正在加载图片...
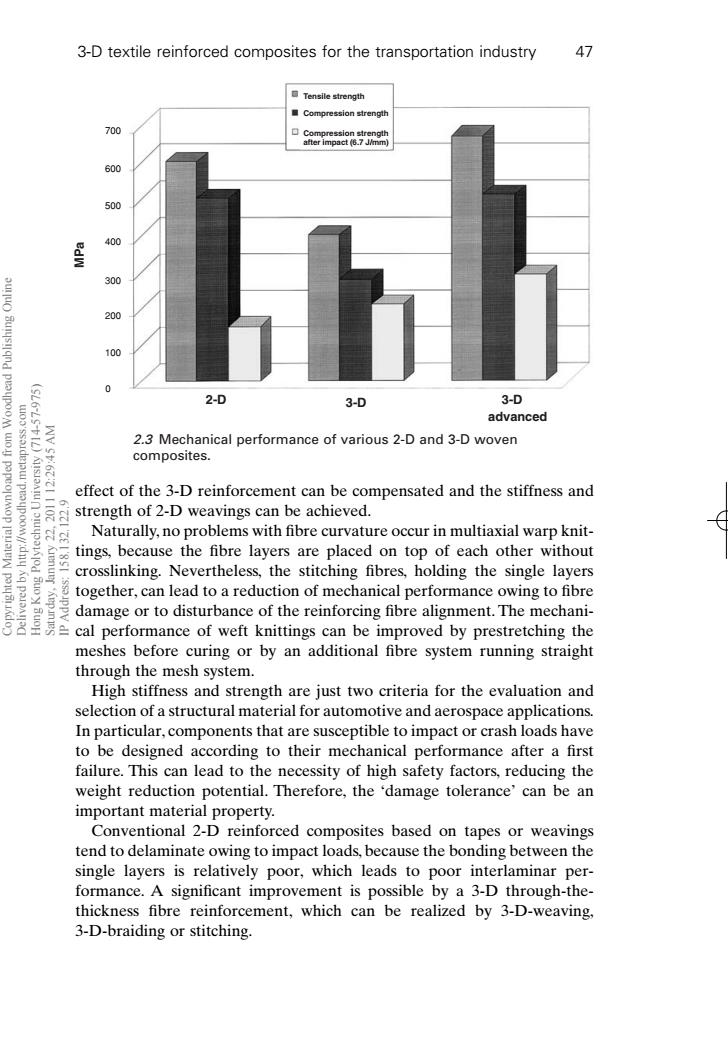
3-D textile reinforced composites for the transportation industry 47 Tensile strength Compression strength 700 Compression strength after impact传7JWmm 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 2-D 3-D 3-D advanced wo'ssaudmau'peaupoo/ WV St:6Z 2.3 Mechanical performance of various 2-D and 3-D woven composites. 2102 effect of the 3-D reinforcement can be compensated and the stiffness and strength of 2-D weavings can be achieved. Naturally,no problems with fibre curvature occur in multiaxial warp knit- tings,because the fibre layers are placed on top of each other without crosslinking.Nevertheless,the stitching fibres,holding the single layers together,can lead to a reduction of mechanical performance owing to fibre damage or to disturbance of the reinforcing fibre alignment.The mechani- cal performance of weft knittings can be improved by prestretching the meshes before curing or by an additional fibre system running straight through the mesh system. High stiffness and strength are just two criteria for the evaluation and selection of a structural material for automotive and aerospace applications. In particular,components that are susceptible to impact or crash loads have to be designed according to their mechanical performance after a first failure.This can lead to the necessity of high safety factors,reducing the weight reduction potential.Therefore,the 'damage tolerance'can be an important material property. Conventional 2-D reinforced composites based on tapes or weavings tend to delaminate owing to impact loads,because the bonding between the single layers is relatively poor,which leads to poor interlaminar per- formance.A significant improvement is possible by a 3-D through-the- thickness fibre reinforcement,which can be realized by 3-D-weaving, 3-D-braiding or stitching.effect of the 3-D reinforcement can be compensated and the stiffness and strength of 2-D weavings can be achieved. Naturally, no problems with fibre curvature occur in multiaxial warp knittings, because the fibre layers are placed on top of each other without crosslinking. Nevertheless, the stitching fibres, holding the single layers together, can lead to a reduction of mechanical performance owing to fibre damage or to disturbance of the reinforcing fibre alignment. The mechanical performance of weft knittings can be improved by prestretching the meshes before curing or by an additional fibre system running straight through the mesh system. High stiffness and strength are just two criteria for the evaluation and selection of a structural material for automotive and aerospace applications. In particular, components that are susceptible to impact or crash loads have to be designed according to their mechanical performance after a first failure. This can lead to the necessity of high safety factors, reducing the weight reduction potential. Therefore, the ‘damage tolerance’ can be an important material property. Conventional 2-D reinforced composites based on tapes or weavings tend to delaminate owing to impact loads, because the bonding between the single layers is relatively poor, which leads to poor interlaminar performance. A significant improvement is possible by a 3-D through-thethickness fibre reinforcement, which can be realized by 3-D-weaving, 3-D-braiding or stitching. 3-D textile reinforced composites for the transportation industry 47 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 Tensile strength Compression strength Compression strength after impact (6.7 J/mm) 2-D 3-D 3-D advanced MPa 2.3 Mechanical performance of various 2-D and 3-D woven composites. RIC2 7/10/99 7:25 PM Page 47 Copyrighted Material downloaded from Woodhead Publishing Online Delivered by http://woodhead.metapress.com Hong Kong Polytechnic University (714-57-975) Saturday, January 22, 2011 12:29:45 AM IP Address: 158.132.122.9