正在加载图片...
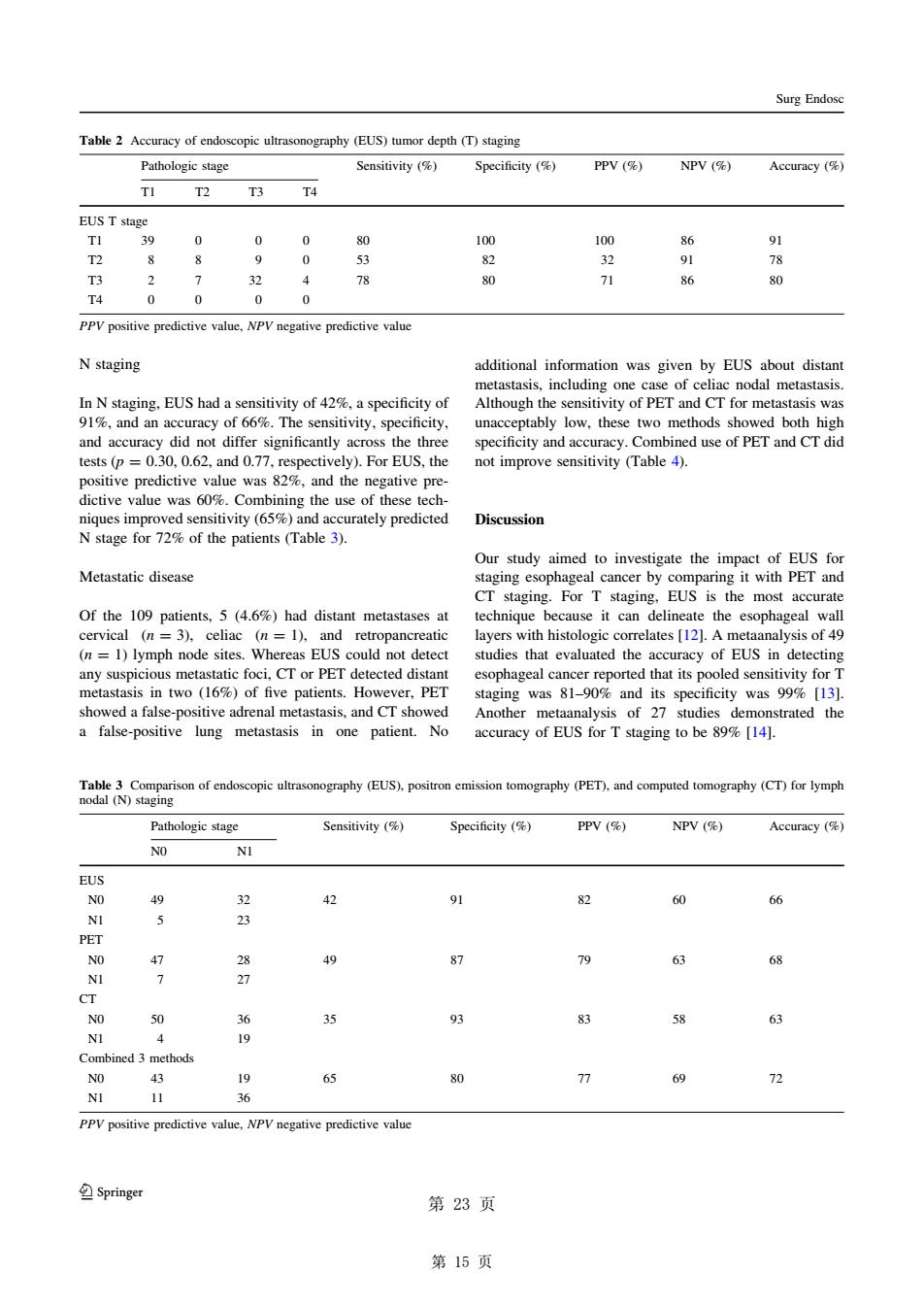
Surg Endose Pathologic stage Sensitivity ( PPV ( NPV ( Accuracy(%) 1 T2 T3 T4 EUST stage 9 人 78 0 71 86 80 T4 0 0 0 0 PPV positive predictive value.NPV negative predictive value N staging additional information was given by EUS about distan In N staging.EUS had a sensitivity of 42%a specificity of 91and an accuracy of 66%.The sensitivity.specificity unacceptably low.these two methods showed both high and d use of PET and CT di dictive value was60%.Combining the use of these tech- Discussion Our study aimed to investigate the impact of EUS fo Metastatic disease staging esophageal cancer by comparing it with PET an For T staging. EUS the me layers with histologic (n=1)lymph node sites.Whereas EUS could not detect studies that evaluated the accuracy of EUS in detecting any si in PET ed that its ed se iL3】 a false-positive lung metastasis in one patient.No accuracy of EUS for T staging to be14]. opic (EUS)(PET)and computed tomoahy (CT)for lymph Sensitivity) PPV() NPV() NO NI EUS N 68 35 63 ined 3 methods NO 65 72 NI 11 36 PPV positive predictive value.NPV negative predictive value Springer 第23页 第15页 N staging In N staging, EUS had a sensitivity of 42%, a specificity of 91%, and an accuracy of 66%. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy did not differ significantly across the three tests (p = 0.30, 0.62, and 0.77, respectively). For EUS, the positive predictive value was 82%, and the negative predictive value was 60%. Combining the use of these techniques improved sensitivity (65%) and accurately predicted N stage for 72% of the patients (Table 3). Metastatic disease Of the 109 patients, 5 (4.6%) had distant metastases at cervical (n = 3), celiac (n = 1), and retropancreatic (n = 1) lymph node sites. Whereas EUS could not detect any suspicious metastatic foci, CT or PET detected distant metastasis in two (16%) of five patients. However, PET showed a false-positive adrenal metastasis, and CT showed a false-positive lung metastasis in one patient. No additional information was given by EUS about distant metastasis, including one case of celiac nodal metastasis. Although the sensitivity of PET and CT for metastasis was unacceptably low, these two methods showed both high specificity and accuracy. Combined use of PET and CT did not improve sensitivity (Table 4). Discussion Our study aimed to investigate the impact of EUS for staging esophageal cancer by comparing it with PET and CT staging. For T staging, EUS is the most accurate technique because it can delineate the esophageal wall layers with histologic correlates [12]. A metaanalysis of 49 studies that evaluated the accuracy of EUS in detecting esophageal cancer reported that its pooled sensitivity for T staging was 81–90% and its specificity was 99% [13]. Another metaanalysis of 27 studies demonstrated the accuracy of EUS for T staging to be 89% [14]. Table 2 Accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) tumor depth (T) staging Pathologic stage Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) PPV (%) NPV (%) Accuracy (%) T1 T2 T3 T4 EUS T stage T1 39 0 0 0 80 100 100 86 91 T2 8 8 9 0 53 82 32 91 78 T3 2 7 32 4 78 80 71 86 80 T4 0 0 0 0 PPV positive predictive value, NPV negative predictive value Table 3 Comparison of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS), positron emission tomography (PET), and computed tomography (CT) for lymph nodal (N) staging Pathologic stage Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) PPV (%) NPV (%) Accuracy (%) N0 N1 EUS N0 49 32 42 91 82 60 66 N1 5 23 PET N0 47 28 49 87 79 63 68 N1 7 27 CT N0 50 36 35 93 83 58 63 N1 4 19 Combined 3 methods N0 43 19 65 80 77 69 72 N1 11 36 PPV positive predictive value, NPV negative predictive value Surg Endosc 123 义 第 15 页��