正在加载图片...
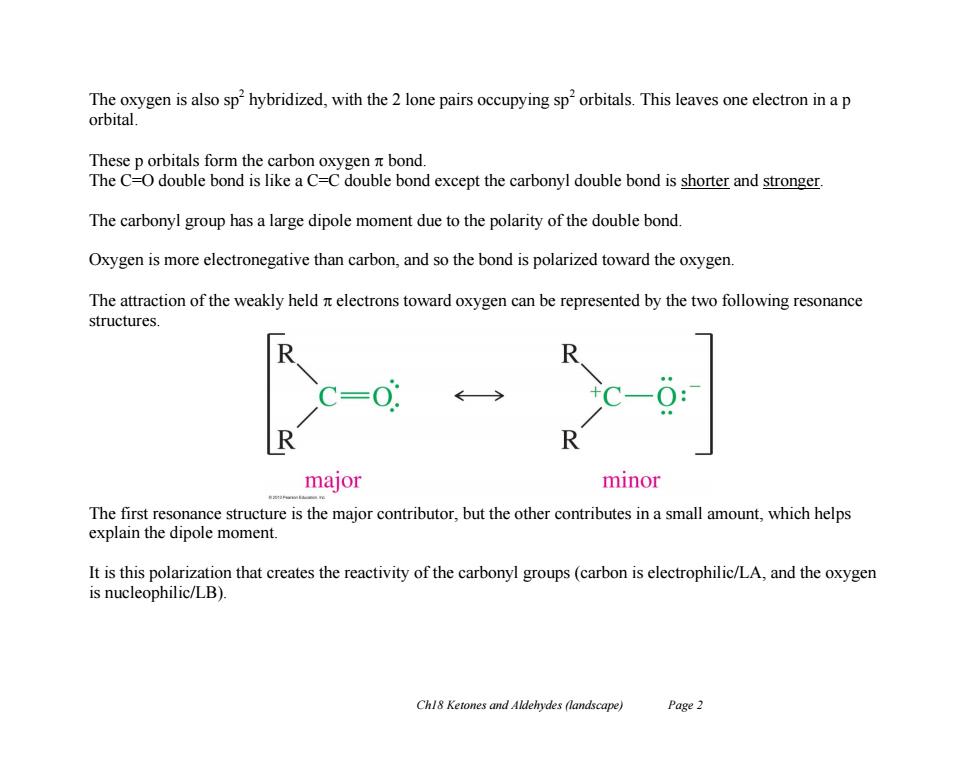
The oxygen is also sp hybridized,with the 2 lone pairs occupying sp'orbitals.This leaves one electron in a p orbital. These p orbitals form the carbon oxygen bond. The C=O double bond is like a C=C double bond except the carbonyl double bond is shorter and stronger. The carbonyl group has a large dipole moment due to the polarity of the double bond. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon,and so the bond is polarized toward the oxygen. The attraction of the weakly held nt electrons toward oxygen can be represented by the two following resonance structures. R major minor The first resonance structure is the major contributor,but the other contributes in a small amount,which helps explain the dipole moment. It is this polarization that creates the reactivity of the carbonyl groups(carbon is electrophilic/LA,and the oxygen is nucleophilic/LB). Chl8 Ketones and Aldehydes (landscape) Page 2Ch18 Ketones and Aldehydes (landscape) Page 2 The oxygen is also sp2 hybridized, with the 2 lone pairs occupying sp2 orbitals. This leaves one electron in a p orbital. These p orbitals form the carbon oxygen bond. The C=O double bond is like a C=C double bond except the carbonyl double bond is shorter and stronger. The carbonyl group has a large dipole moment due to the polarity of the double bond. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, and so the bond is polarized toward the oxygen. The attraction of the weakly held electrons toward oxygen can be represented by the two following resonance structures. The first resonance structure is the major contributor, but the other contributes in a small amount, which helps explain the dipole moment. It is this polarization that creates the reactivity of the carbonyl groups (carbon is electrophilic/LA, and the oxygen is nucleophilic/LB)