正在加载图片...
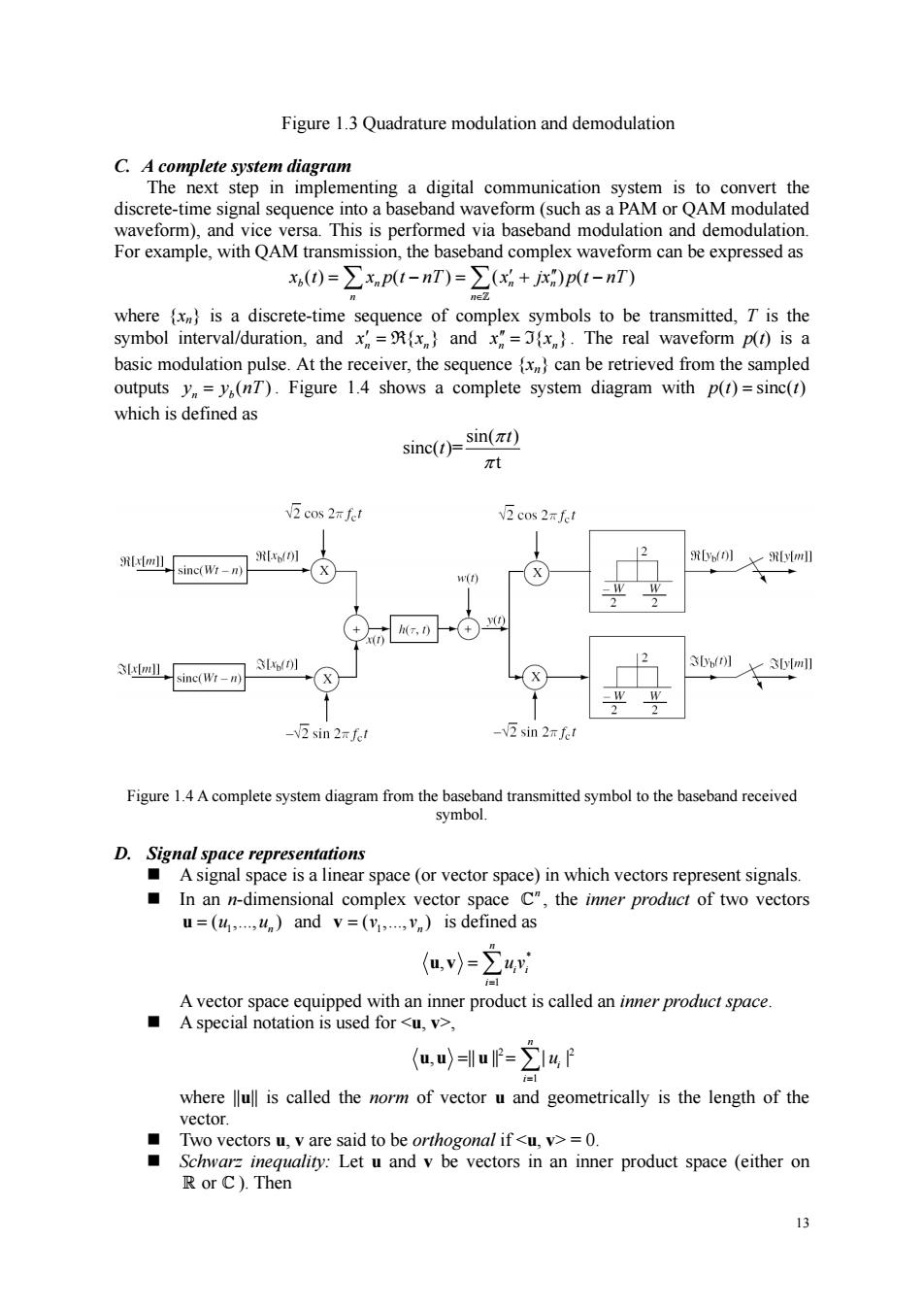
Figure 1.3 Quadrature modulation and demodulation C.A complete system diagram discrane next step in implemen seband waveform (such as a PAM discrete-time signal sequence into a baseband waveform (such asa waveform),and ormed via baseband modulation an For example.with OAM transmission.the baseband complex waveform can be expressed as x()=∑xp1-nT)=∑(x+jx)pt-nT) where is a discrete-tim ymbol aveform p()is basic modulation pulse.At the receiver,the sequence can be retrieved from the sampled outputs y=y(nT).Figure 1.4 shows a complete system diagram with p(t)=sinc(t) which is defined as sinc(t)=sin(t) t 互c0s2过 cos 2f ⊙四 12 ,sM-回aw01 (8 m大 -V2 sin 2mfet 2 sin 2x fet D.Signal space representations A signal space is a linear space(or vector space)in which vectors represent signals. In an n-dimensional complex vector space C",the inner product of two vectors u=(uu)and v=(v.v.)is defined as A vector space equipped with an inner product is called an inmer product space. A special notation is used for <u,v>, (u)=u=∑I4P where llull is called the norm of vector u and geometrically is the length of the vector. orthogonal if<u,v>=0 13 13 Figure 1.3 Quadrature modulation and demodulation C. A complete system diagram The next step in implementing a digital communication system is to convert the discrete-time signal sequence into a baseband waveform (such as a PAM or QAM modulated waveform), and vice versa. This is performed via baseband modulation and demodulation. For example, with QAM transmission, the baseband complex waveform can be expressed as () ( ) ( ) ( ) b n nn n n x t x p t nT x jx p t nT ∈ = −= + − ∑ ∑ ′ ′′ Z where {xn} is a discrete-time sequence of complex symbols to be transmitted, T is the symbol interval/duration, and { } n n x′ = R x and { } n n x′′ = I x . The real waveform p(t) is a basic modulation pulse. At the receiver, the sequence {xn} can be retrieved from the sampled outputs ( ) n b y = y nT . Figure 1.4 shows a complete system diagram with p( ) sinc( ) t t = which is defined as sin( ) sinc( )= t t t π π Figure 1.4 A complete system diagram from the baseband transmitted symbol to the baseband received symbol. D. Signal space representations A signal space is a linear space (or vector space) in which vectors represent signals. In an n-dimensional complex vector space n C , the inner product of two vectors 1 ( ,., ) n u = u u and 1 ( ,., ) n v = v v is defined as * 1 , n i i i u v = u v = ∑ A vector space equipped with an inner product is called an inner product space. A special notation is used for <u, v>, 2 2 1 , || || | | n i i u = uu u = = ∑ where ||u|| is called the norm of vector u and geometrically is the length of the vector. Two vectors u, v are said to be orthogonal if <u, v> = 0. Schwarz inequality: Let u and v be vectors in an inner product space (either on R C or ). Then