正在加载图片...
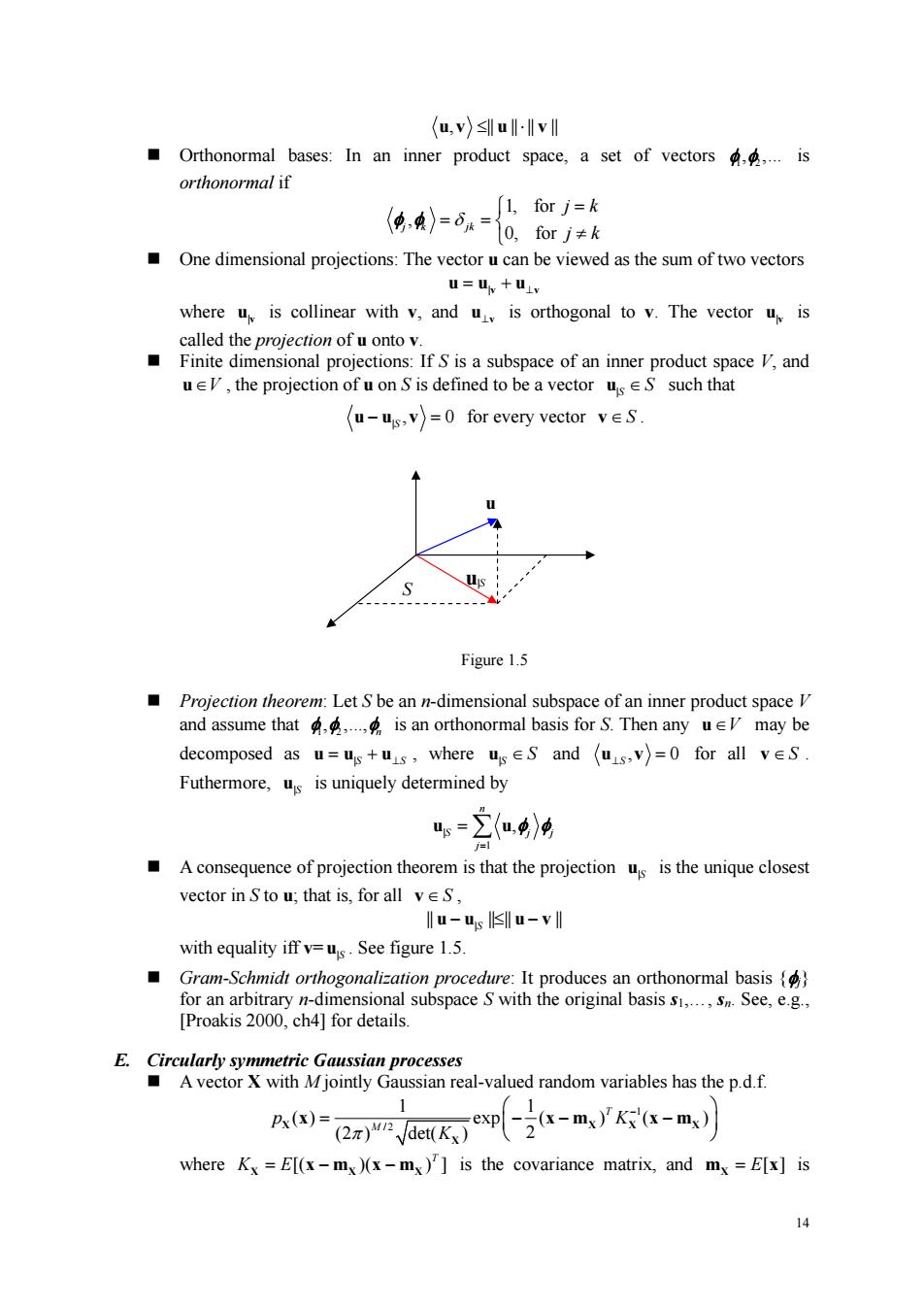
(u.v)slull-Ivl Orthonormal bases:In an inner product space,a set of vectors is orthonormal if %-6-收 One dimensional projections:The vector ucan be viewed as the sum of two vectors U=U+u where u is collinear with v,and u is orthogonal to v.The vector u is Ifis a subspace of an inner product space,and u,the projection of u onS is defined to be a vector usS such that (u-us.v)=0 for every vector ves Proiection theoren let s be an n-dimensional subspace of an inner product space v and assume that is an orthonormal basis for S.Then any u may be decomposed as u=us+us,where us∈Sand(us,v)=0 for all v∈S Futhermore,us is uniquely determined by “5=2(u》两 Aconsequence of projection theorem is that the projections is the unique closest vector in S to u;that is,for all veS, llu-us lsllu-vll with figure 1.5. Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization procedure:It produces an orthonormal basis for an arbitrary n-dimensional subspace S with the original basis s.s.See,e.g. [Proakis 2000,ch4]for details. tan processes ssian real-valued random variables has the p.d.f ()-n dei(K)exp-m)'(-m) where Kx=E[(x-mx)(x-mx)is the covariance matrix,and mx =E[x]is 1414 uv u v , || || || || ≤ ⋅ Orthonormal bases: In an inner product space, a set of vectors 1 2 φ , ,. φ is orthonormal if 1, for , 0, for j k jk j k j k δ ⎧ = = = ⎨ ⎩ ≠ φ φ One dimensional projections: The vector u can be viewed as the sum of two vectors uu u = |v v + ⊥ where u|v is collinear with v, and u⊥v is orthogonal to v. The vector u|v is called the projection of u onto v. Finite dimensional projections: If S is a subspace of an inner product space V, and u∈V , the projection of u on S is defined to be a vector |S u ∈ S such that | , 0 uuv − = S for every vector v ∈ S . Figure 1.5 Projection theorem: Let S be an n-dimensional subspace of an inner product space V and assume that 1 2 , ,., φ φ φn is an orthonormal basis for S. Then any u∈V may be decomposed as uu u = + |S S ⊥ , where |S u ∈ S and , 0 u v ⊥S = for all v ∈ S . Futhermore, u|S is uniquely determined by | 1 , n S jj j= u u = ∑ φ φ A consequence of projection theorem is that the projection u|S is the unique closest vector in S to u; that is, for all v ∈ S , | || || || || uu uv − S ≤ − with equality iff v= u|S . See figure 1.5. Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization procedure: It produces an orthonormal basis {φj} for an arbitrary n-dimensional subspace S with the original basis s1,., sn. See, e.g., [Proakis 2000, ch4] for details. E. Circularly symmetric Gaussian processes A vector X with M jointly Gaussian real-valued random variables has the p.d.f. 1 / 2 1 1 ( ) exp ( ) ( ) (2 ) det( ) 2 T M p K π K ⎛ ⎞ − = −− − ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ X XX X X x xm xm where [( )( ) ] T K E X XX =− − xm xm is the covariance matrix, and [ ] m x X = E is u S u|S