正在加载图片...
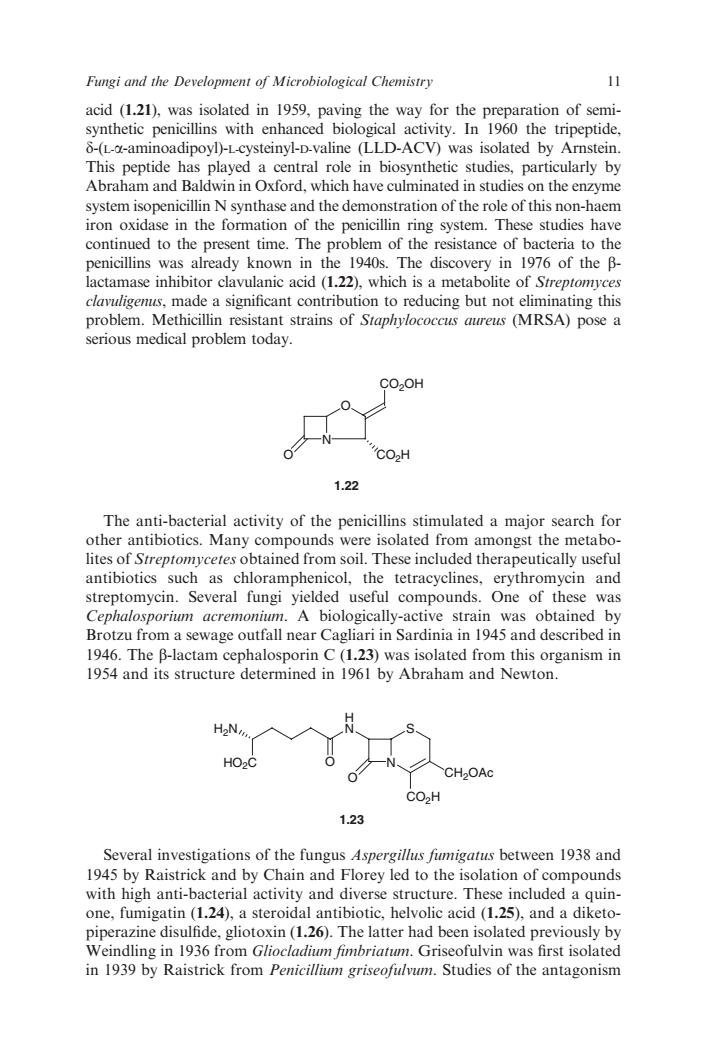
Fungi and the Development of Microbiological Chemistry 11 acid (1.21),was isolated in 1959,paving the way for the preparation of semi- synthetic penicillins with enhanced biological activity.In 1960 the tripeptide 8-(La-aminoadipoyD)-L cysteinvl-D-valine (LLD-ACV)was isolated by Arnstein This aved a tral role in biosynthetic studies. on the enzyme system isopenicillin N synthase and the demonstration of the role of this non-haem iron oxidase in the formation of the penicillin ring system.These studies have continued to the present time.The problem of the resistance of bacteria to the penicillins was already known in the 1940s.The discovery in 1976 of the B- lactamase inhibitor clavulanic acid (1.22),which is a metabolite of Streptomyces clavuligems,made a significant contribution to reducing but not eliminating this problem.Methicillin resistant strains of Staphylococcu aureus(MRSA)pose a erious medical problem today CO2OH CO.H 1.22 The anti-bacterial activity of the s stimulated a major search fo other antibiotics.Many compounds were isolated from amongst the metabo lites of Streptomycetes obtained from soil.These included therapeutically useful antibiotics such as chloramphenicol,the tetracyclines,erythromycin and streptomycin.Several fungi yielded useful compounds.One of these was Cephalosporium acremonium.A biologically-active strain was obtained by Brotzu from a sewage outfall near Cagliari in Sardinia in 1945 and described in 1946.The B-lactam phalosporin C(123)was isolated from this its structure determined by Abraham and Newton organism in 1954 and H2N HO2C CO2H 1.23 Several investigations of the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus between 1938 and 1945 by Raistrick and by Chain and Florey led to the isolation of compounds with high anti-bacterial activity and diverse structure.These included a quin- one,fumigatin (1.24),a steroidal antibiotic,helvolic acid(1.25),and a diketo- piperazine disulfide,gliotoxin(1.26).The latter had been isolated previously by Weindling in 1936 from Gliocladium fimbriatum.Griseofulvin was first isolated in 1939 by Raistrick from Penicillium griseofulvum.Studies of the antagonism acid (1.21), was isolated in 1959, paving the way for the preparation of semisynthetic penicillins with enhanced biological activity. In 1960 the tripeptide, d-(L-a-aminoadipoyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine (LLD-ACV) was isolated by Arnstein. This peptide has played a central role in biosynthetic studies, particularly by Abraham and Baldwin in Oxford, which have culminated in studies on the enzyme system isopenicillin N synthase and the demonstration of the role of this non-haem iron oxidase in the formation of the penicillin ring system. These studies have continued to the present time. The problem of the resistance of bacteria to the penicillins was already known in the 1940s. The discovery in 1976 of the blactamase inhibitor clavulanic acid (1.22), which is a metabolite of Streptomyces clavuligenus, made a significant contribution to reducing but not eliminating this problem. Methicillin resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pose a serious medical problem today. N O CO2OH O CO2H 1.22 The anti-bacterial activity of the penicillins stimulated a major search for other antibiotics. Many compounds were isolated from amongst the metabolites of Streptomycetes obtained from soil. These included therapeutically useful antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, the tetracyclines, erythromycin and streptomycin. Several fungi yielded useful compounds. One of these was Cephalosporium acremonium. A biologically-active strain was obtained by Brotzu from a sewage outfall near Cagliari in Sardinia in 1945 and described in 1946. The b-lactam cephalosporin C (1.23) was isolated from this organism in 1954 and its structure determined in 1961 by Abraham and Newton. S N H N HO2C O O CO2H CH2OAc H2N 1.23 Several investigations of the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus between 1938 and 1945 by Raistrick and by Chain and Florey led to the isolation of compounds with high anti-bacterial activity and diverse structure. These included a quinone, fumigatin (1.24), a steroidal antibiotic, helvolic acid (1.25), and a diketopiperazine disulfide, gliotoxin (1.26). The latter had been isolated previously by Weindling in 1936 from Gliocladium fimbriatum. Griseofulvin was first isolated in 1939 by Raistrick from Penicillium griseofulvum. Studies of the antagonism Fungi and the Development of Microbiological Chemistry 11