正在加载图片...
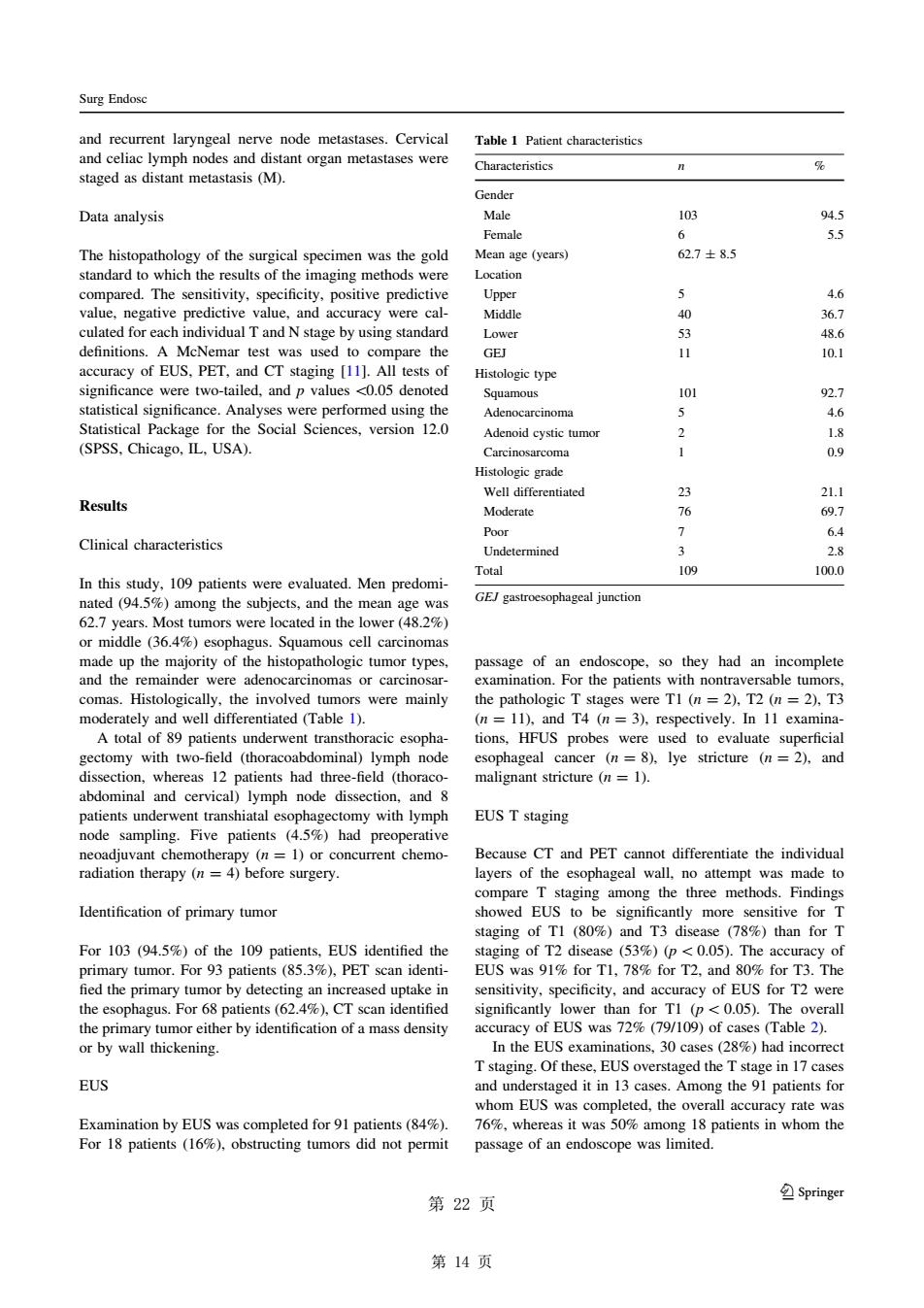
Surg Endose and were staged as distant metastasis(M). Characteristics Data analysis 103 Female The histopathology of the surgical specimen was the gold Mean age (years) 627±85 hich th ults of the imaging method 4.6 were cal- 36.7 culated for each dividual T and N stage by using standard 48.6 and Cas (111.th 10.1 PET significance were two-tailed.and pvalues 0.05 denoted logie type 1o1 46 SPSS.Pa Adenoid 2 18 0 Well di Results 21.1 Moderate 76 69.7 Clinical characteristics Poor 6.4 109 GE/gastroesophageal junction 62.7 years.Most tumors were located in the lower or middle (36.4%) esophagus.Squamous cell carcinomas comas.Histologically.the involved tumors were mainly the pathologic T stages were TI (n=2).T2 (n=2).T3 I we with twp-fiel (thor bdominal) node cal cancer 8)ve stricture and ssection,whereas 12 patients had three-field (thoraco malignant stricture (n=1). abdon and cervica al)lymph node and node sampling.Five patients (45%)had EUS T staging t chemother Because CT and PET canno differentiate the individual ayers of the attempt Identification of primary tumor showed EUS to be signific more sitive for T taging of TI (80%)and T3 disease (78%)than for T For103(94.5% de the EUS s91%oL8 fied the primary tumor by detect sed untake in ensitivity s uracy of EUs for T?wen the esophagus.For68 patients (62.)CT scan identified 8) Tstaging.Of these.EUS overstaged the T stage in 17case EUS and unde c050% th Examination by eUs was ted for 91 pa sage of an endoscope was limited 第22页 Springe 第14页and recurrent laryngeal nerve node metastases. Cervical and celiac lymph nodes and distant organ metastases were staged as distant metastasis (M). Data analysis The histopathology of the surgical specimen was the gold standard to which the results of the imaging methods were compared. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy were calculated for each individual T and N stage by using standard definitions. A McNemar test was used to compare the accuracy of EUS, PET, and CT staging [11]. All tests of significance were two-tailed, and p values \0.05 denoted statistical significance. Analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 12.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Results Clinical characteristics In this study, 109 patients were evaluated. Men predominated (94.5%) among the subjects, and the mean age was 62.7 years. Most tumors were located in the lower (48.2%) or middle (36.4%) esophagus. Squamous cell carcinomas made up the majority of the histopathologic tumor types, and the remainder were adenocarcinomas or carcinosarcomas. Histologically, the involved tumors were mainly moderately and well differentiated (Table 1). A total of 89 patients underwent transthoracic esophagectomy with two-field (thoracoabdominal) lymph node dissection, whereas 12 patients had three-field (thoracoabdominal and cervical) lymph node dissection, and 8 patients underwent transhiatal esophagectomy with lymph node sampling. Five patients (4.5%) had preoperative neoadjuvant chemotherapy (n = 1) or concurrent chemoradiation therapy (n = 4) before surgery. Identification of primary tumor For 103 (94.5%) of the 109 patients, EUS identified the primary tumor. For 93 patients (85.3%), PET scan identi- fied the primary tumor by detecting an increased uptake in the esophagus. For 68 patients (62.4%), CT scan identified the primary tumor either by identification of a mass density or by wall thickening. EUS Examination by EUS was completed for 91 patients (84%). For 18 patients (16%), obstructing tumors did not permit passage of an endoscope, so they had an incomplete examination. For the patients with nontraversable tumors, the pathologic T stages were T1 (n = 2), T2 (n = 2), T3 (n = 11), and T4 (n = 3), respectively. In 11 examinations, HFUS probes were used to evaluate superficial esophageal cancer (n = 8), lye stricture (n = 2), and malignant stricture (n = 1). EUS T staging Because CT and PET cannot differentiate the individual layers of the esophageal wall, no attempt was made to compare T staging among the three methods. Findings showed EUS to be significantly more sensitive for T staging of T1 (80%) and T3 disease (78%) than for T staging of T2 disease (53%) (p\ 0.05). The accuracy of EUS was 91% for T1, 78% for T2, and 80% for T3. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of EUS for T2 were significantly lower than for T1 (p\0.05). The overall accuracy of EUS was 72% (79/109) of cases (Table 2). In the EUS examinations, 30 cases (28%) had incorrect T staging. Of these, EUS overstaged the T stage in 17 cases and understaged it in 13 cases. Among the 91 patients for whom EUS was completed, the overall accuracy rate was 76%, whereas it was 50% among 18 patients in whom the passage of an endoscope was limited. Table 1 Patient characteristics Characteristics n % Gender Male 103 94.5 Female 6 5.5 Mean age (years) 62.7 ± 8.5 Location Upper 5 4.6 Middle 40 36.7 Lower 53 48.6 GEJ 11 10.1 Histologic type Squamous 101 92.7 Adenocarcinoma 5 4.6 Adenoid cystic tumor 2 1.8 Carcinosarcoma 1 0.9 Histologic grade Well differentiated 23 21.1 Moderate 76 69.7 Poor 7 6.4 Undetermined 3 2.8 Total 109 100.0 GEJ gastroesophageal junction Surg Endosc 义 123 第 14 页��