正在加载图片...
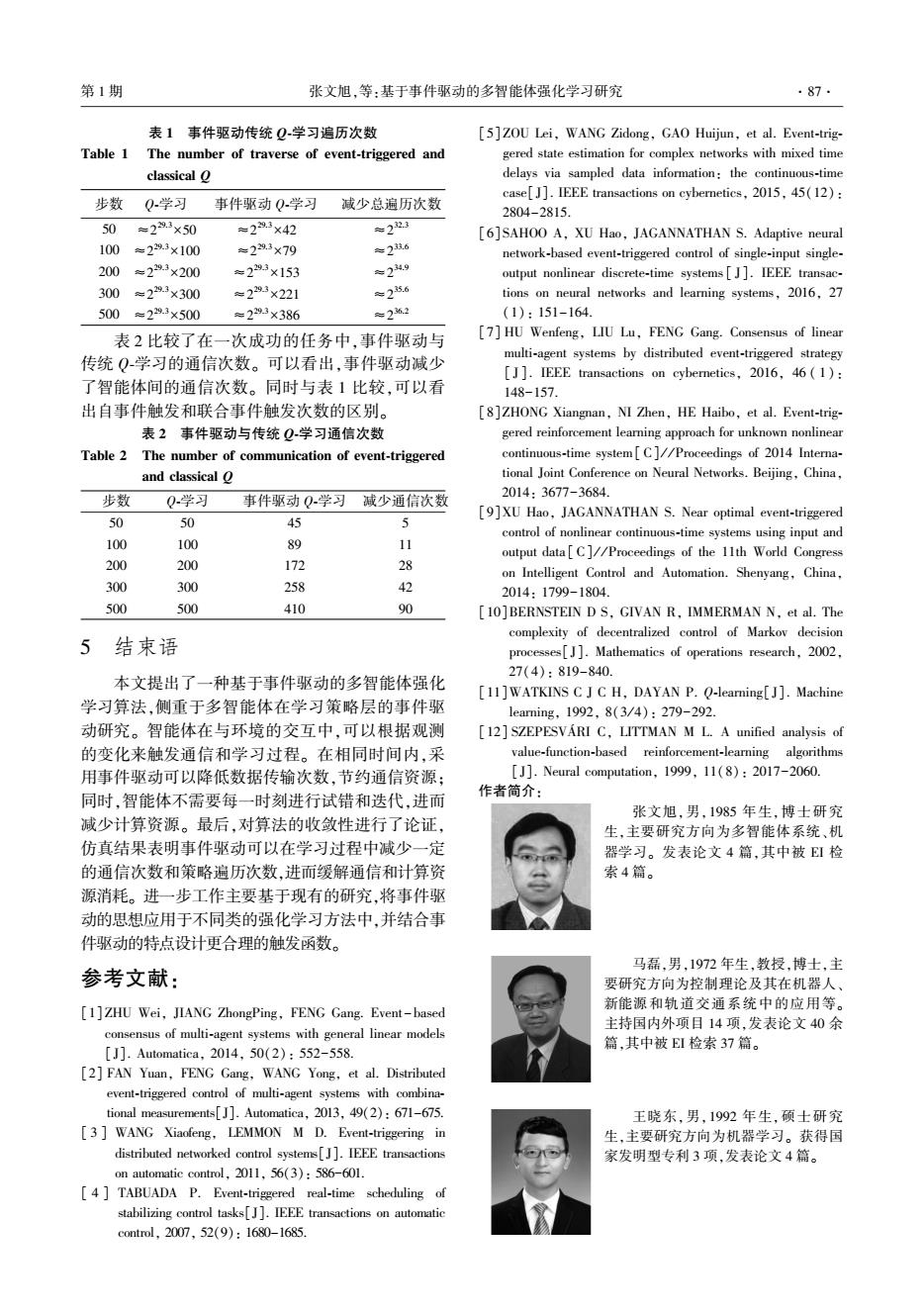
第1期 张文旭,等:基于事件驱动的多智能体强化学习研究 .87. 表1事件驱动传统Q学习遍历次数 [5]ZOU Lei,WANG Zidong,GAO Huijun,et al.Event-trig- Table 1 The number of traverse of event-triggered and gered state estimation for complex networks with mixed time classical o delays via sampled data information:the continuous-time case[J].IEEE transactions on cybernetics,2015,45(12): 步数 Q学习 事件驱动Q学习 减少总遍历次数 2804-2815. 50 =29.3×50 =293×42 年223 [6]SAHOO A,XU Hao,JAGANNATHAN S.Adaptive neural 100 =229.3×100 =2293×79 年2超6 network-based event-triggered control of single-input single- 200 =29.3×200 =229.3×153 六24.9 output nonlinear discrete-time systems[J].IEEE transac- 300 =229.3×300 =2293×221 ≈25.6 tions on neural networks and learning systems,2016,27 500=29.3×500 =2293×386 产262 (1):151-164 表2比较了在一次成功的任务中,事件驱动与 [7]HU Wenfeng,LIU Lu,FENG Gang.Consensus of linear 传统Q学习的通信次数。可以看出,事件驱动减少 multi-agent systems by distributed event-triggered strategy [J].IEEE transactions on cybernetics,2016,46(1): 了智能体间的通信次数。同时与表1比较,可以看 148-157. 出自事件触发和联合事件触发次数的区别。 [8 ]ZHONG Xiangnan,NI Zhen,HE Haibo,et al.Event-trig- 表2事件驱动与传统Q学习通信次数 gered reinforcement learning approach for unknown nonlinear Table 2 The number of communication of event-triggered continuous-time system[C]//Proceedings of 2014 Interna- and classical O tional Joint Conference on Neural Networks.Beijing,China, 步数 Q学习 事件驱动Q学习减少通信次数 2014:3677-3684. 50 50 45 J [9]XU Hao,JAGANNATHAN S.Near optimal event-triggered control of nonlinear continuous-time systems using input and 100 100 89 11 output data[C]//Proceedings of the 11th World Congress 200 200 172 子 on Intelligent Control and Automation.Shenyang,China, 300 300 258 名 2014:1799-1804. 500 500 410 % [10]BERNSTEIN D S,GIVAN R,IMMERMAN N,et al.The complexity of decentralized control of Markov decision 5 结束语 processes[J].Mathematics of operations research,2002. 27(4):819-840. 本文提出了一种基于事件驱动的多智能体强化 [11]WATKINS C J C H,DAYAN P.Q-learning[J].Machine 学习算法,侧重于多智能体在学习策略层的事件驱 1 earning,1992,8(3/4):279-292. 动研究。智能体在与环境的交互中,可以根据观测 [12]SZEPESVARI C,LITTMAN M L.A unified analysis of 的变化来触发通信和学习过程。在相同时间内,采 value-function-based reinforcement-learning algorithms 用事件驱动可以降低数据传输次数,节约通信资源: [J].Neural computation,1999,11(8):2017-2060. 作者简介: 同时,智能体不需要每一时刻进行试错和迭代,进而 张文旭,男,1985年生,博士研究 减少计算资源。最后,对算法的收敛性进行了论证, 生,主要研究方向为多智能体系统、机 仿真结果表明事件驱动可以在学习过程中减少一定 器学习。发表论文4篇,其中被EI检 的通信次数和策略遍历次数,进而缓解通信和计算资 索4篇。 源消耗。进一步工作主要基于现有的研究,将事件驱 动的思想应用于不同类的强化学习方法中,并结合事 件驱动的特点设计更合理的触发函数。 马磊,男,1972年生,教授,博士,主 参考文献: 要研究方向为控制理论及其在机器人、 [1]ZHU Wei,JIANG ZhongPing,FENG Gang.Event-based 新能源和轨道交通系统中的应用等。 主持国内外项目14项,发表论文40余 consensus of multi-agent systems with general linear models 篇,其中被EI检索37篇。 [J].Automatica,2014,50(2):552-558. [2]FAN Yuan,FENG Gang,WANG Yong,et al.Distributed event-triggered control of multi-agent systems with combina- tional measurements[].Automatica,2013,49(2):671-675. 王晓东,男,1992年生,硕士研究 [3 WANG Xiaofeng,LEMMON M D.Event-triggering in 生,主要研究方向为机器学习。获得国 distributed networked control systems[J].IEEE transactions 家发明型专利3项,发表论文4篇。 on automatic control,2011,56(3):586-601. [4 TABUADA P.Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks[].IEEE transactions on automatic control..2007,52(9):1680-1685.表 1 事件驱动传统 Q⁃学习遍历次数 Table 1 The number of traverse of event⁃triggered and classical Q 步数 Q⁃学习 事件驱动 Q⁃学习 减少总遍历次数 50 ≈2 29.3×50 ≈2 29.3×42 ≈2 32.3 100 ≈2 29.3×100 ≈2 29.3×79 ≈2 33.6 200 ≈2 29.3×200 ≈2 29.3×153 ≈2 34.9 300 ≈2 29.3×300 ≈2 29.3×221 ≈2 35.6 500 ≈2 29.3×500 ≈2 29.3×386 ≈2 36.2 表 2 比较了在一次成功的任务中,事件驱动与 传统 Q⁃学习的通信次数。 可以看出,事件驱动减少 了智能体间的通信次数。 同时与表 1 比较,可以看 出自事件触发和联合事件触发次数的区别。 表 2 事件驱动与传统 Q⁃学习通信次数 Table 2 The number of communication of event⁃triggered and classical Q 步数 Q⁃学习 事件驱动 Q⁃学习 减少通信次数 50 50 45 5 100 100 89 11 200 200 172 28 300 300 258 42 500 500 410 90 5 结束语 本文提出了一种基于事件驱动的多智能体强化 学习算法,侧重于多智能体在学习策略层的事件驱 动研究。 智能体在与环境的交互中,可以根据观测 的变化来触发通信和学习过程。 在相同时间内,采 用事件驱动可以降低数据传输次数,节约通信资源; 同时,智能体不需要每一时刻进行试错和迭代,进而 减少计算资源。 最后,对算法的收敛性进行了论证, 仿真结果表明事件驱动可以在学习过程中减少一定 的通信次数和策略遍历次数,进而缓解通信和计算资 源消耗。 进一步工作主要基于现有的研究,将事件驱 动的思想应用于不同类的强化学习方法中,并结合事 件驱动的特点设计更合理的触发函数。 参考文献: [1]ZHU Wei, JIANG ZhongPing, FENG Gang. Event -based consensus of multi⁃agent systems with general linear models [J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(2): 552-558. [2] FAN Yuan, FENG Gang, WANG Yong, et al. Distributed event⁃triggered control of multi⁃agent systems with combina⁃ tional measurements[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(2): 671-675. [ 3 ] WANG Xiaofeng, LEMMON M D. Event⁃triggering in distributed networked control systems[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2011, 56(3): 586-601. [ 4 ] TABUADA P. Event⁃triggered real⁃time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2007, 52(9): 1680-1685. [5] ZOU Lei, WANG Zidong, GAO Huijun, et al. Event⁃trig⁃ gered state estimation for complex networks with mixed time delays via sampled data information: the continuous⁃time case[J]. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 2015, 45(12): 2804-2815. [6] SAHOO A, XU Hao, JAGANNATHAN S. Adaptive neural network⁃based event⁃triggered control of single⁃input single⁃ output nonlinear discrete⁃time systems [ J]. IEEE transac⁃ tions on neural networks and learning systems, 2016, 27 (1): 151-164. [7] HU Wenfeng, LIU Lu, FENG Gang. Consensus of linear multi⁃agent systems by distributed event⁃triggered strategy [ J]. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 2016, 46 ( 1 ): 148-157. [8]ZHONG Xiangnan, NI Zhen, HE Haibo, et al. Event⁃trig⁃ gered reinforcement learning approach for unknown nonlinear continuous⁃time system[ C] / / Proceedings of 2014 Interna⁃ tional Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Beijing, China, 2014: 3677-3684. [9]XU Hao, JAGANNATHAN S. Near optimal event⁃triggered control of nonlinear continuous⁃time systems using input and output data [ C] / / Proceedings of the 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation. Shenyang, China, 2014: 1799-1804. [10]BERNSTEIN D S, GIVAN R, IMMERMAN N, et al. The complexity of decentralized control of Markov decision processes[ J]. Mathematics of operations research, 2002, 27(4): 819-840. [11]WATKINS C J C H, DAYAN P. Q⁃learning[ J]. Machine learning, 1992, 8(3 / 4): 279-292. [12] SZEPESVÁRI C, LITTMAN M L. A unified analysis of value⁃function⁃based reinforcement⁃learning algorithms [J]. Neural computation, 1999, 11(8): 2017-2060. 作者简介: 张文旭,男,1985 年生,博士研究 生,主要研究方向为多智能体系统、机 器学习。 发表论文 4 篇,其中被 EI 检 索 4 篇。 马磊,男,1972 年生,教授,博士,主 要研究方向为控制理论及其在机器人、 新能源和轨道交通系统中的应用等。 主持国内外项目 14 项,发表论文 40 余 篇,其中被 EI 检索 37 篇。 王晓东,男,1992 年生,硕士研究 生,主要研究方向为机器学习。 获得国 家发明型专利 3 项,发表论文 4 篇。 第 1 期 张文旭,等:基于事件驱动的多智能体强化学习研究 ·87·