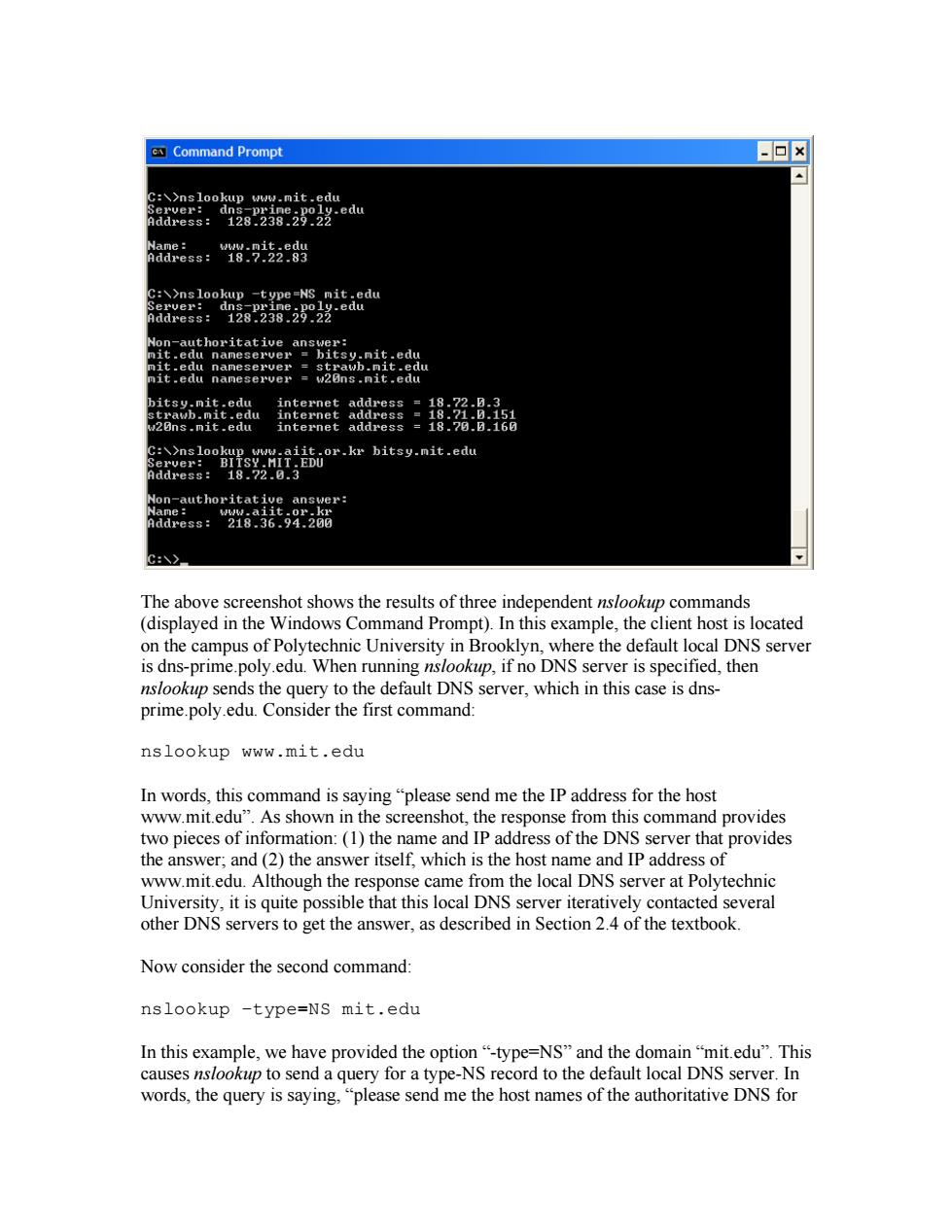
Command Prompt 回风 address:18-712283 器 莲要点 oe bitsy.nic.edw The above mmands shows thetreend amp on the campus of Pol ONS server kup,if no I server is specified, nslookup sends the query to the default DNS server,which in this case is dns- prime.poly.edu.Consider the first command: nslookup www.mit.edu In words,this command is saying"please send me the IP address for the host www.mit.edu".As shown in the screenshot,the response from this command provides two pieces of information:(1)the name and IP address of the DNS server that provides the answer;and(2)the answer itself,which is the host name and IP address of www.mit.edu.Although the response came from the local DNS server at Polytechnic University.it is quite possible that this local DNS server iteratively contacted several other DNS servers to get the answer,as described in Section 2.4 of the textbook. Now consider the second command: nslookup -type=NS mit.edu -type-NS"and the y for a type ecord t the d ult local me the host names of the authoritative DNS for The above screenshot shows the results of three independent nslookup commands (displayed in the Windows Command Prompt). In this example, the client host is located on the campus of Polytechnic University in Brooklyn, where the default local DNS server is dns-prime.poly.edu. When running nslookup, if no DNS server is specified, then nslookup sends the query to the default DNS server, which in this case is dnsprime.poly.edu. Consider the first command: nslookup www.mit.edu In words, this command is saying “please send me the IP address for the host www.mit.edu”. As shown in the screenshot, the response from this command provides two pieces of information: (1) the name and IP address of the DNS server that provides the answer; and (2) the answer itself, which is the host name and IP address of www.mit.edu. Although the response came from the local DNS server at Polytechnic University, it is quite possible that this local DNS server iteratively contacted several other DNS servers to get the answer, as described in Section 2.4 of the textbook. Now consider the second command: nslookup –type=NS mit.edu In this example, we have provided the option “-type=NS” and the domain “mit.edu”. This causes nslookup to send a query for a type-NS record to the default local DNS server. In words, the query is saying, “please send me the host names of the authoritative DNS for