正在加载图片...
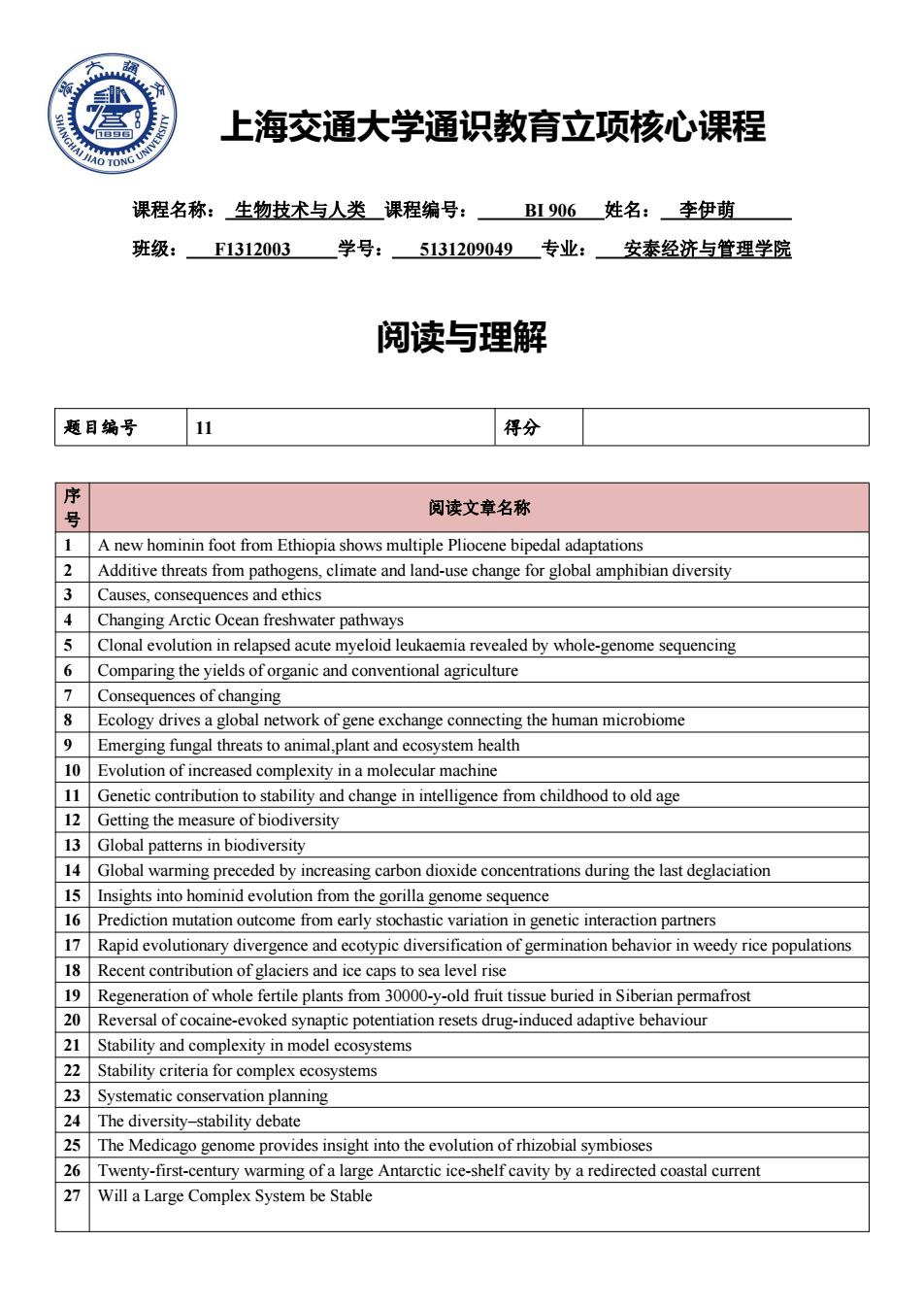
上海交通大学通识教育立项核心课程 课程名称:生物技术与人类课程编号:B1906姓名:李伊萌 班级:F1312003 学号: 5131209049专业:安泰经济与管理学院 阅读与理解 题目编号 11 得分 序 阅读文章名称 1 A new hominin foot from Ethiopia shows multiple Pliocene bipedal adaptations 2 Additive threats from pathogens,climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity 3 Causes,consequences and ethics 4 Changing Arctic Ocean freshwater pathways 5 Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing 6 Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture 7 Consequences of changing 8 Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome 9 Emerging fungal threats to animal,plant and ecosystem health 10 Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine 11 Genetic contribution to stability and change in intelligence from childhood to old age 12 Getting the measure of biodiversity 13 Global patterns in biodiversity 14 Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation 15 Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence 16 Prediction mutation outcome from early stochastic variation in genetic interaction partners 17 Rapid evolutionary divergence and ecotypic diversification of germination behavior in weedy rice populations 18 Recent contribution of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise 19 Regeneration of whole fertile plants from 30000-y-old fruit tissue buried in Siberian permafrost 20 Reversal of cocaine-evoked synaptic potentiation resets drug-induced adaptive behaviour 21 Stability and complexity in model ecosystems 22 Stability criteria for complex ecosystems 23 Systematic conservation planning 24 The diversity-stability debate 25 The Medicago genome provides insight into the evolution of rhizobial symbioses 26 Twenty-first-century warming of a large Antarctic ice-shelf cavity by a redirected coastal current 27 Will a Large Complex System be Stable上海交通大学通识教育立项核心课程 课程名称: 生物技术与人类 课程编号: BI 906 姓名: 李伊萌 班级: F1312003 学号: 5131209049 专业: 安泰经济与管理学院 阅读与理解 题目编号 11 得分 序 号 阅读文章名称 1 A new hominin foot from Ethiopia shows multiple Pliocene bipedal adaptations 2 Additive threats from pathogens, climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity 3 Causes, consequences and ethics 4 Changing Arctic Ocean freshwater pathways 5 Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing 6 Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture 7 Consequences of changing 8 Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome 9 Emerging fungal threats to animal,plant and ecosystem health 10 Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine 11 Genetic contribution to stability and change in intelligence from childhood to old age 12 Getting the measure of biodiversity 13 Global patterns in biodiversity 14 Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation 15 Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence 16 Prediction mutation outcome from early stochastic variation in genetic interaction partners 17 Rapid evolutionary divergence and ecotypic diversification of germination behavior in weedy rice populations 18 Recent contribution of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise 19 Regeneration of whole fertile plants from 30000-y-old fruit tissue buried in Siberian permafrost 20 Reversal of cocaine-evoked synaptic potentiation resets drug-induced adaptive behaviour 21 Stability and complexity in model ecosystems 22 Stability criteria for complex ecosystems 23 Systematic conservation planning 24 The diversity–stability debate 25 The Medicago genome provides insight into the evolution of rhizobial symbioses 26 Twenty-first-century warming of a large Antarctic ice-shelf cavity by a redirected coastal current 27 Will a Large Complex System be Stable