正在加载图片...
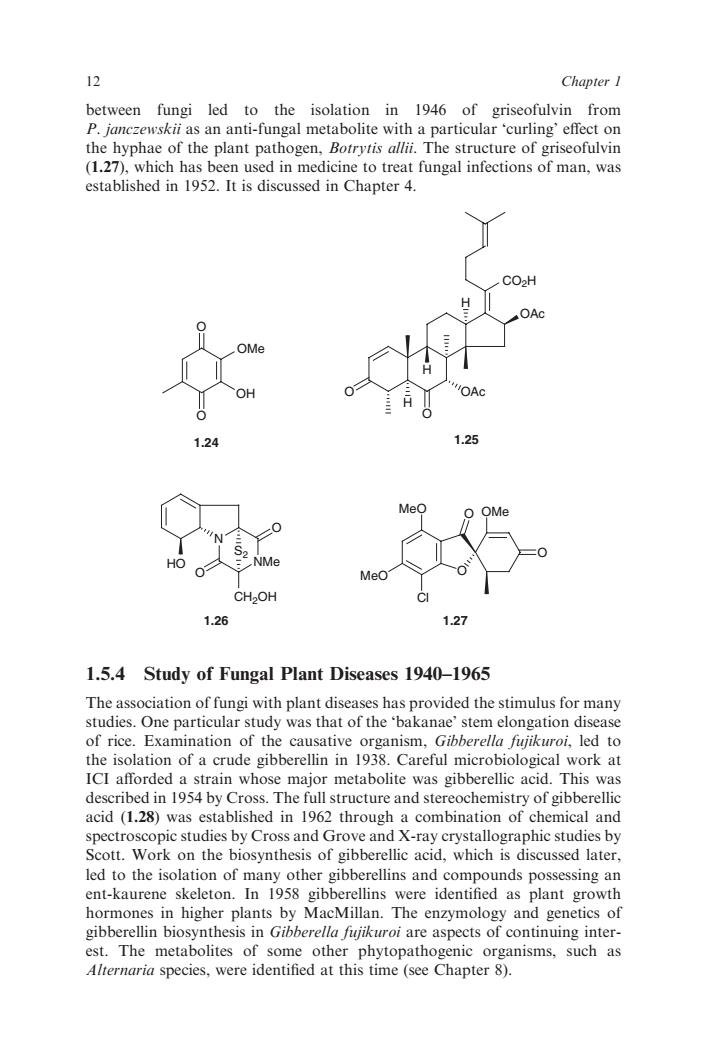
12 between fungi led to the isolation in 1946 of griseofulvin from P.janczewskii as an anti-fungal metabolite with a particular'curling'effect on the hyphae of the plant pathogen,Botrytis allii.The structure of griseofulvin (1.27),which has been used in medicine to treat fungal infections of man,was established in 1952.It is discussed in Chapter 4. 124 125 CH2OH 1.26 1.27 1.5.4 Study of Fungal Plant Diseases 1940-1965 to thpproided the y was that of the Gibberell longation the isolation of a crude gibberellin in 1938.Careful microbiological work at ICI afforded a strain whose major metabolite was gibberellic acid.This was described in 1954 by Cross.The full structure and stereochemistry of gibberellic acid (1.28)was established in 1962 through a combination of chemical and spectroscopic studies by Cross and Grove and X-ray crystallographic studies by Scott.Work on the biosynthesis of gibberellic acid.which is discussed later. led to the isolation of m other gibberellins and co unds po ssessing ent-kaurene n1958 vere identi d as plant growt hormones in higher plants by MacMillan.The enzymology and genetics of gibberellin biosynthesis in Gibberella fujikuroi are aspects of continuing inter- est.The metabolites of some other phytopathogenic organisms,such as Alternaria species,were identified at this time (see Chapter 8).between fungi led to the isolation in 1946 of griseofulvin from P. janczewskii as an anti-fungal metabolite with a particular ‘curling’ effect on the hyphae of the plant pathogen, Botrytis allii. The structure of griseofulvin (1.27), which has been used in medicine to treat fungal infections of man, was established in 1952. It is discussed in Chapter 4. O OMe OH O 1.24 CO2H O O H OAc H H OAc 1.25 MeO O MeO Cl O OMe O 1.27 N NMe O O CH2OH S2 HO 1.26 1.5.4 Study of Fungal Plant Diseases 1940–1965 The association of fungi with plant diseases has provided the stimulus for many studies. One particular study was that of the ‘bakanae’ stem elongation disease of rice. Examination of the causative organism, Gibberella fujikuroi, led to the isolation of a crude gibberellin in 1938. Careful microbiological work at ICI afforded a strain whose major metabolite was gibberellic acid. This was described in 1954 by Cross. The full structure and stereochemistry of gibberellic acid (1.28) was established in 1962 through a combination of chemical and spectroscopic studies by Cross and Grove and X-ray crystallographic studies by Scott. Work on the biosynthesis of gibberellic acid, which is discussed later, led to the isolation of many other gibberellins and compounds possessing an ent-kaurene skeleton. In 1958 gibberellins were identified as plant growth hormones in higher plants by MacMillan. The enzymology and genetics of gibberellin biosynthesis in Gibberella fujikuroi are aspects of continuing interest. The metabolites of some other phytopathogenic organisms, such as Alternaria species, were identified at this time (see Chapter 8). 12 Chapter 1